Atrioventricular (AV) block is a bradyarrhythmia caused by delay, or interruption, in the electrical conduction between the atria and the ventricles. Atrioventricular block occurs due to either anatomic or functional impairment and is classified into 3 types. The 1st-degree block is due to delayed conduction through the AV node. The 2nd-degree block is characterized by progressive conduction delay or intermittently blocked conduction. The 3rd-degree block involves total interruption in conduction between the atria and ventricles, causing complete AV dissociation. Patients may be asymptomatic or may present with syncope, chest pain, dyspnea, and bradycardia depending on the severity of the block. Electrocardiography (ECG) establishes the diagnosis, and treatment is based on the type of block and hemodynamic stability of the patient.
Last updated: Jan 5, 2026
Atrioventricular (AV) block is a delay, or interruption, in the electrical impulse as it passes from the atria to the ventricles through the AV node or the His-Purkinje system. Atrioventricular block Atrioventricular block Atrioventricular (AV) block is a bradyarrhythmia caused by delay, or interruption, in the electrical conduction between the atria and the ventricles. Atrioventricular block occurs due to either anatomic or functional impairment, and is classified into 3 types. Atrioventricular block (AV block) is classified based on the severity of the disruption.
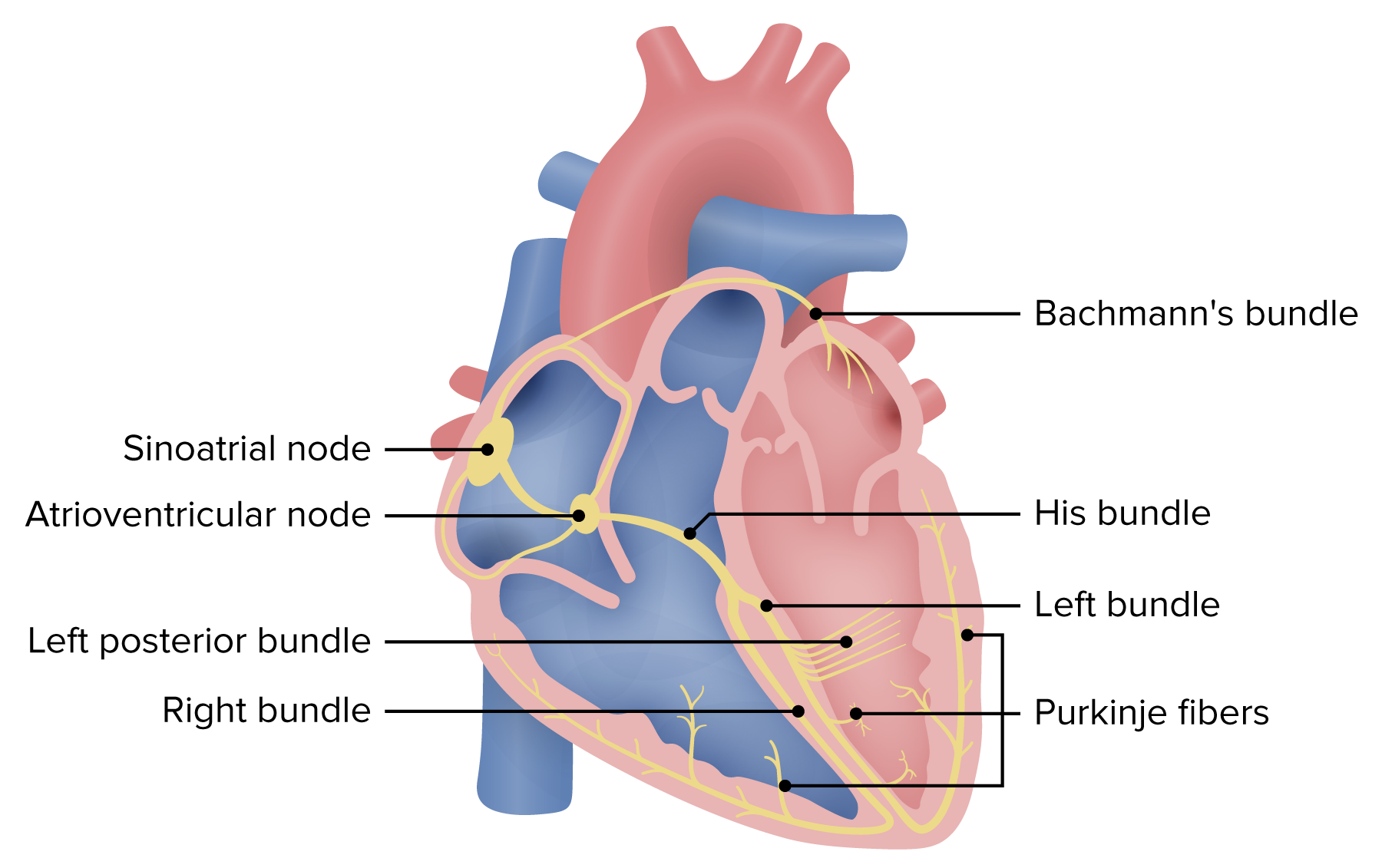
Schematic of the electrical system of the heart. Atrioventricular block may occur within the AV node, His bundle, or the bundle branches. Blocks at the level of the AV node or the His bundle will generally be narrow. Infrahisian (below the His bundle) blocks result in wide QRS complexes.
Image by Lecturio.2nd-degree AV block AV block Atrioventricular (AV) block is a bradyarrhythmia caused by delay, or interruption, in the electrical conduction between the atria and the ventricles. Atrioventricular block occurs due to either anatomic or functional impairment, and is classified into 3 types. Atrioventricular block (AV block) is further divided into 2 subtypes:
The diagnosis is made by electrocardiography Electrocardiography Recording of the moment-to-moment electromotive forces of the heart as projected onto various sites on the body’s surface, delineated as a scalar function of time. The recording is monitored by a tracing on slow moving chart paper or by observing it on a cardioscope, which is a cathode ray tube display. Electrocardiogram (ECG) ( ECG ECG An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphic representation of the electrical activity of the heart plotted against time. Adhesive electrodes are affixed to the skin surface allowing measurement of cardiac impulses from many angles. The ECG provides 3-dimensional information about the conduction system of the heart, the myocardium, and other cardiac structures. Electrocardiogram (ECG)), and the findings depend on the type of AV block AV block Atrioventricular (AV) block is a bradyarrhythmia caused by delay, or interruption, in the electrical conduction between the atria and the ventricles. Atrioventricular block occurs due to either anatomic or functional impairment, and is classified into 3 types. Atrioventricular block (AV block).
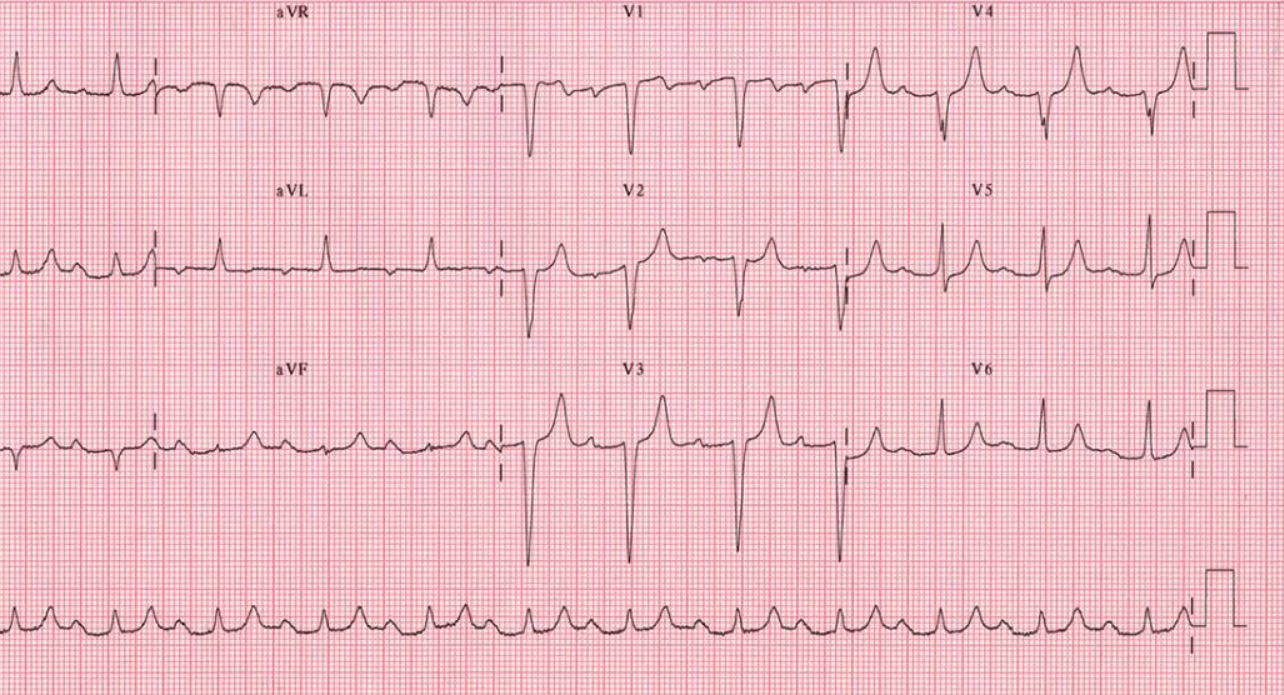
Twelve-lead ECG showing 1st-degree AV block: Notice the uniformly prolonged PR intervals. There are no “dropped” QRS complexes.
Image: “12-lead ECG ” by the Department of Cardiac Surgery, Tor Vergata University of Rome, Italy. License: CC BY 2.0.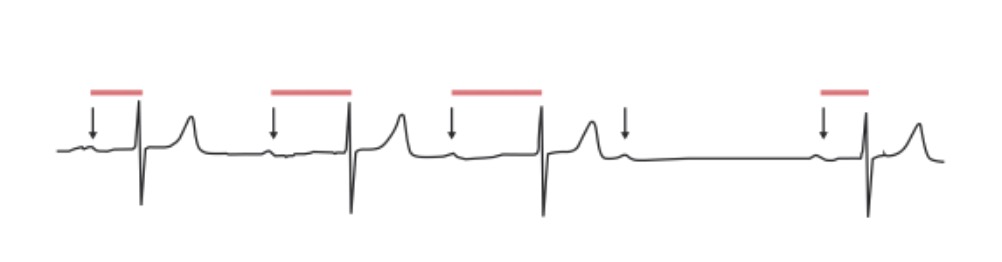
2nd-degree AV block, Mobitz 1: The PR interval progressively lengthens in an irregular rhythm until a QRS complex is “dropped”. Arrows: P waves; red lines: progressively prolonging PR interval.
Image by Lecturio.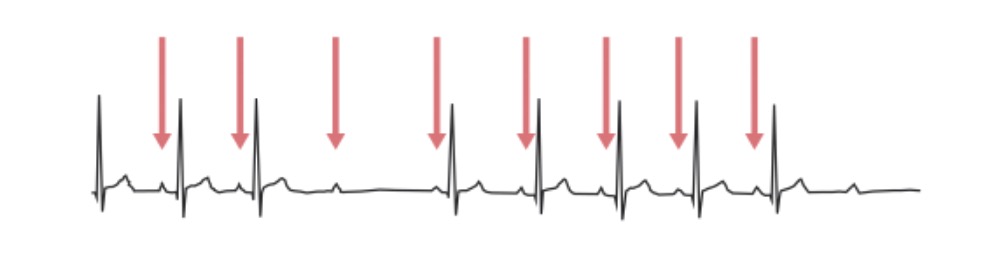
2nd-degree AV block, Mobitz 2: ECG shows impulse from the SA node is periodically “dropped”, resulting in a normal P wave followed by a drop of the QRS complex and T wave. The red arrows indicate P waves.
Image by Lecturio.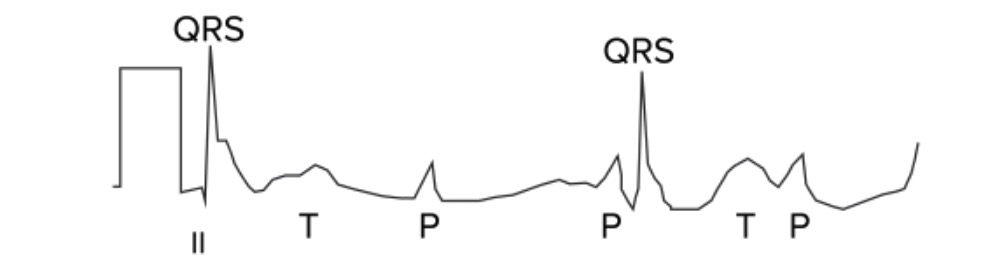
3rd-degree AV block: The atria and ventricles are out of sync and follow their own pacemakers. In this ECG, there is complete asynchronicity between P waves and QRS complexes.
Image by Lecturio.Laboratory studies:
Continuous ECG ECG An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphic representation of the electrical activity of the heart plotted against time. Adhesive electrodes are affixed to the skin surface allowing measurement of cardiac impulses from many angles. The ECG provides 3-dimensional information about the conduction system of the heart, the myocardium, and other cardiac structures. Electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring:
Cardiac imaging:
Electrophysiologic study (EPS):
Management may vary depending on practice location. The following information is based on current US and UK guidelines. See your local guidelines for additional information. Consultation with cardiology should be pursued in the presence of symptoms, instability, or possible need for pacemaker Pacemaker A device designed to stimulate, by electric impulses, contraction of the heart muscles. It may be temporary (external) or permanent (internal or internal-external). Bradyarrhythmias placement.
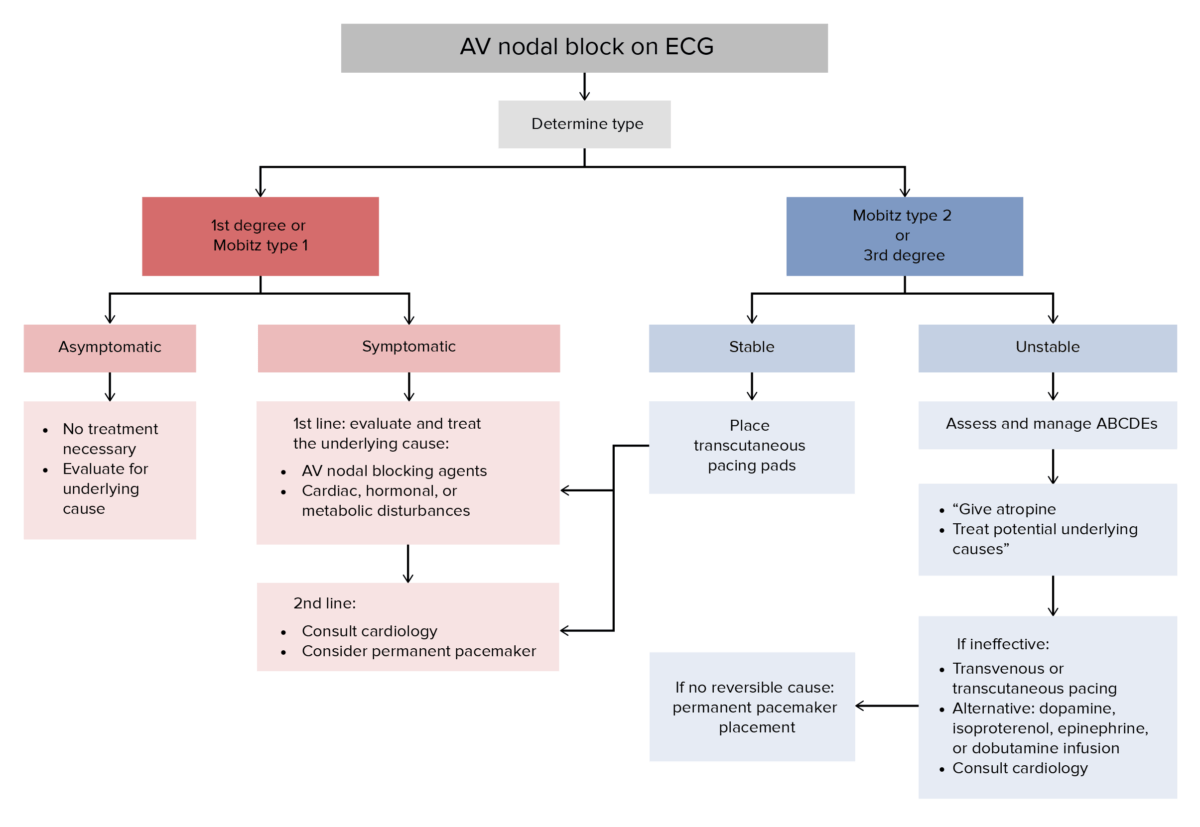
General algorithm for the approach to management of AV block[8–10,13]
ABCDE: airway, breathing, circulation, drugs, and environment
| Intervention | Dose | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Atropine Atropine An alkaloid, originally from atropa belladonna, but found in other plants, mainly solanaceae. Hyoscyamine is the 3(s)-endo isomer of atropine. Anticholinergic Drugs | ||
| Aminophylline (an alternative to atropine Atropine An alkaloid, originally from atropa belladonna, but found in other plants, mainly solanaceae. Hyoscyamine is the 3(s)-endo isomer of atropine. Anticholinergic Drugs) | 100–200 mg IV (slow injection) | |
| Dopamine Dopamine One of the catecholamine neurotransmitters in the brain. It is derived from tyrosine and is the precursor to norepinephrine and epinephrine. Dopamine is a major transmitter in the extrapyramidal system of the brain, and important in regulating movement. Receptors and Neurotransmitters of the CNS | 3‒20 µg/kg/min IV infusion (titrated) | |
| Epinephrine Epinephrine The active sympathomimetic hormone from the adrenal medulla. It stimulates both the alpha- and beta- adrenergic systems, causes systemic vasoconstriction and gastrointestinal relaxation, stimulates the heart, and dilates bronchi and cerebral vessels. Sympathomimetic Drugs | 0.1‒0.5 µg/kg/min IV infusion (titrated) | |
| Isoproterenol Isoproterenol Isopropyl analog of epinephrine; beta-sympathomimetic that acts on the heart, bronchi, skeletal muscle, alimentary tract, etc. It is used mainly as bronchodilator and heart stimulant. Sympathomimetic Drugs | 1‒20 µg/minute IV infusion (titrated) | |
| Dobutamine Dobutamine A catecholamine derivative with specificity for beta-1 adrenergic receptors. Sympathomimetic Drugs | 2‒5 µg/kg/min (titrated) | |
| Transcutaneous pacing |
Diagnosis Codes:
These codes are used to specify the severity of an Atrioventricular (AV) block, a delay or interruption in the electrical signal from the atria to the ventricles, ranging from a mild first-degree to a complete third-degree block.
| Domain | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ICD-10-CM | I44.0 | Atrioventricular block Atrioventricular block Atrioventricular (AV) block is a bradyarrhythmia caused by delay, or interruption, in the electrical conduction between the atria and the ventricles. Atrioventricular block occurs due to either anatomic or functional impairment, and is classified into 3 types. Atrioventricular block (AV block), first degree |
| ICD-10-CM | I44.1 | Atrioventricular block Atrioventricular block Atrioventricular (AV) block is a bradyarrhythmia caused by delay, or interruption, in the electrical conduction between the atria and the ventricles. Atrioventricular block occurs due to either anatomic or functional impairment, and is classified into 3 types. Atrioventricular block (AV block), second degree |
| ICD-10-CM | I44.2 | Atrioventricular block Atrioventricular block Atrioventricular (AV) block is a bradyarrhythmia caused by delay, or interruption, in the electrical conduction between the atria and the ventricles. Atrioventricular block occurs due to either anatomic or functional impairment, and is classified into 3 types. Atrioventricular block (AV block), complete |
| SNOMED CT | 27885002 | Atrioventricular block Atrioventricular block Atrioventricular (AV) block is a bradyarrhythmia caused by delay, or interruption, in the electrical conduction between the atria and the ventricles. Atrioventricular block occurs due to either anatomic or functional impairment, and is classified into 3 types. Atrioventricular block (AV block) (disorder) |
Evaluation & Workup:
These codes are used to order the tests needed to diagnose and characterize an AV block AV block Atrioventricular (AV) block is a bradyarrhythmia caused by delay, or interruption, in the electrical conduction between the atria and the ventricles. Atrioventricular block occurs due to either anatomic or functional impairment, and is classified into 3 types. Atrioventricular block (AV block). A standard 12-lead ECG ECG An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphic representation of the electrical activity of the heart plotted against time. Adhesive electrodes are affixed to the skin surface allowing measurement of cardiac impulses from many angles. The ECG provides 3-dimensional information about the conduction system of the heart, the myocardium, and other cardiac structures. Electrocardiogram (ECG) can identify the block, while a Holter monitor is used to detect intermittent blocks over a longer period.
| Domain | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CPT | 93000 | Electrocardiogram Electrocardiogram An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphic representation of the electrical activity of the heart plotted against time. Adhesive electrodes are affixed to the skin surface allowing measurement of cardiac impulses from many angles. The ECG provides 3-dimensional information about the conduction system of the heart, the myocardium, and other cardiac structures. Electrocardiogram (ECG), routine ECG ECG An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphic representation of the electrical activity of the heart plotted against time. Adhesive electrodes are affixed to the skin surface allowing measurement of cardiac impulses from many angles. The ECG provides 3-dimensional information about the conduction system of the heart, the myocardium, and other cardiac structures. Electrocardiogram (ECG) with at least 12 leads |
| CPT | 93224 | External electrocardiographic recording up to 48 hours by continuous rhythm recording and storage (Holter) |
Procedures/Interventions:
This CPT code is used to bill for the implantation Implantation Endometrial implantation of embryo, mammalian at the blastocyst stage. Fertilization and First Week of a permanent pacemaker Pacemaker A device designed to stimulate, by electric impulses, contraction of the heart muscles. It may be temporary (external) or permanent (internal or internal-external). Bradyarrhythmias, the definitive treatment for symptomatic or high-grade AV blocks to ensure the ventricles contract at an adequate rate.
| Domain | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CPT | 33208 | Insertion of new or replacement of permanent pacemaker Pacemaker A device designed to stimulate, by electric impulses, contraction of the heart muscles. It may be temporary (external) or permanent (internal or internal-external). Bradyarrhythmias with transvenous electrode(s); atrial and ventricular |
| CPT | 33206 | Insertion of new or replacement of permanent pacemaker Pacemaker A device designed to stimulate, by electric impulses, contraction of the heart muscles. It may be temporary (external) or permanent (internal or internal-external). Bradyarrhythmias with transvenous electrode(s); atrial |
Medications:
This code is used to prescribe atropine Atropine An alkaloid, originally from atropa belladonna, but found in other plants, mainly solanaceae. Hyoscyamine is the 3(s)-endo isomer of atropine. Anticholinergic Drugs, a medication used in emergency settings to temporarily increase the heart rate Heart rate The number of times the heart ventricles contract per unit of time, usually per minute. Cardiac Physiology in patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship who are symptomatic from a slow heart rate Heart rate The number of times the heart ventricles contract per unit of time, usually per minute. Cardiac Physiology ( bradycardia Bradycardia Bradyarrhythmia is a rhythm in which the heart rate is less than 60/min. Bradyarrhythmia can be physiologic, without symptoms or hemodynamic change. Pathologic bradyarrhythmia results in reduced cardiac output and hemodynamic instability causing syncope, dizziness, or dyspnea. Bradyarrhythmias) caused by an AV block AV block Atrioventricular (AV) block is a bradyarrhythmia caused by delay, or interruption, in the electrical conduction between the atria and the ventricles. Atrioventricular block occurs due to either anatomic or functional impairment, and is classified into 3 types. Atrioventricular block (AV block).
| Domain | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| RxNorm | 1223 | Atropine Atropine An alkaloid, originally from atropa belladonna, but found in other plants, mainly solanaceae. Hyoscyamine is the 3(s)-endo isomer of atropine. Anticholinergic Drugs (ingredient) |
| ATC | A03BA01 | Atropine Atropine An alkaloid, originally from atropa belladonna, but found in other plants, mainly solanaceae. Hyoscyamine is the 3(s)-endo isomer of atropine. Anticholinergic Drugs |
Complications & Supportive Procedures:
These codes are used to document the primary clinical consequences of a high-grade AV block AV block Atrioventricular (AV) block is a bradyarrhythmia caused by delay, or interruption, in the electrical conduction between the atria and the ventricles. Atrioventricular block occurs due to either anatomic or functional impairment, and is classified into 3 types. Atrioventricular block (AV block), which include episodes of fainting ( syncope Syncope Syncope is a short-term loss of consciousness and loss of postural stability followed by spontaneous return of consciousness to the previous neurologic baseline without the need for resuscitation. The condition is caused by transient interruption of cerebral blood flow that may be benign or related to a underlying life-threatening condition. Syncope) due to insufficient blood flow Blood flow Blood flow refers to the movement of a certain volume of blood through the vasculature over a given unit of time (e.g., mL per minute). Vascular Resistance, Flow, and Mean Arterial Pressure to the brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification and the risk of asystole Asystole No discernible electrical activity, flatline on electrocardiogram (P waves and QRS complexes are not present). Cardiac Arrest (complete cessation of heart activity).
| Domain | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ICD-10-CM | R55 | Syncope Syncope Syncope is a short-term loss of consciousness and loss of postural stability followed by spontaneous return of consciousness to the previous neurologic baseline without the need for resuscitation. The condition is caused by transient interruption of cerebral blood flow that may be benign or related to a underlying life-threatening condition. Syncope and collapse |
| ICD-10-CM | I46.8 | Cardiac arrest Cardiac arrest Cardiac arrest is the sudden, complete cessation of cardiac output with hemodynamic collapse. Patients present as pulseless, unresponsive, and apneic. Rhythms associated with cardiac arrest are ventricular fibrillation/tachycardia, asystole, or pulseless electrical activity. Cardiac Arrest with successful resuscitation Resuscitation The restoration to life or consciousness of one apparently dead. . Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome |