Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a functional bowel disease characterized by chronic abdominal pain Abdominal Pain Acute Abdomen and altered bowel habits without an identifiable organic cause. The etiology and pathophysiology of this disease are not well understood, and there are many factors that may contribute. Irritable bowel syndrome is a diagnosis of exclusion, and organic causes should be ruled out. Once diagnosed, the emphasis is on education and reassurance Reassurance Clinician–Patient Relationship. Dietary modifications and symptom-control measures may also be instituted, depending on the predominant symptoms.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Although no specific organic cause has been identified, there are several possible pathogenic mechanisms.
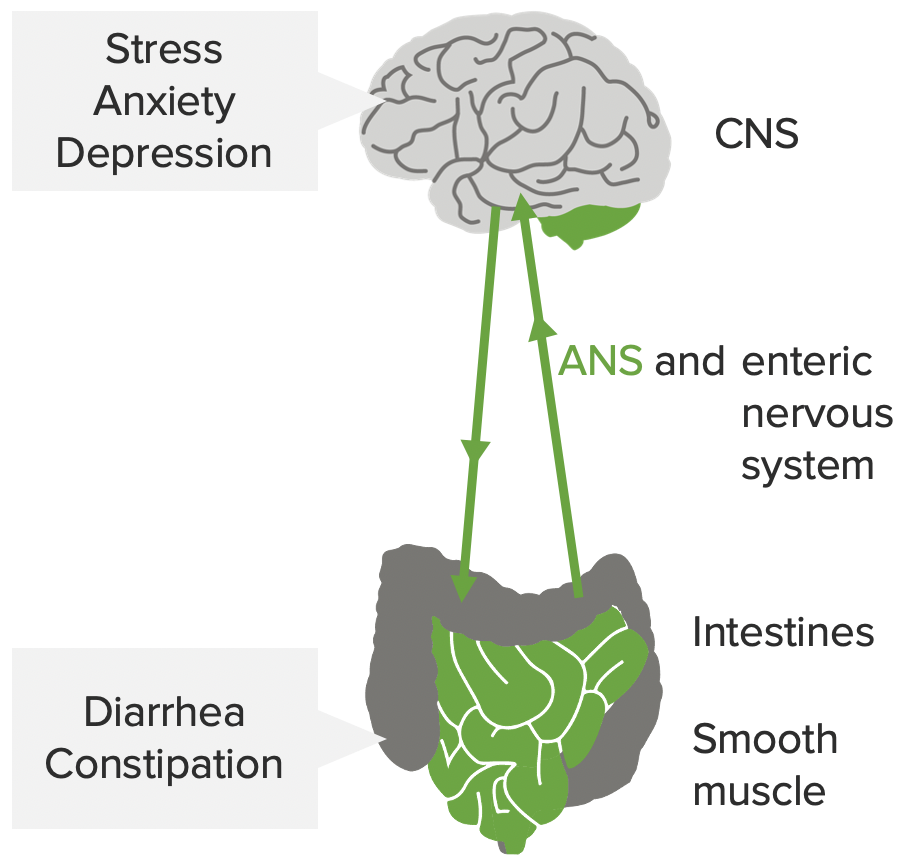
The mind-gut interaction contributing to the pathophysiology of IBS: stress, anxiety, and depression influence the CNS, autonomic nervous system (ANS), and enteric nervous system. This may affect the smooth muscles in the intestines, leading to the symptoms of IBS.
Image by Lecturio.Irritable bowel syndrome is classified based on the clinical presentation.
Irritable bowel syndrome is a diagnosis of exclusion, but the Rome IV criteria Rome Iv Criteria Elimination Disorders help provide a standardized diagnosis:
Work-up will be guided by the patient’s clinical presentation.
IBS-D:
IBS-C:
Abdominal pain Abdominal Pain Acute Abdomen and bloating Bloating Constipation: