Hemolytic uremic syndrome Hemolytic uremic syndrome A syndrome that is associated with microvascular diseases of the kidney, such as renal cortical necrosis. It is characterized by hemolytic anemia; thrombocytopenia; and acute renal failure. Hypocoagulable Conditions (HUS) is a clinical phenomenon most commonly seen in children that consists of a classic triad of microangiopathic hemolytic anemia Hemolytic Anemia Hemolytic anemia (HA) is the term given to a large group of anemias that are caused by the premature destruction/hemolysis of circulating red blood cells (RBCs). Hemolysis can occur within (intravascular hemolysis) or outside the blood vessels (extravascular hemolysis). Hemolytic Anemia, thrombocytopenia Thrombocytopenia Thrombocytopenia occurs when the platelet count is < 150,000 per microliter. The normal range for platelets is usually 150,000-450,000/µL of whole blood. Thrombocytopenia can be a result of decreased production, increased destruction, or splenic sequestration of platelets. Patients are often asymptomatic until platelet counts are < 50,000/µL. Thrombocytopenia, and acute kidney injury Acute Kidney Injury Acute kidney injury refers to sudden and often reversible loss of renal function, which develops over days or weeks. Azotemia refers to elevated levels of nitrogen-containing substances in the blood that accompany AKI, which include BUN and creatinine. Acute Kidney Injury. Hemolytic uremic syndrome Hemolytic uremic syndrome A syndrome that is associated with microvascular diseases of the kidney, such as renal cortical necrosis. It is characterized by hemolytic anemia; thrombocytopenia; and acute renal failure. Hypocoagulable Conditions is a major cause of acute kidney injury Acute Kidney Injury Acute kidney injury refers to sudden and often reversible loss of renal function, which develops over days or weeks. Azotemia refers to elevated levels of nitrogen-containing substances in the blood that accompany AKI, which include BUN and creatinine. Acute Kidney Injury in children and is most commonly associated with a prodrome Prodrome Symptoms that appear 24–48 hours prior to migraine onset. Migraine Headache of diarrheal illness caused by Shiga-like toxin-producing bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases. Bacteriology. Laboratory analysis confirms microangiopathic hemolytic anemia Hemolytic Anemia Hemolytic anemia (HA) is the term given to a large group of anemias that are caused by the premature destruction/hemolysis of circulating red blood cells (RBCs). Hemolysis can occur within (intravascular hemolysis) or outside the blood vessels (extravascular hemolysis). Hemolytic Anemia (hemoglobin < 8 g/dL, schistocytes, and negative direct Coombs), thrombocytopenia Thrombocytopenia Thrombocytopenia occurs when the platelet count is < 150,000 per microliter. The normal range for platelets is usually 150,000-450,000/µL of whole blood. Thrombocytopenia can be a result of decreased production, increased destruction, or splenic sequestration of platelets. Patients are often asymptomatic until platelet counts are < 50,000/µL. Thrombocytopenia (platelet count < 140,000/mm³), and acute kidney injury Acute Kidney Injury Acute kidney injury refers to sudden and often reversible loss of renal function, which develops over days or weeks. Azotemia refers to elevated levels of nitrogen-containing substances in the blood that accompany AKI, which include BUN and creatinine. Acute Kidney Injury (elevated creatinine and blood urea Urea A compound formed in the liver from ammonia produced by the deamination of amino acids. It is the principal end product of protein catabolism and constitutes about one half of the total urinary solids. Urea Cycle nitrogen Nitrogen An element with the atomic symbol n, atomic number 7, and atomic weight [14. 00643; 14. 00728]. Nitrogen exists as a diatomic gas and makes up about 78% of the earth's atmosphere by volume. It is a constituent of proteins and nucleic acids and found in all living cells. Urea Cycle (BUN)). The management of HUS is primarily through supportive care.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Hemolytic uremic syndrome Hemolytic uremic syndrome A syndrome that is associated with microvascular diseases of the kidney, such as renal cortical necrosis. It is characterized by hemolytic anemia; thrombocytopenia; and acute renal failure. Hypocoagulable Conditions (HUS) is a disease of the capillaries Capillaries Capillaries are the primary structures in the circulatory system that allow the exchange of gas, nutrients, and other materials between the blood and the extracellular fluid (ECF). Capillaries are the smallest of the blood vessels. Because a capillary diameter is so small, only 1 RBC may pass through at a time. Capillaries: Histology (microangiopathy) that causes the formation of blood clots, anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types caused by the destruction of RBC in these clotted capillaries Capillaries Capillaries are the primary structures in the circulatory system that allow the exchange of gas, nutrients, and other materials between the blood and the extracellular fluid (ECF). Capillaries are the smallest of the blood vessels. Because a capillary diameter is so small, only 1 RBC may pass through at a time. Capillaries: Histology ( hemolytic anemia Hemolytic Anemia Hemolytic anemia (HA) is the term given to a large group of anemias that are caused by the premature destruction/hemolysis of circulating red blood cells (RBCs). Hemolysis can occur within (intravascular hemolysis) or outside the blood vessels (extravascular hemolysis). Hemolytic Anemia), acute kidney injury Acute Kidney Injury Acute kidney injury refers to sudden and often reversible loss of renal function, which develops over days or weeks. Azotemia refers to elevated levels of nitrogen-containing substances in the blood that accompany AKI, which include BUN and creatinine. Acute Kidney Injury, and low platelets Platelets Platelets are small cell fragments involved in hemostasis. Thrombopoiesis takes place primarily in the bone marrow through a series of cell differentiation and is influenced by several cytokines. Platelets are formed after fragmentation of the megakaryocyte cytoplasm. Platelets: Histology ( thrombocytopenia Thrombocytopenia Thrombocytopenia occurs when the platelet count is < 150,000 per microliter. The normal range for platelets is usually 150,000-450,000/µL of whole blood. Thrombocytopenia can be a result of decreased production, increased destruction, or splenic sequestration of platelets. Patients are often asymptomatic until platelet counts are < 50,000/µL. Thrombocytopenia).
Etiology is classified as acquired (infectious versus noninfectious) or hereditary.
The pathophysiology for HUS secondary to Shiga-like toxin has been well described.
Other forms of HUS:
Symptoms usually occur 5–7 days after diarrhea Diarrhea Diarrhea is defined as ≥ 3 watery or loose stools in a 24-hour period. There are a multitude of etiologies, which can be classified based on the underlying mechanism of disease. The duration of symptoms (acute or chronic) and characteristics of the stools (e.g., watery, bloody, steatorrheic, mucoid) can help guide further diagnostic evaluation. Diarrhea and may include:
Diagnosis is clinical, based on the classic triad of:
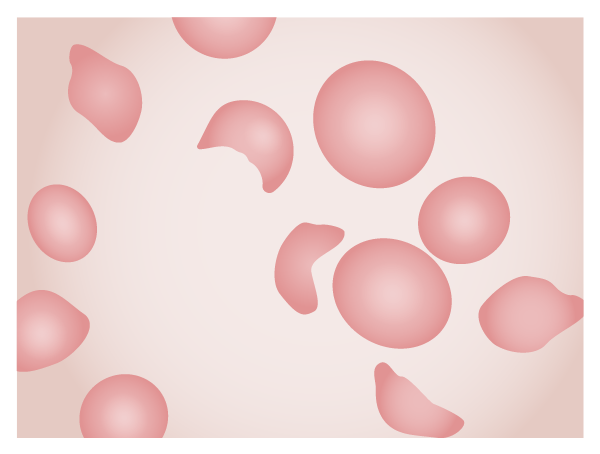
Blood slide of a patient with HUS. Note the schistocytes, fragments of erythrocytes left after mechanical injury of the cells in the microvasculature.
Image by Lecturio.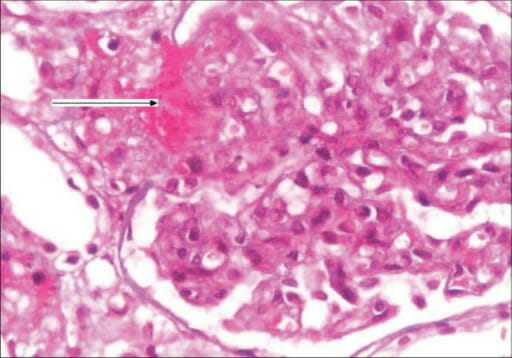
Kidney biopsy of hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS): Kidney biopsy showing the glomerulus with an increase in mesangial matrix, focal endocapillary cell swelling, arterioles with platelet-fibrin thrombi (arrow), and fibrinoid necrosis (H&E stain, 400x)
Image: “F0002: Kidney biopsy showing glomerulus with increase in mesangial matrix, focal endocapillary cell swelling and arterioles with platelet fibrin thrombi (arrow), and fibrinoid necrosis. (H&E stain, magnification ×400)” by G. Lakshminarayana, R. Rajesh, A. Jojo, G. Kurian, and V. N. Unni. License: CC BY 2.0Management of HUS is primarily through supportive care.
Note that antibiotic treatment during bloody diarrheal illnesses caused by Shiga toxin-producing bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases. Bacteriology is associated with an increased risk of developing HUS.