Juvenile idiopathic Idiopathic Dermatomyositis arthritis Arthritis Acute or chronic inflammation of joints. Osteoarthritis (JIA), formerly known as juvenile rheumatoid arthritis Arthritis Acute or chronic inflammation of joints. Osteoarthritis, is a heterogeneous group of inflammatory diseases characterized by inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body's defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation of 1 or more joints and is the most common pediatric rheumatic disease. Juvenile idiopathic Idiopathic Dermatomyositis arthritis Arthritis Acute or chronic inflammation of joints. Osteoarthritis is classified according to its clinical presentation, and diagnosis is made with examination findings as well as confirmatory lab testing showing evidence of inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body's defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation and characteristic X-ray X-ray Penetrating electromagnetic radiation emitted when the inner orbital electrons of an atom are excited and release radiant energy. X-ray wavelengths range from 1 pm to 10 nm. Hard x-rays are the higher energy, shorter wavelength x-rays. Soft x-rays or grenz rays are less energetic and longer in wavelength. The short wavelength end of the x-ray spectrum overlaps the gamma rays wavelength range. The distinction between gamma rays and x-rays is based on their radiation source. Pulmonary Function Tests findings. Treatment is directed at preventing loss of function Loss of Function Inflammation and controlling or limiting joint damage, with a variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables prognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual's condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas depending on the type.
Last updated: Mar 12, 2024
Juvenile idiopathic Idiopathic Dermatomyositis arthritis Arthritis Acute or chronic inflammation of joints. Osteoarthritis, formerly known as juvenile rheumatoid arthritis Arthritis Acute or chronic inflammation of joints. Osteoarthritis, is the most common chronic rheumatological disease in the pediatric population. While there are multiple subgroups with distinct pathogeneses, the key feature is arthritis Arthritis Acute or chronic inflammation of joints. Osteoarthritis.
Juvenile idiopathic Idiopathic Dermatomyositis arthritis Arthritis Acute or chronic inflammation of joints. Osteoarthritis is a term used to describe a group of inflammatory conditions of the joints affecting children younger than 16 and lasting 6 weeks or longer.
Classification according to symptomatology Symptomatology Scarlet Fever (as per the International League of Associations for Rheumatology):
| Oligoarticular | Polyarticular | Systemic | |
|---|---|---|---|
| % of JIA cases | 50% | 35% | 10% |
| Gender Gender Gender Dysphoria | Girls > boys | Girls > boys | Girls = boys |
| Age | 2–3 years old, rare > 10 years old | 2–5 years old, 10–14 years old | Any < 16 |
While genetic susceptibility plays a role in JIA, the exact etiology and pathogenesis of the disease is incompletely understood. Juvenile idiopathic Idiopathic Dermatomyositis arthritis Arthritis Acute or chronic inflammation of joints. Osteoarthritis is believed to be caused by an interplay between environmental exposures and genetic predisposition.
Environmental component:
Genetic component:
The presentation of JIA is variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables secondary to the heterogeneous nature of the various subgroups, but there are some common features.
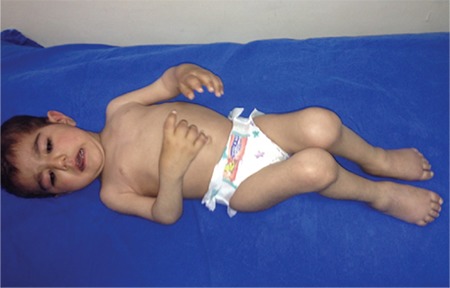
Widespread joint involvement in polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA)
Image: “Widespread joint involvement in polyarticular juvenile idopathic arthritis” by Kenan Barut et al. License: CC BY 2.5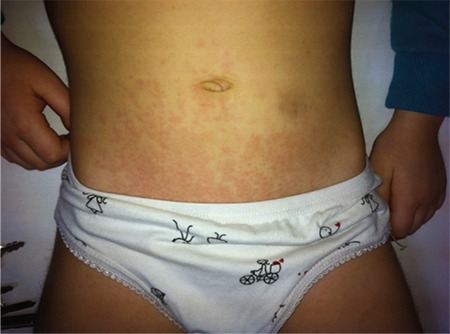
Typical rash in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA)
Image: “Typical rash in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis” by Kenan Barut et al. License: CC BY 2.5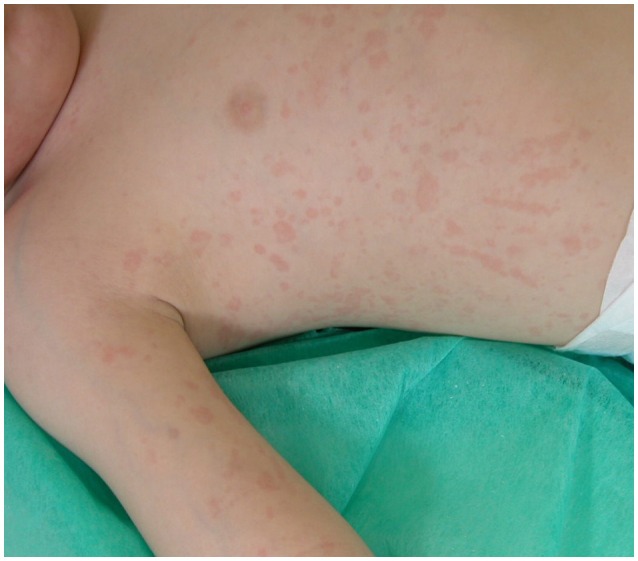
Salmon-macular rash in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA)
Image: “Salmon-macular rash in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis” by Gabriella Giancane et al. License: CC BY 4.0| Oligoarticular | Polyarticular | Systemic | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of joints affected | Fewer than 5 | > 5 | Any |
| Types of joints affected |
|
|
|
| Systemic features |
|
Less frequent uveitis Uveitis Uveitis is the inflammation of the uvea, the pigmented middle layer of the eye, which comprises the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. The condition is categorized based on the site of disease; anterior uveitis is the most common. Diseases of the Uvea |
|
Diagnosis of JIA is primarily based on history and physical exam findings. The laboratory data and imaging contribute to the confirmation of the diagnosis and the exclusion of other diseases.
Variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables findings related to severity and type of disease; often used to evaluate for other diagnoses:
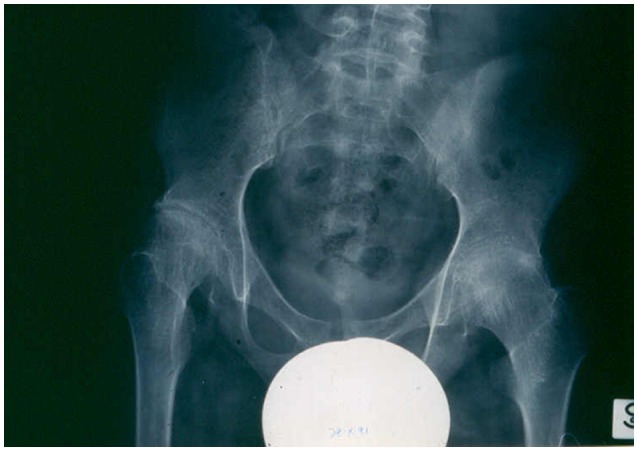
X-ray showing advanced destructive changes in the hips of a systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) patient
Image: “X-ray showing advanced destructive changes in the hips of a systemic JIA patient” by Gabriella Giancane et al. License: CC BY 4.0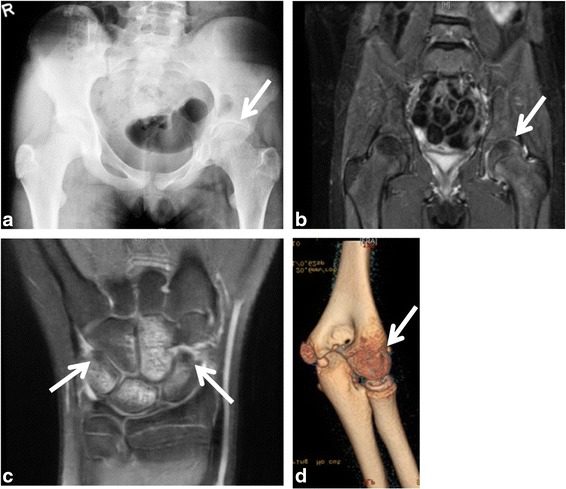
Representative images of severe monoarthritis in children diagnosed with oligoarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA):
a) X-ray of the hips showed shortening of the left femoral neck and decreased joint space.
b) MRI with gadolinium revealed enhancement and mild thickening of the left hip synovium on T2-weighted imaging.
c) MRI of the right wrist demonstrated carpal synovitis, marked bone marrow edema (BME), bone cysts, and erosions on T1-weighted imaging.
d) Non-contrast-enhanced CT (NCCT) of the left elbow showed bone erosions, hyperostosis of the trochlea-olecranon complex and reduced joint space. White arrows point toward the abnormal findings.
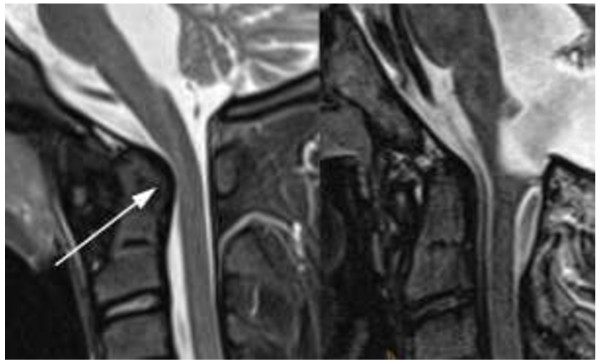
Short tau inversion recovery (STIR) imaging with and without JIA:
Left: 13-year-old girl with juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA), STIR 3 mm sagittal: enlarged dens with bulging dorsal contour (arrow) and narrowing of the spinal canal at the craniocervical junction (arrowheads)
Right: Normal control image taken of a 13-year-old boy without JIA and normal size of his dens
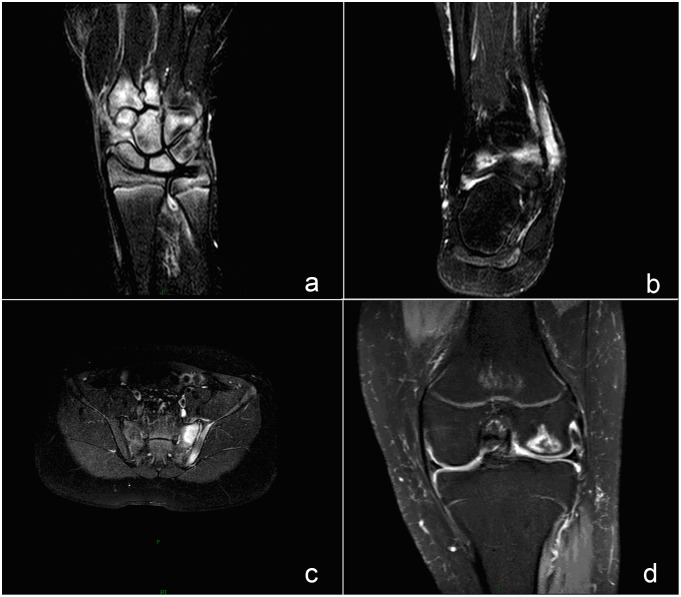
Magnetic resonance imaging findings of frequently involved joints in juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA):
Bone marrow edema (BME) appears as a hyperintense signal in spectral attenuated inversion recovery (SPAIR) sequence, reflecting active inflammatory lesion.
a) A SPAIR image of a wrist demonstrates BME on the carpal.
b) A SPAIR image of an ankle shows BME at the tibiofibular joint.
c) A SPAIR image of sacroiliac joint shows BME on the left of a sacroiliac (SI) joint.
d) A SPAIR image of a knee joint shows BME at the distal femur.
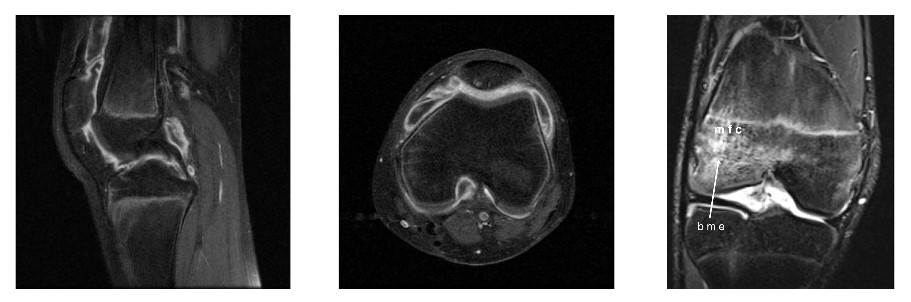
Magnetic resonance imaging of a knee in a patient with juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA):
Notice the erosive changes and inflammation demonstrated here.
The primary goal in the management of JIA is to limit Limit A value (e.g., pressure or time) that should not be exceeded and which is specified by the operator to protect the lung Invasive Mechanical Ventilation the extent of joint damage and restrict the loss of function Loss of Function Inflammation. Juvenile idiopathic Idiopathic Dermatomyositis arthritis Arthritis Acute or chronic inflammation of joints. Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease, and inducing remission Remission A spontaneous diminution or abatement of a disease over time, without formal treatment. Cluster Headaches with the least amount of toxicity Toxicity Dosage Calculation is essential.
American College of Rheumatology criteria for complete remission Remission A spontaneous diminution or abatement of a disease over time, without formal treatment. Cluster Headaches: