Mitral regurgitation Regurgitation Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) ( MR MR Calculated as the ratio of the total number of people who die due to all causes over a specific time period to the total number of people in the selected population. Measures of Health Status) is the backflow of blood from the left ventricle (LV) to the left atrium (LA) during systole Systole Period of contraction of the heart, especially of the heart ventricles. Cardiac Cycle. Mitral regurgitation Regurgitation Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) may be acute ( myocardial infarction Myocardial infarction MI is ischemia and death of an area of myocardial tissue due to insufficient blood flow and oxygenation, usually from thrombus formation on a ruptured atherosclerotic plaque in the epicardial arteries. Clinical presentation is most commonly with chest pain, but women and patients with diabetes may have atypical symptoms. Myocardial Infarction) or chronic (myxomatous degeneration). Acute and decompensated chronic MR MR Calculated as the ratio of the total number of people who die due to all causes over a specific time period to the total number of people in the selected population. Measures of Health Status can lead to pulmonary venous congestion, resulting in symptoms of dyspnea Dyspnea Dyspnea is the subjective sensation of breathing discomfort. Dyspnea is a normal manifestation of heavy physical or psychological exertion, but also may be caused by underlying conditions (both pulmonary and extrapulmonary). Dyspnea, orthopnea Orthopnea Pulmonary Edema, and fatigue Fatigue The state of weariness following a period of exertion, mental or physical, characterized by a decreased capacity for work and reduced efficiency to respond to stimuli. Fibromyalgia. Acute MR MR Calculated as the ratio of the total number of people who die due to all causes over a specific time period to the total number of people in the selected population. Measures of Health Status is an emergency because it can cause cardiogenic shock Cardiogenic shock Shock resulting from diminution of cardiac output in heart disease. Types of Shock, and requires medical stabilization and surgery. In chronic severe MR MR Calculated as the ratio of the total number of people who die due to all causes over a specific time period to the total number of people in the selected population. Measures of Health Status, patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship are evaluated for surgical repair or replacement.
Last updated: Dec 29, 2025
Mitral regurgitation Regurgitation Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) ( MR MR Calculated as the ratio of the total number of people who die due to all causes over a specific time period to the total number of people in the selected population. Measures of Health Status) is the backflow of blood to the left atrium (LA) through the mitral valve Mitral valve The valve between the left atrium and left ventricle of the heart. Heart: Anatomy (MV) during ventricular contraction.
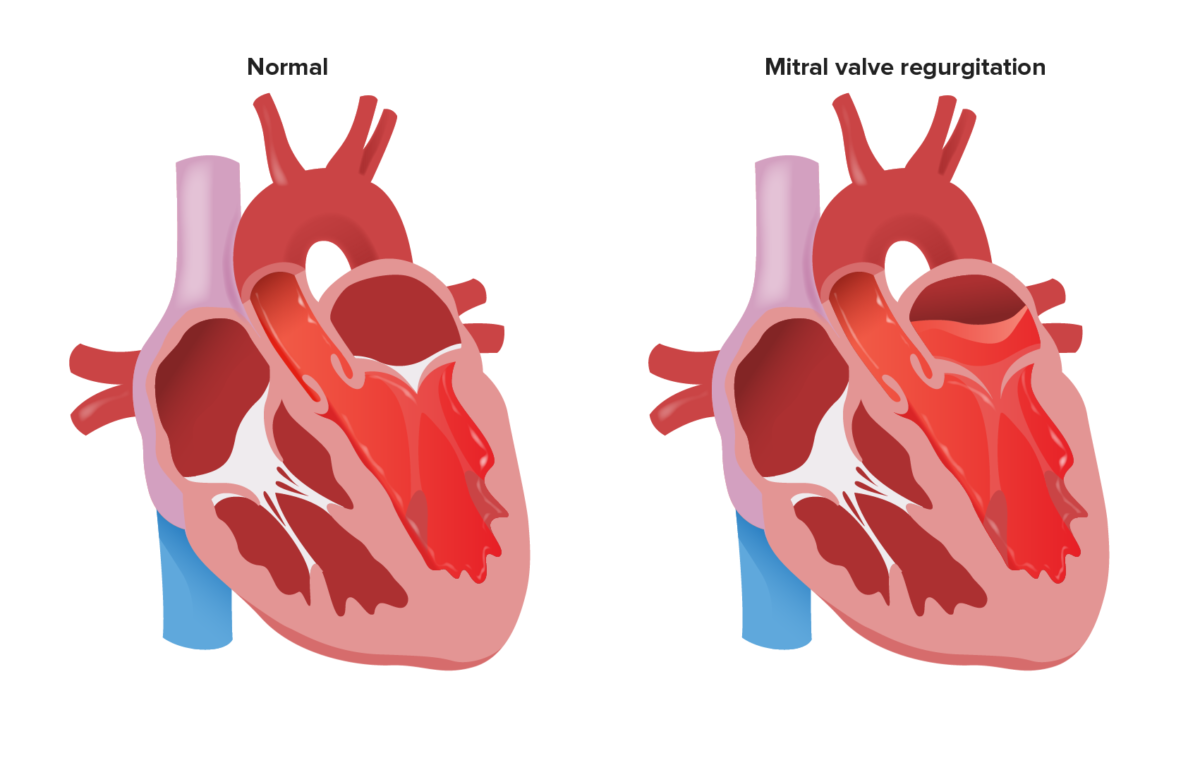
Reflux of blood into the LA during systole with MR
Image by Lecturio.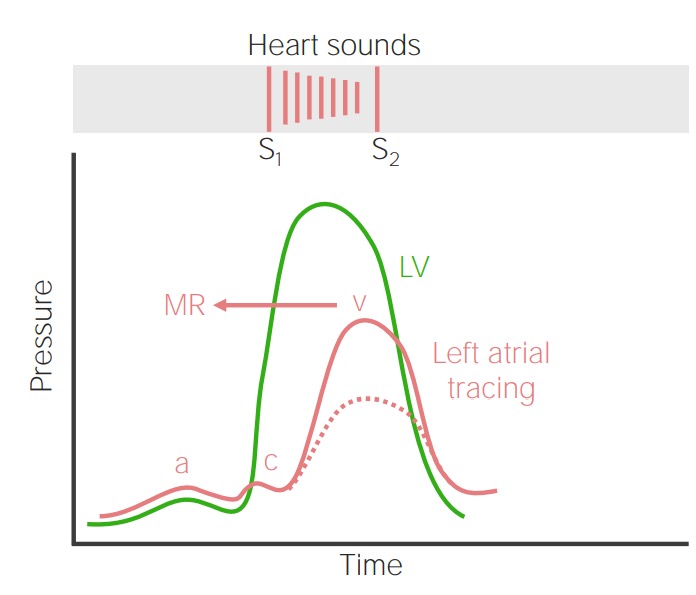
Relationship between LV pressure (green line), normal LA pressure (dashed red line), and LA pressure in MR (solid red line) throughout the cardiac cycle: In MR, LV contraction ejects blood into the LA, leading to a systolic murmur and elevation of the LA pressure (increased v wave).
Image by Lecturio.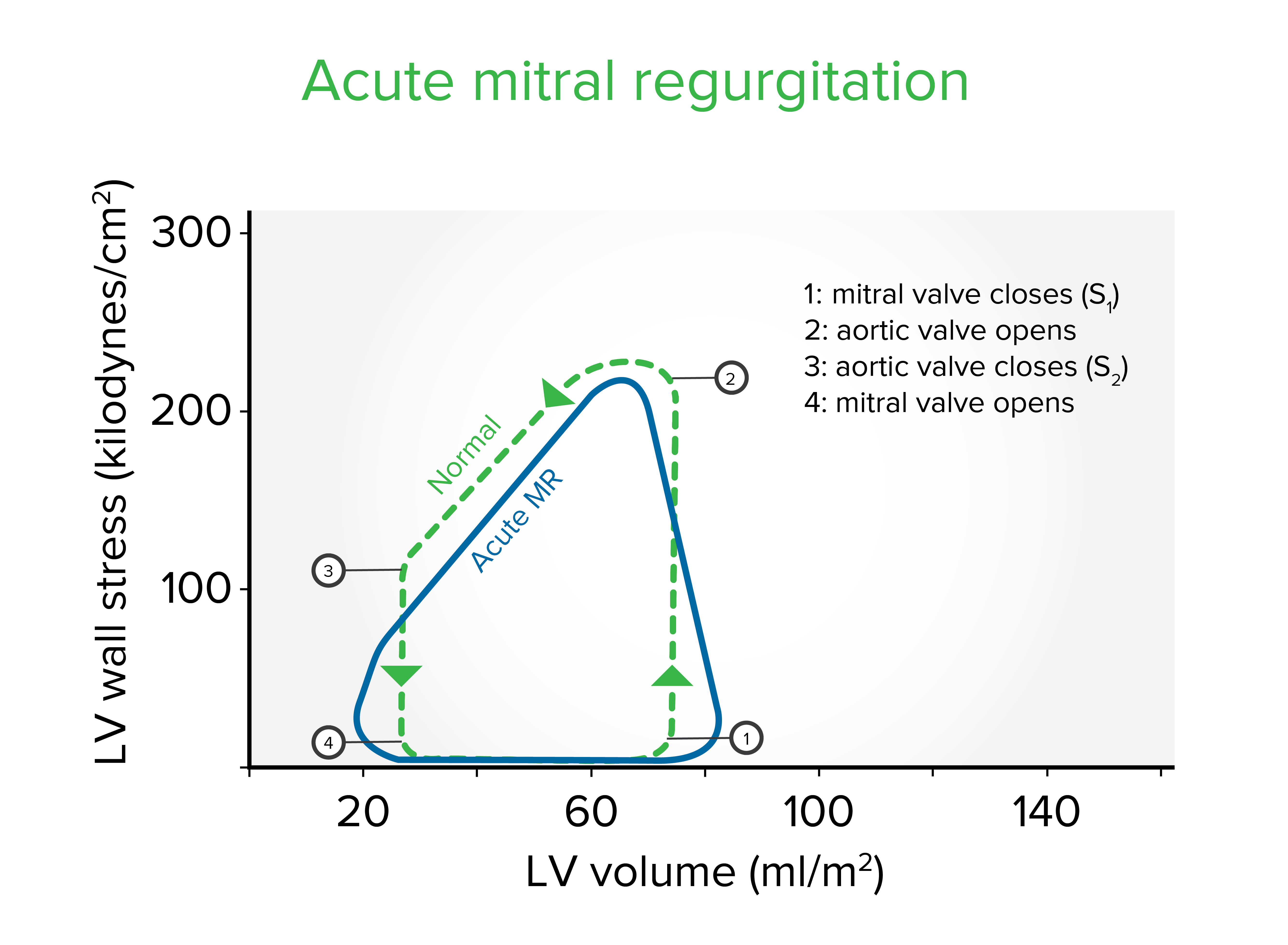
Left ventricle (LV) wall stress-volume loop in acute mitral regurgitation (MR): Early adaptation to acute MR comprises an increase in end-diastolic volume, a characteristic systolic unloading, and a decrease in end-systolic volume. As a result, the total stroke volume increases.
Image by Lecturio.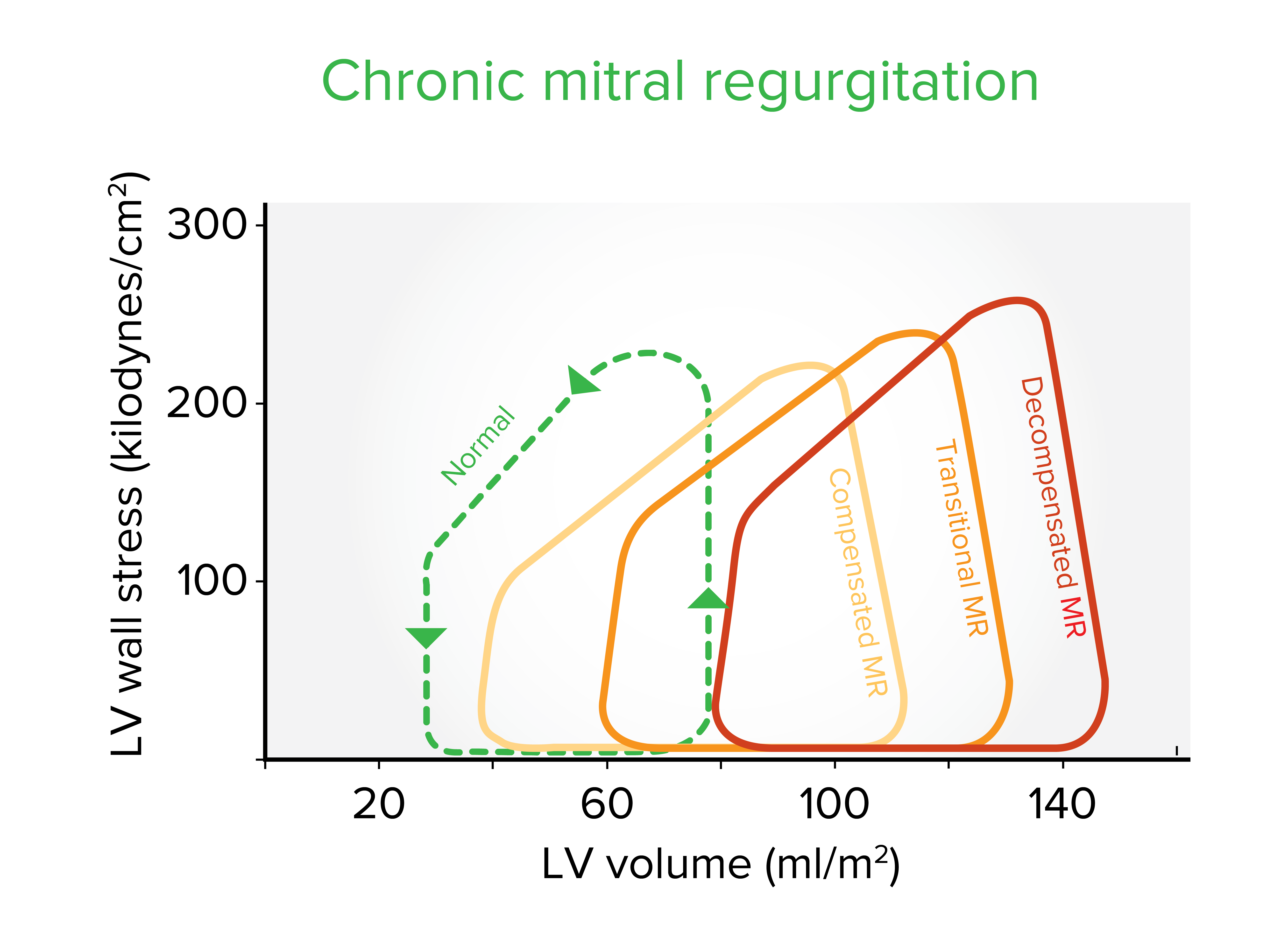
Left ventricle (LV) wall stress-volume loops in the 3 stages of chronic mitral regurgitation (MR): As the ventricle adapts to the chronic hemodynamic burden, a progressive increase in LV end-diastolic volume and systolic wall stress occurs. The ejection fraction progressively lowers from 65% in compensated MR, to 55% during the transitional stage, and finally to ≤ 45% in decompensated MR.
Image by Lecturio.Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship will often present with signs and symptoms of acute heart failure Heart Failure A heterogeneous condition in which the heart is unable to pump out sufficient blood to meet the metabolic need of the body. Heart failure can be caused by structural defects, functional abnormalities (ventricular dysfunction), or a sudden overload beyond its capacity. Chronic heart failure is more common than acute heart failure which results from sudden insult to cardiac function, such as myocardial infarction. Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return (TAPVR) or cardiogenic shock Cardiogenic shock Shock resulting from diminution of cardiac output in heart disease. Types of Shock:
Audio:
This audio clip is an example of an acute mitral regurgitation Regurgitation Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) murmur. An early systolic murmur is heard, which decrescendos and ends before S2 S2 Heart Sounds.
Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship will often be asymptomatic for years. Symptoms tend to develop with a decrease in cardiac output Cardiac output The volume of blood passing through the heart per unit of time. It is usually expressed as liters (volume) per minute so as not to be confused with stroke volume (volume per beat). Cardiac Mechanics or cardiac dysfunction:
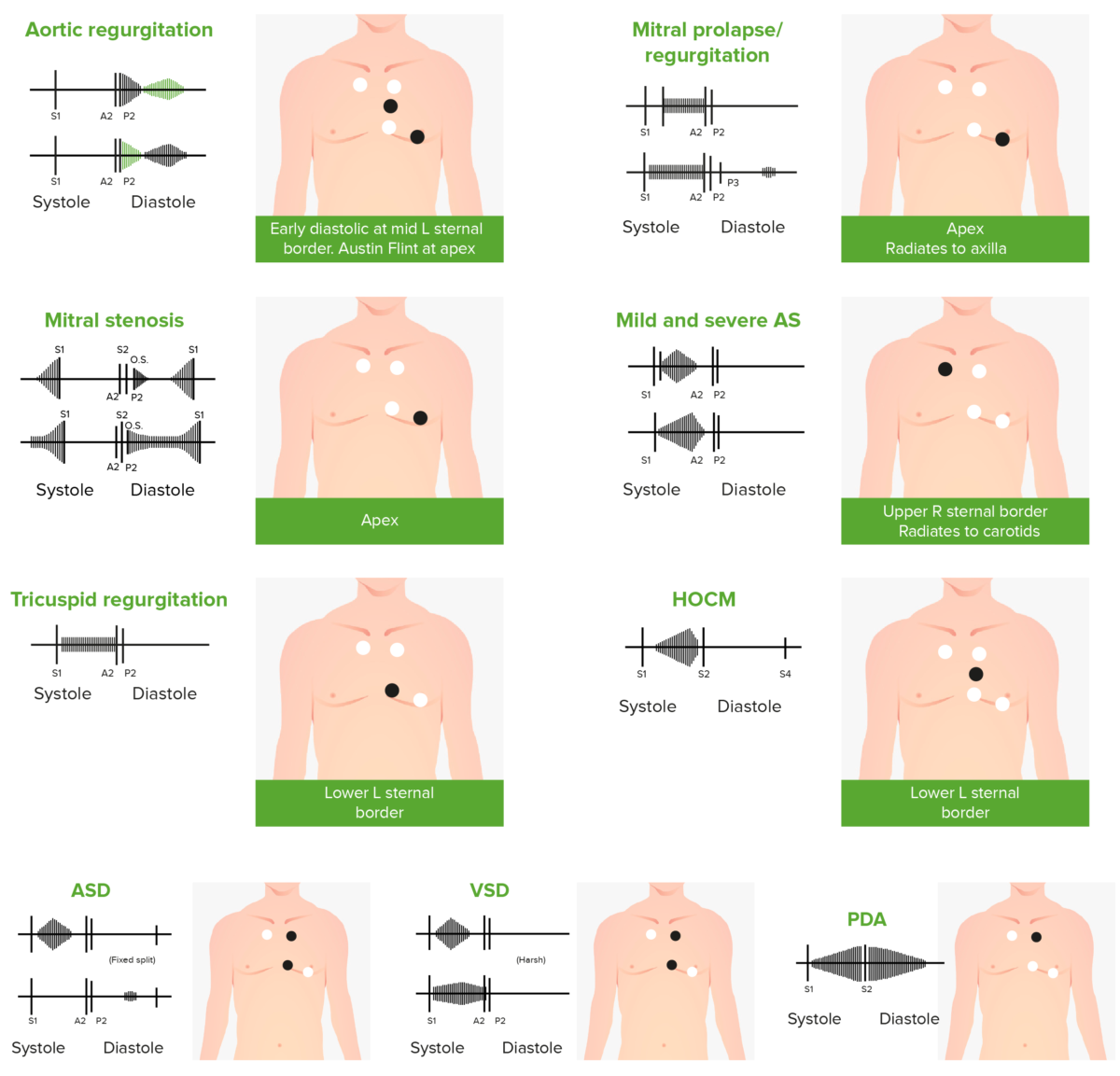
Phonocardiograms of abnormal heart sounds caused by the following cardiac defects:
aortic regurgitation, mitral valve prolapse, mitral stenosis (MS), aortic stenosis (AS), tricuspid regurgitation, hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (HOCM), atrial septal defect (ASD), ventricular septal defect (VSD), and patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
Audio:
This audio clip is an example of a holosystolic murmur Holosystolic Murmur Tricuspid Valve Atresia (TVA) from mitral regurgitation Regurgitation Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD). The murmur gives a high-pitched, “blowing” sound through the entirety of systole Systole Period of contraction of the heart, especially of the heart ventricles. Cardiac Cycle.
Audio:
This audio clip is an example of an S3 gallop S3 gallop Heart Failure in addition to a holosystolic mitral regurgitation Regurgitation Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) murmur. This extra heart sound after S2 S2 Heart Sounds can result due to increased flow Flow Blood flows through the heart, arteries, capillaries, and veins in a closed, continuous circuit. Flow is the movement of volume per unit of time. Flow is affected by the pressure gradient and the resistance fluid encounters between 2 points. Vascular resistance is the opposition to flow, which is caused primarily by blood friction against vessel walls. Vascular Resistance, Flow, and Mean Arterial Pressure or dilation of the left ventricle.
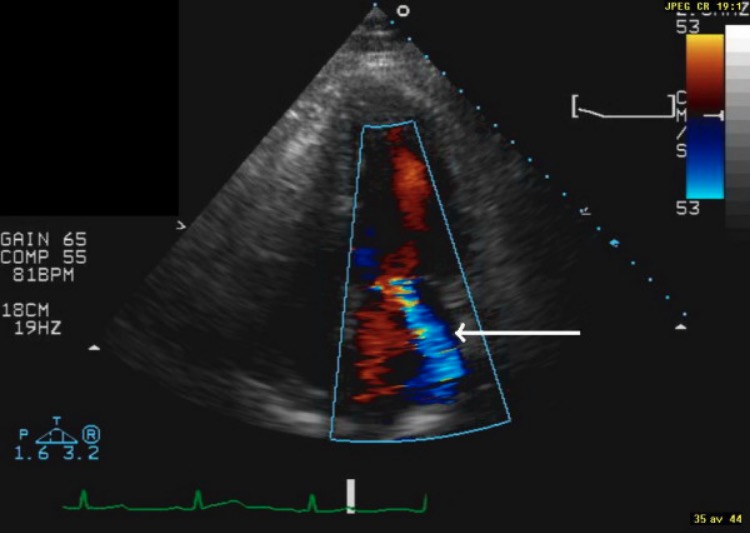
Display of end-systolic image from apical 4-chamber view: The white, thicker, arrow indicates moderate MR.
Image: “F2” by the Department of Clinical Sciences, Division of Diabetes & Endocrinology, Lund University, Malmö University Hospital, Malmö, Sweden. License: CC BY 2.0.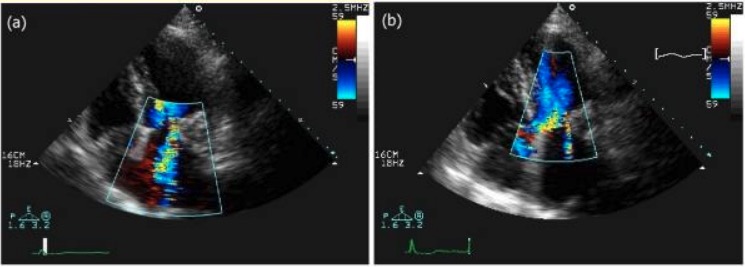
Two-dimensional (2D) echocardiogram with apical 4-chamber view and color Doppler. A: Pre-operative: Moderate-to-severe MR is present.
B: Postoperative: Trivial MR is seen in the LA.
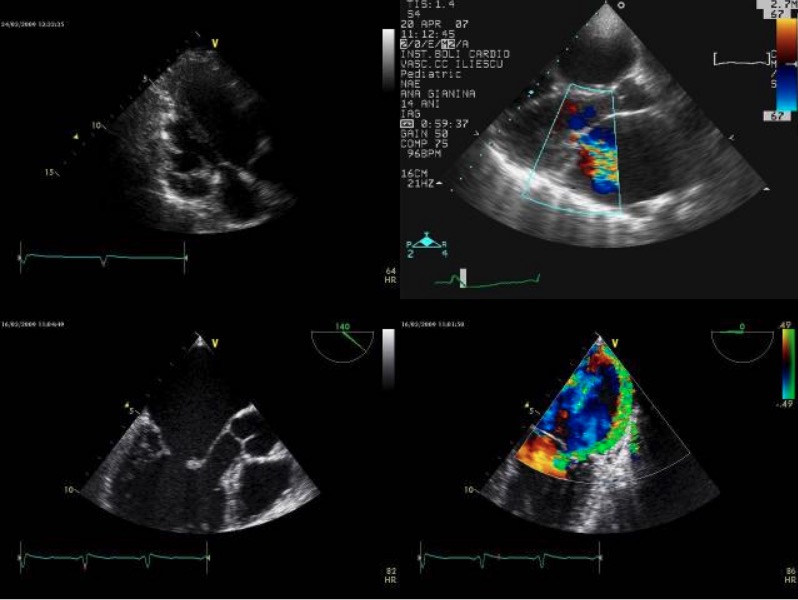
Transthoracic echocardiography. A: parasternal long-axis modified view; B: normal parasternal long-axis view with color Doppler flow from an adult patient with moderate MR and shortened chordae tendineae; C: 2D TEE and D: color flow Doppler from another adult patient with severe MR and shortened cordae tendineae
(Note the posterior mitral leaflet with limited mobility (arrow), and the eccentric regurgitant jet oriented to the posterior atrial wall.)
Image: “Transthoracic echocardiography” by Prof. C.C. Iliescu Emergency Institute of Cardiovascular Diseases, 258 Fundeni Street, District 2, Bucharest, Romania. License: CC BY 2.0.Acute MR MR Calculated as the ratio of the total number of people who die due to all causes over a specific time period to the total number of people in the selected population. Measures of Health Status is a medical emergency that requires medical stabilization and supportive care until surgery can be performed: