Atrial flutter is a regular supraventricular tachycardia characterized by an atrial heart rate between 240/min and 340/min (typically 300/min), atrioventricular (AV) node conduction block, and a “sawtooth” pattern on an electrocardiogram (ECG). There are many cardiac and non-cardiac causes, but patients will usually have underlying structural heart disease. Symptoms include palpitations, shortness of breath, chest pain, dizziness, and nausea. Management is similar to atrial fibrillation, with a focus on rhythm control and preventing systemic embolization.
Last updated: May 16, 2024
Atrial flutter is caused by a macroreentrant electrical loop (reentrant circuit covers a large area of the atrium):
Typical atrial flutter:
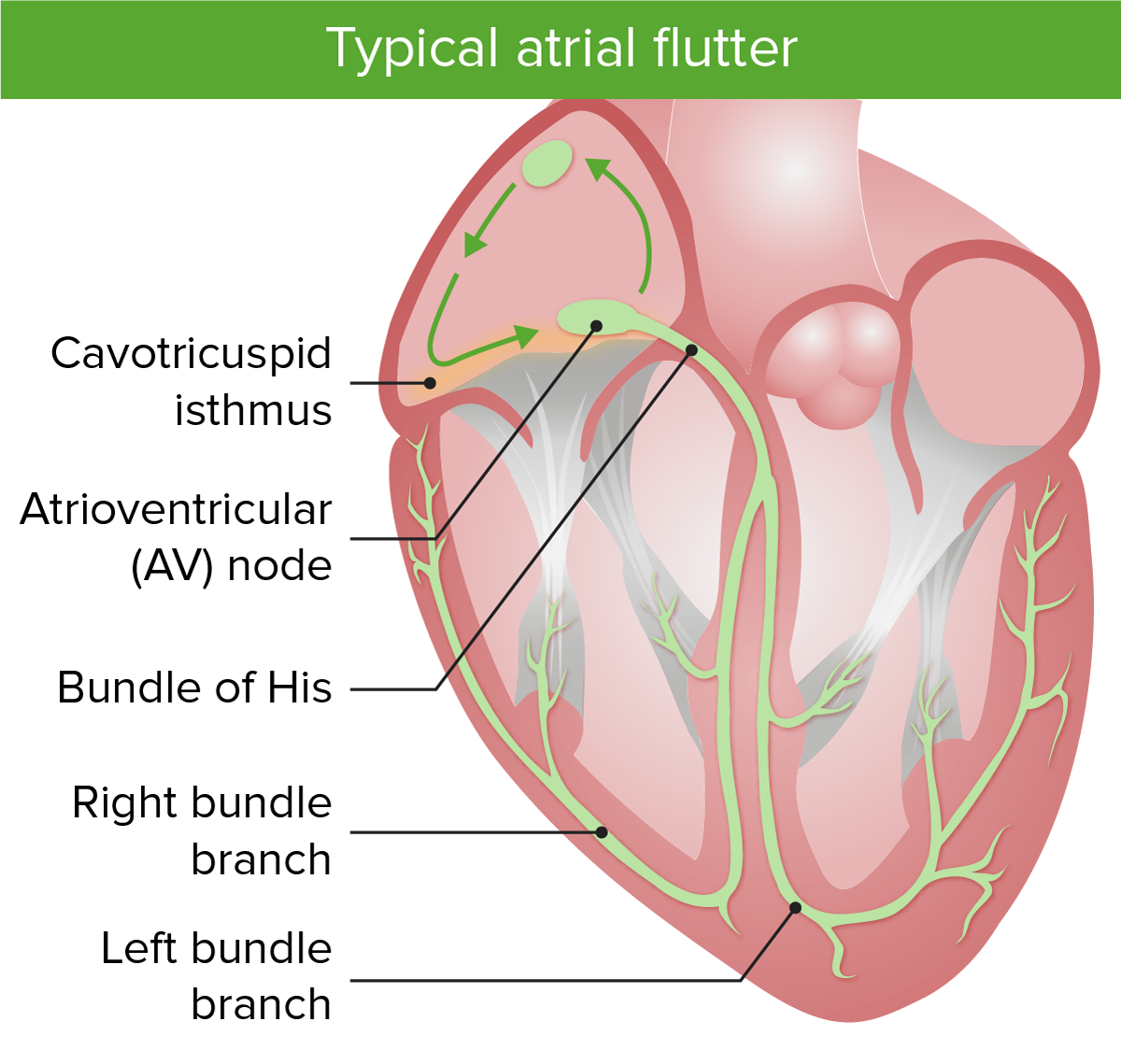
Image shows the macroreentrant circuits in typical atrial flutter. Notice that the cavotricuspid isthmus is involved in typical atrial flutter.
Image by Lecturio.Atypical atrial flutter:
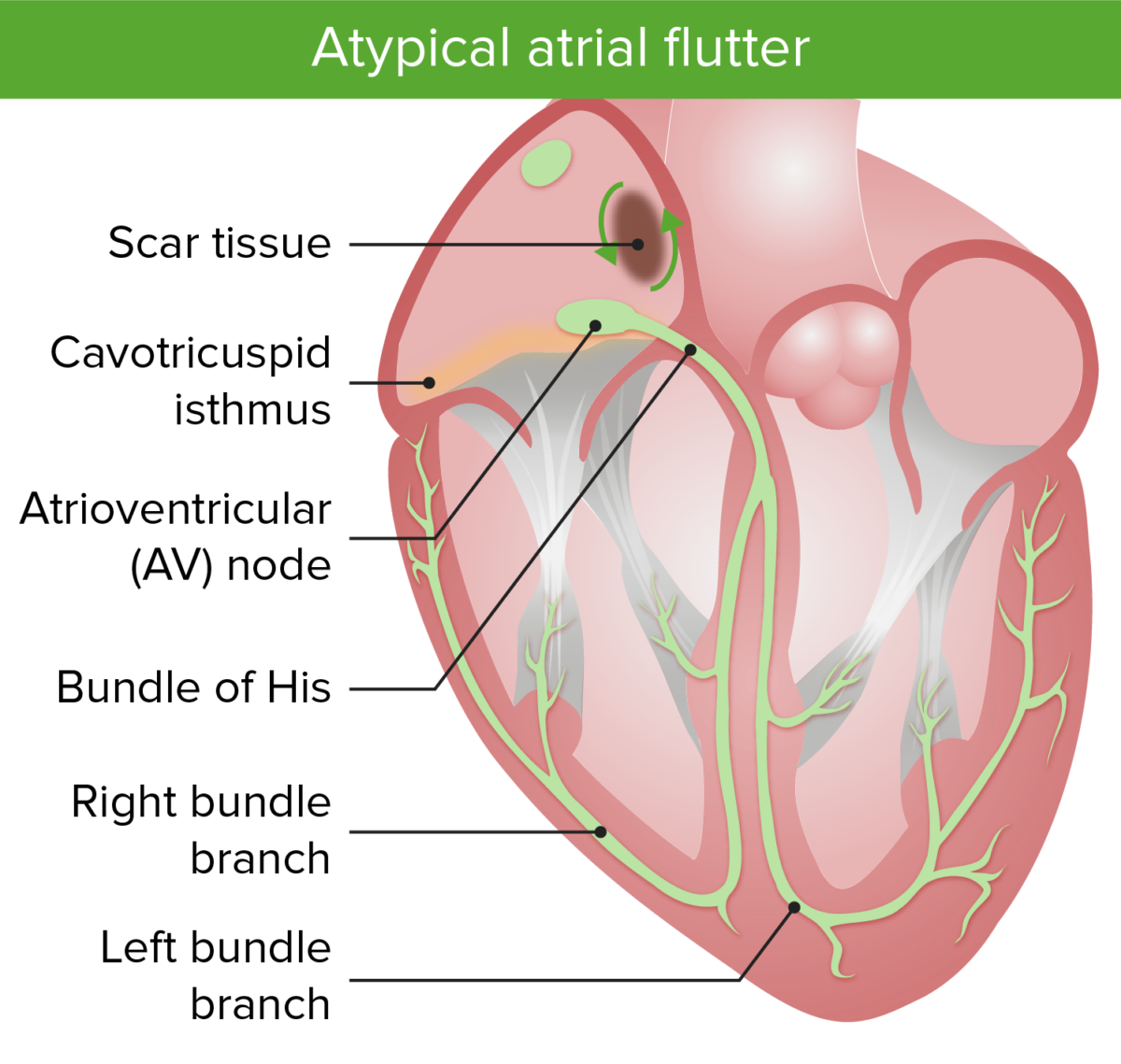
Image shows the macroreentrant circuits in atypical atrial flutter. Notice that the atypical flutter is focused around an area of scar tissue.
Image by Lecturio.| Complication | Possible symptoms | Exam findings | |
|---|---|---|---|
Cardiac:
|
Heart failure Heart Failure A heterogeneous condition in which the heart is unable to pump out sufficient blood to meet the metabolic need of the body. Heart failure can be caused by structural defects, functional abnormalities (ventricular dysfunction), or a sudden overload beyond its capacity. Chronic heart failure is more common than acute heart failure which results from sudden insult to cardiac function, such as myocardial infarction. Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return (TAPVR) |
|
|
| Myocardial ischemia Myocardial ischemia A disorder of cardiac function caused by insufficient blood flow to the muscle tissue of the heart. The decreased blood flow may be due to narrowing of the coronary arteries (coronary artery disease), to obstruction by a thrombus (coronary thrombosis), or less commonly, to diffuse narrowing of arterioles and other small vessels within the heart. Coronary Heart Disease |
|
|
|
Thromboembolic:
|
Stroke/ transient ischemic attack Transient ischemic attack Transient ischemic attack (TIA) is a temporary episode of neurologic dysfunction caused by ischemia without infarction that resolves completely when blood supply is restored. Transient ischemic attack is a neurologic emergency that warrants urgent medical attention. Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) ( TIA TIA Transient ischemic attack (TIA) is a temporary episode of neurologic dysfunction caused by ischemia without infarction that resolves completely when blood supply is restored. Transient ischemic attack is a neurologic emergency that warrants urgent medical attention. Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA)) |
|
Focal deficits on neurologic exam |
| Splenic infarct Infarct Area of necrotic cells in an organ, arising mainly from hypoxia and ischemia Ischemic Cell Damage |
|
|
|
| Bowel infarct Infarct Area of necrotic cells in an organ, arising mainly from hypoxia and ischemia Ischemic Cell Damage |
|
|
|
| Renal infarct Infarct Area of necrotic cells in an organ, arising mainly from hypoxia and ischemia Ischemic Cell Damage |
|
|
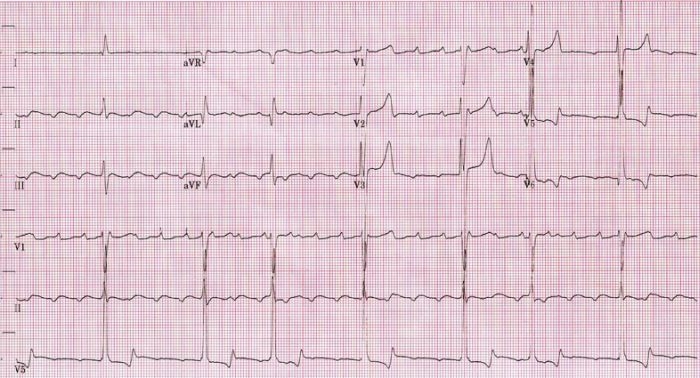
An ECG showing slow atrial flutter at an atrial cycle length of 400 ms (atrial rate of 150/min).
Image: “Atrial rate of 150/min” by Dept. of Cardiology, Beth Israel Medical Center. 16th Street and 1st Avenue. New York, New York 10003, USA. License: CC BY 2.5.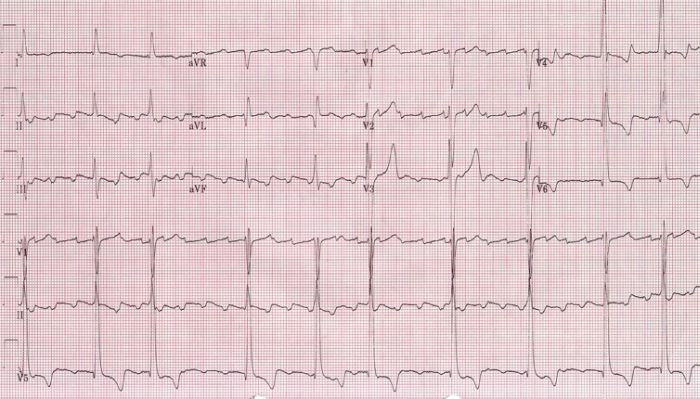
An ECG showing a faster atrial flutter at an atrial cycle length of 280 ms (atrial rate of 214/min).
Image: “Atrial rate of 214/min” by Dept. of Cardiology, Beth Israel Medical Center. 16th Street and 1st Avenue. New York, New York 10003, USA. License: CC BY 2.5.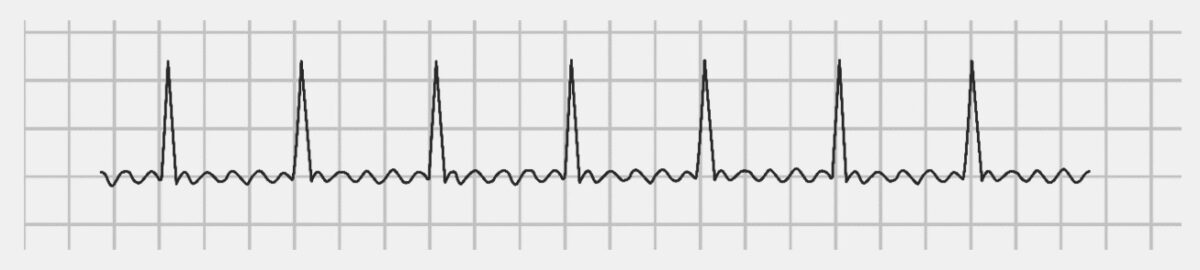
An ECG showing the classic “sawtooth” appearance in atrial flutter.
Image by Lecturio.| C | Congestive heart failure Heart Failure A heterogeneous condition in which the heart is unable to pump out sufficient blood to meet the metabolic need of the body. Heart failure can be caused by structural defects, functional abnormalities (ventricular dysfunction), or a sudden overload beyond its capacity. Chronic heart failure is more common than acute heart failure which results from sudden insult to cardiac function, such as myocardial infarction. Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return (TAPVR) | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| H | Hypertension Hypertension Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common disease that manifests as elevated systemic arterial pressures. Hypertension is most often asymptomatic and is found incidentally as part of a routine physical examination or during triage for an unrelated medical encounter. Hypertension | 1 |
| A | Age (≥ 75 years) | 2 |
| D | Diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus mellitus | 1 |
| S | Stroke, TIA TIA Transient ischemic attack (TIA) is a temporary episode of neurologic dysfunction caused by ischemia without infarction that resolves completely when blood supply is restored. Transient ischemic attack is a neurologic emergency that warrants urgent medical attention. Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA), or thromboembolism Thromboembolism Obstruction of a blood vessel (embolism) by a blood clot (thrombus) in the blood stream. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus | 2 |
| V | Vascular disease | 1 |
| A | Age 65–74 years | 1 |
| Sc | Sex Sex The totality of characteristics of reproductive structure, functions, phenotype, and genotype, differentiating the male from the female organism. Gender Dysphoria category (female) | 1 |