Antivirals against hepatitis C Hepatitis C Hepatitis C is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). The infection can be transmitted through infectious blood or body fluids and may be transmitted during childbirth or through IV drug use or sexual intercourse. Hepatitis C virus can cause both acute and chronic hepatitis, ranging from a mild to a serious, lifelong illness including liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis C Virus include a wide range of drug classes. The previous treatment regimen included interferon alfa (IFN-α) and ribavirin, which target viral entry, immune modulation, and viral replication. New, direct-acting antiviral Antiviral Antivirals for Hepatitis B (DAV) agents target specific nonstructural (NS) proteins Proteins Linear polypeptides that are synthesized on ribosomes and may be further modified, crosslinked, cleaved, or assembled into complex proteins with several subunits. The specific sequence of amino acids determines the shape the polypeptide will take, during protein folding, and the function of the protein. Energy Homeostasis of hepatitis C Hepatitis C Hepatitis C is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). The infection can be transmitted through infectious blood or body fluids and may be transmitted during childbirth or through IV drug use or sexual intercourse. Hepatitis C virus can cause both acute and chronic hepatitis, ranging from a mild to a serious, lifelong illness including liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis C Virus virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology ( HCV HCV Hepatitis C is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). Hepatitis C virus is an RNA virus and a member of the genus Hepacivirus and the family Flaviviridae. The infection can be transmitted through infectious blood or body fluids and may be transmitted during childbirth or through IV drug use or sexual intercourse. Hepatitis C Virus), which are important for viral replication. These agents include NS3A/4A protease inhibitors Protease Inhibitors Compounds which inhibit or antagonize biosynthesis or actions of proteases (endopeptidases). Anti-HIV Drugs, NS5A inhibitors, and NS5B polymerase inhibitors. DAVs are often given in combination therapy and are the preferred management of hepatitis C Hepatitis C Hepatitis C is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). The infection can be transmitted through infectious blood or body fluids and may be transmitted during childbirth or through IV drug use or sexual intercourse. Hepatitis C virus can cause both acute and chronic hepatitis, ranging from a mild to a serious, lifelong illness including liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis C Virus due to their high success rate and milder side effect profile.
Last updated: Aug 18, 2022
Hepatitis C Hepatitis C Hepatitis C is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). The infection can be transmitted through infectious blood or body fluids and may be transmitted during childbirth or through IV drug use or sexual intercourse. Hepatitis C virus can cause both acute and chronic hepatitis, ranging from a mild to a serious, lifelong illness including liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis C Virus virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure encodes:
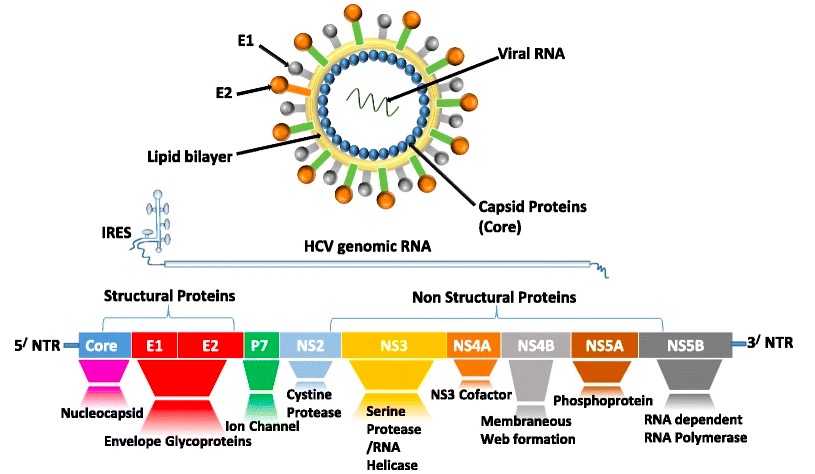
Viral structure of hepatitis C and the proteins that are translated from its genome:
Structural proteins include core, envelope 1 (E1), and E2. NS2, NS3, NS4A, NS4B, NS5A, and NS5B are nonstructural (NS) proteins, most of which are the targets for direct-acting antiviral therapy.
Interferons Interferons Interferon (IFN) is a cytokine with antiviral properties (it interferes with viral infections) and various roles in immunoregulation. The different types are type I IFN (IFN-ɑ and IFN-β), type II IFN (IFN-ɣ), and type III IFN (IFN-ƛ). Interferons are a type of signaling protein belonging to the cytokines Cytokines Non-antibody proteins secreted by inflammatory leukocytes and some non-leukocytic cells, that act as intercellular mediators. They differ from classical hormones in that they are produced by a number of tissue or cell types rather than by specialized glands. They generally act locally in a paracrine or autocrine rather than endocrine manner. Adaptive Immune Response family.
IFN-α works through several mechanisms:
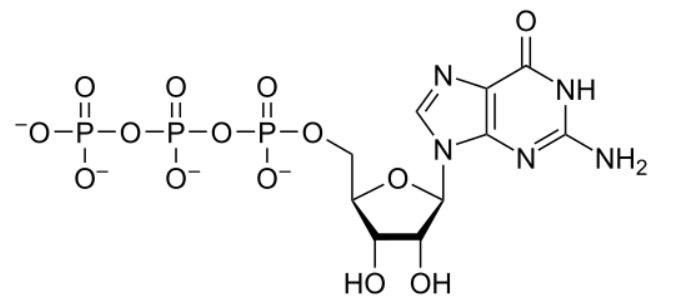
The chemical structure of guanosine triphosphate (GTP)
Image: “GTP chemical structure” by Hbf878. License: CC0 1.0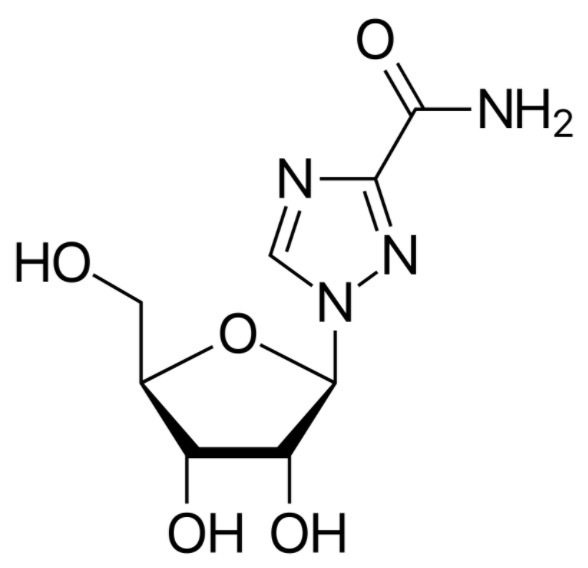
The chemical structure of ribavirin:
It is very similar to guanosine, which plays an important role in its antiviral action.
NS3A/4A protease inhibitors Protease Inhibitors Compounds which inhibit or antagonize biosynthesis or actions of proteases (endopeptidases). Anti-HIV Drugs is a drug class that inhibits NS3/4A serine Serine A non-essential amino acid occurring in natural form as the l-isomer. It is synthesized from glycine or threonine. It is involved in the biosynthesis of purines; pyrimidines; and other amino acids. Synthesis of Nonessential Amino Acids protease Protease Enzyme of the human immunodeficiency virus that is required for post-translational cleavage of gag and gag-pol precursor polyproteins into functional products needed for viral assembly. HIV protease is an aspartic protease encoded by the amino terminus of the pol gene. HIV Infection and AIDS, which is necessary for HCV HCV Hepatitis C is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). Hepatitis C virus is an RNA virus and a member of the genus Hepacivirus and the family Flaviviridae. The infection can be transmitted through infectious blood or body fluids and may be transmitted during childbirth or through IV drug use or sexual intercourse. Hepatitis C Virus replication.
NS3A/4A protease inhibitors Protease Inhibitors Compounds which inhibit or antagonize biosynthesis or actions of proteases (endopeptidases). Anti-HIV Drugs are used (usually in combination therapy with another DAV) to treat chronic hepatitis C Hepatitis C Hepatitis C is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). The infection can be transmitted through infectious blood or body fluids and may be transmitted during childbirth or through IV drug use or sexual intercourse. Hepatitis C virus can cause both acute and chronic hepatitis, ranging from a mild to a serious, lifelong illness including liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis C Virus.
These medications are used (usually in combination therapy with another DAV) for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C Hepatitis C Hepatitis C is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). The infection can be transmitted through infectious blood or body fluids and may be transmitted during childbirth or through IV drug use or sexual intercourse. Hepatitis C virus can cause both acute and chronic hepatitis, ranging from a mild to a serious, lifelong illness including liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis C Virus.
NS5B RNA-dependent RNA polymerase RNA-dependent RNA polymerase An enzyme that catalyses rna-template-directed extension of the 3′- end of an RNA strand by one nucleotide at a time, and can initiate a chain de novo. Virology inhibitors target NS5B (an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase RNA-dependent RNA polymerase An enzyme that catalyses rna-template-directed extension of the 3′- end of an RNA strand by one nucleotide at a time, and can initiate a chain de novo. Virology).
NS5B RNA-dependent RNA polymerase RNA-dependent RNA polymerase An enzyme that catalyses rna-template-directed extension of the 3′- end of an RNA strand by one nucleotide at a time, and can initiate a chain de novo. Virology inhibitors are used (usually in combination therapy with another DAV) for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C Hepatitis C Hepatitis C is an infection of the liver caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). The infection can be transmitted through infectious blood or body fluids and may be transmitted during childbirth or through IV drug use or sexual intercourse. Hepatitis C virus can cause both acute and chronic hepatitis, ranging from a mild to a serious, lifelong illness including liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis C Virus.