Pulmonary hypoplasia Hypoplasia Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS) is the lack of normal fetal development of the pulmonary parenchyma. The condition is characterized by a decreased number of alveoli Alveoli Small polyhedral outpouchings along the walls of the alveolar sacs, alveolar ducts and terminal bronchioles through the walls of which gas exchange between alveolar air and pulmonary capillary blood takes place. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) and bronchial generations. Oligohydramnios Oligohydramnios Oligohydramnios refers to amniotic fluid volume less than expected for the current gestational age. Oligohydramnios is diagnosed by ultrasound and defined as an amniotic fluid index (AFI) of ‰¤ 5 cm or a single deep pocket (SDP) of < 2 cm in the 2nd or 3rd trimester. Oligohydramnios is a notable cause, but conditions that restrict lung development or lead to fetal lung compression Compression Blunt Chest Trauma can also result in pulmonary hypoplasia Hypoplasia Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS). A diagnosis of pulmonary hypoplasia Hypoplasia Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS) can be suspected on prenatal ultrasound. Findings include reduced amniotic fluid Amniotic fluid A clear, yellowish liquid that envelopes the fetus inside the sac of amnion. In the first trimester, it is likely a transudate of maternal or fetal plasma. In the second trimester, amniotic fluid derives primarily from fetal lung and kidney. Cells or substances in this fluid can be removed for prenatal diagnostic tests (amniocentesis). Placenta, Umbilical Cord, and Amniotic Cavity, congenital abnormalities Congenital Abnormalities Malformations of organs or body parts during development in utero. Omphalocele, and characteristic anatomical measurements. A more complete picture at birth points to the diagnosis based on clinical findings (respiratory distress, typical anomalies) and further evaluation (reduced lung volume on imaging). Treatment is focused on antenatal lung maturity and postnatal ventilatory support, with subsequent correction of associated causes and defects. Survival depends on the degree of lung underdevelopment.
Last updated: Jan 28, 2025
Pulmonary hypoplasia Hypoplasia Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS) is the insufficient or defective development of one or both lungs Lungs Lungs are the main organs of the respiratory system. Lungs are paired viscera located in the thoracic cavity and are composed of spongy tissue. The primary function of the lungs is to oxygenate blood and eliminate CO2. Lungs: Anatomy, resulting in underdeveloped or undeveloped pulmonary parenchyma with decreased alveoli Alveoli Small polyhedral outpouchings along the walls of the alveolar sacs, alveolar ducts and terminal bronchioles through the walls of which gas exchange between alveolar air and pulmonary capillary blood takes place. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) and airway Airway ABCDE Assessment branches.
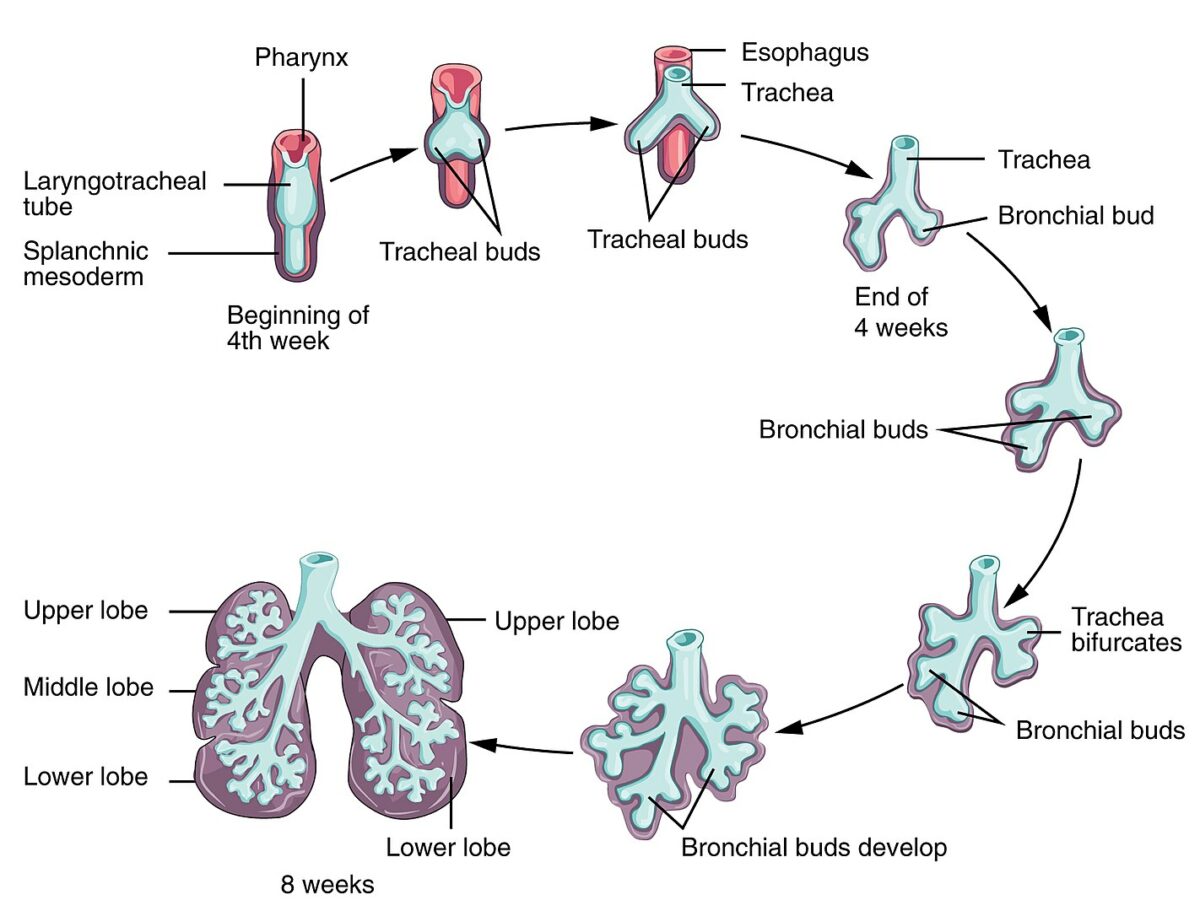
Development of the lungs:
The respiratory system begins development by week 4 of gestation. The olfactory pit forms from the ectoderm, one of the structures to become the nasal cavity. The laryngotracheal bud forms from the primitive pharynx. From this bud, the longitudinal extension becomes the tracheal and bronchial buds.
The process of elongation and branching of buds continues as conducting airways up to 16 weeks of gestation. Major maturation occurs by 24 weeks, with significant alveolar precursors developing and an increased amount of surfactant produced. By 28 weeks of gestation, there usually will be enough mature alveoli.
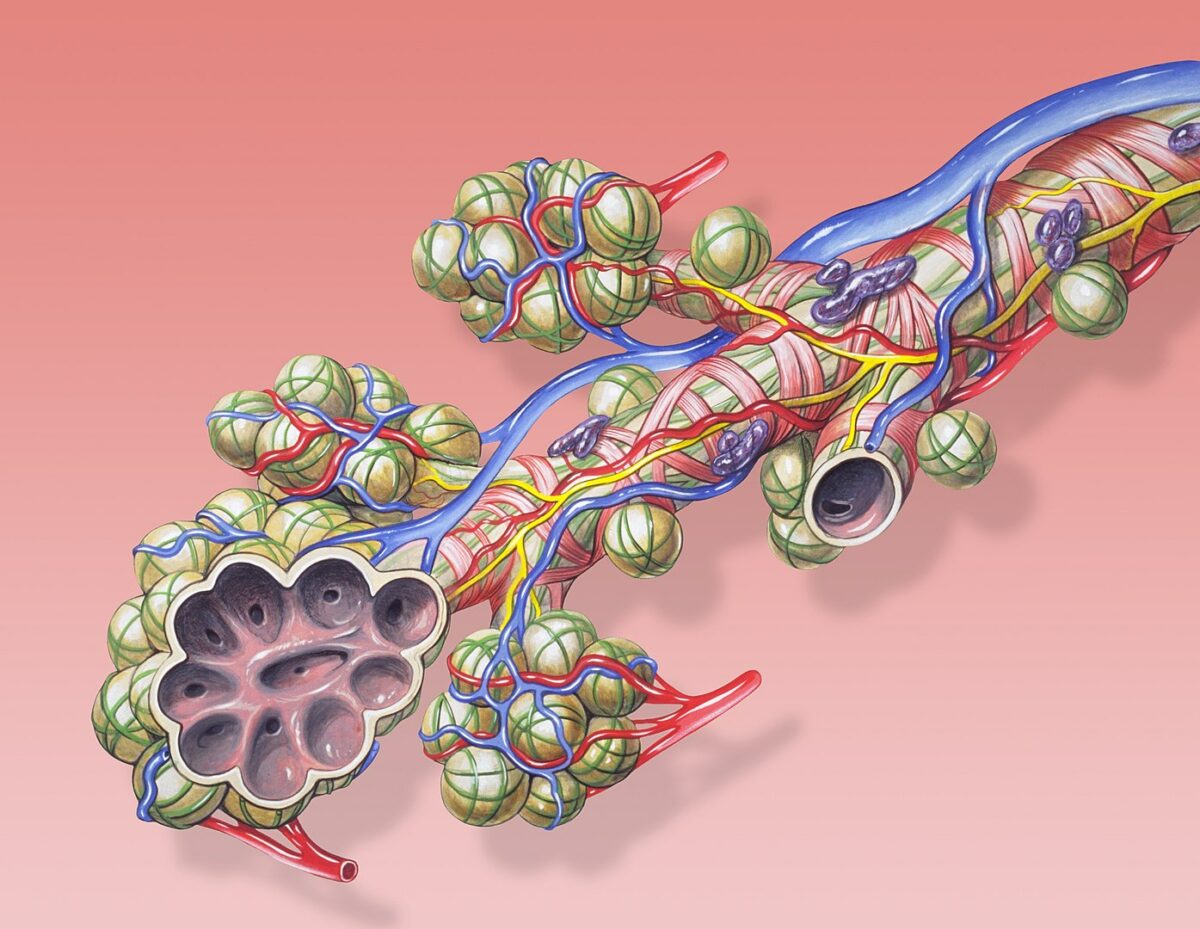
Mature structures of the lung: alveoli, bronchiole and pulmonary circulation
Image: “Bronchial anatomy” by Patrick J. Lynch. License: CC BY 2.5Multiple aspects of the impairment of fetal lung growth can lead to hypoplasia Hypoplasia Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS).
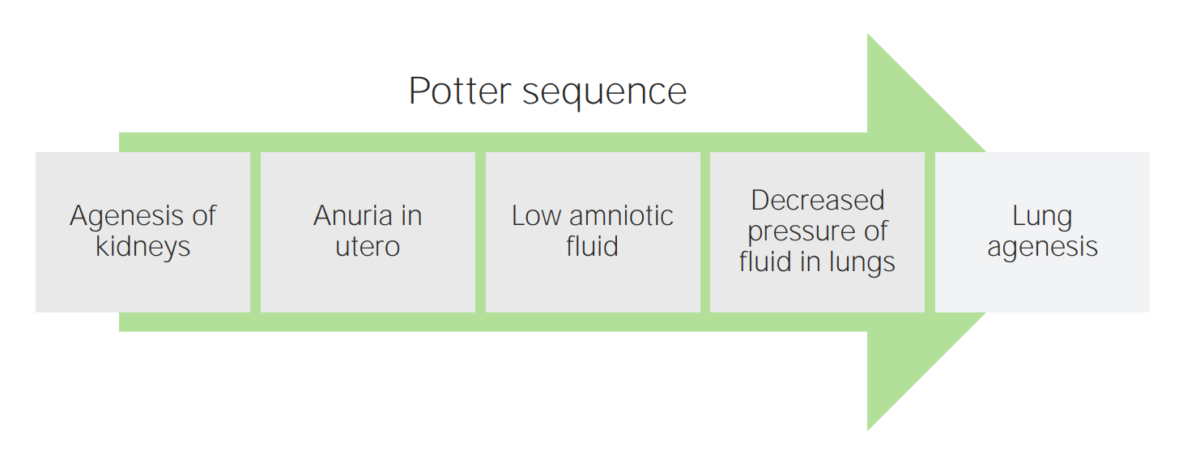
A diagram of the Potter sequence
Image by Lecturio.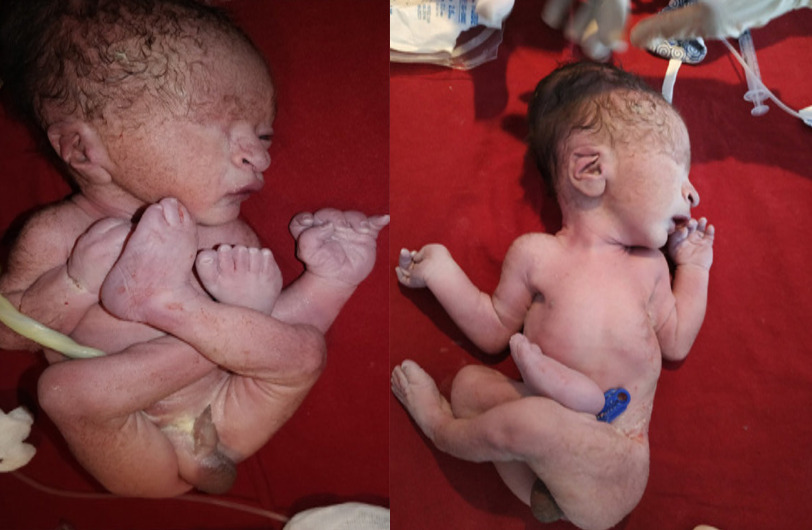
Potter sequence:
Pregnancy complicated by oligohydramnios can lead to newborn abnormalities.
Images show Potter facies (micrognathia, low-set ears, flattened nasal bridge, beaked nose). Limb deformities include persistently flexed and dislocated hip with bilateral clubbed foot. The newborn in the images also has an absent right eye.
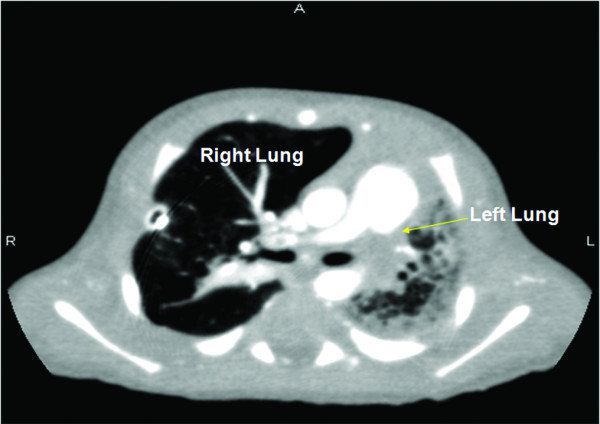
Pulmonary hypoplasia:
CT of the lung of a neonate with left lung hypoplasia