Burkholderia species are gram-negative bacilli Bacilli Shigella with 2 clinically relevant pathogens: B. pseudomallei (causing melioidosis) and B. cepacia complex (causing opportunistic infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease). Melioidosis is commonly seen in Asia ASIA Spinal Cord Injuries and Australia. Infection is transmitted by contact with contaminated soil or water (via skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions wounds). The disease affects multiple systems, and can present with pneumonia Pneumonia Pneumonia or pulmonary inflammation is an acute or chronic inflammation of lung tissue. Causes include infection with bacteria, viruses, or fungi. In more rare cases, pneumonia can also be caused through toxic triggers through inhalation of toxic substances, immunological processes, or in the course of radiotherapy. Pneumonia, encephalomyelitis, and skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions abscesses. Diagnosis is by culture of specimen (depending on the organ involved). Treatment requires an initial intensive antibiotic therapy followed by prolonged eradication therapy. Burkholderia cepacia complex (BCC) generally affects immunocompromised immunocompromised A human or animal whose immunologic mechanism is deficient because of an immunodeficiency disorder or other disease or as the result of the administration of immunosuppressive drugs or radiation. Gastroenteritis individuals such as those with cystic Cystic Fibrocystic Change fibrosis Fibrosis Any pathological condition where fibrous connective tissue invades any organ, usually as a consequence of inflammation or other injury. Bronchiolitis Obliterans (CF). It can be transmitted from person to person or through contaminated devices. While BCC is a rare infection, it is important to diagnose, as BCC is multi-drug resistant and infection is a relative contraindication to lung transplantation Lung transplantation The transference of either one or both of the lungs from one human or animal to another. Organ Transplantation.
Last updated: Dec 28, 2024
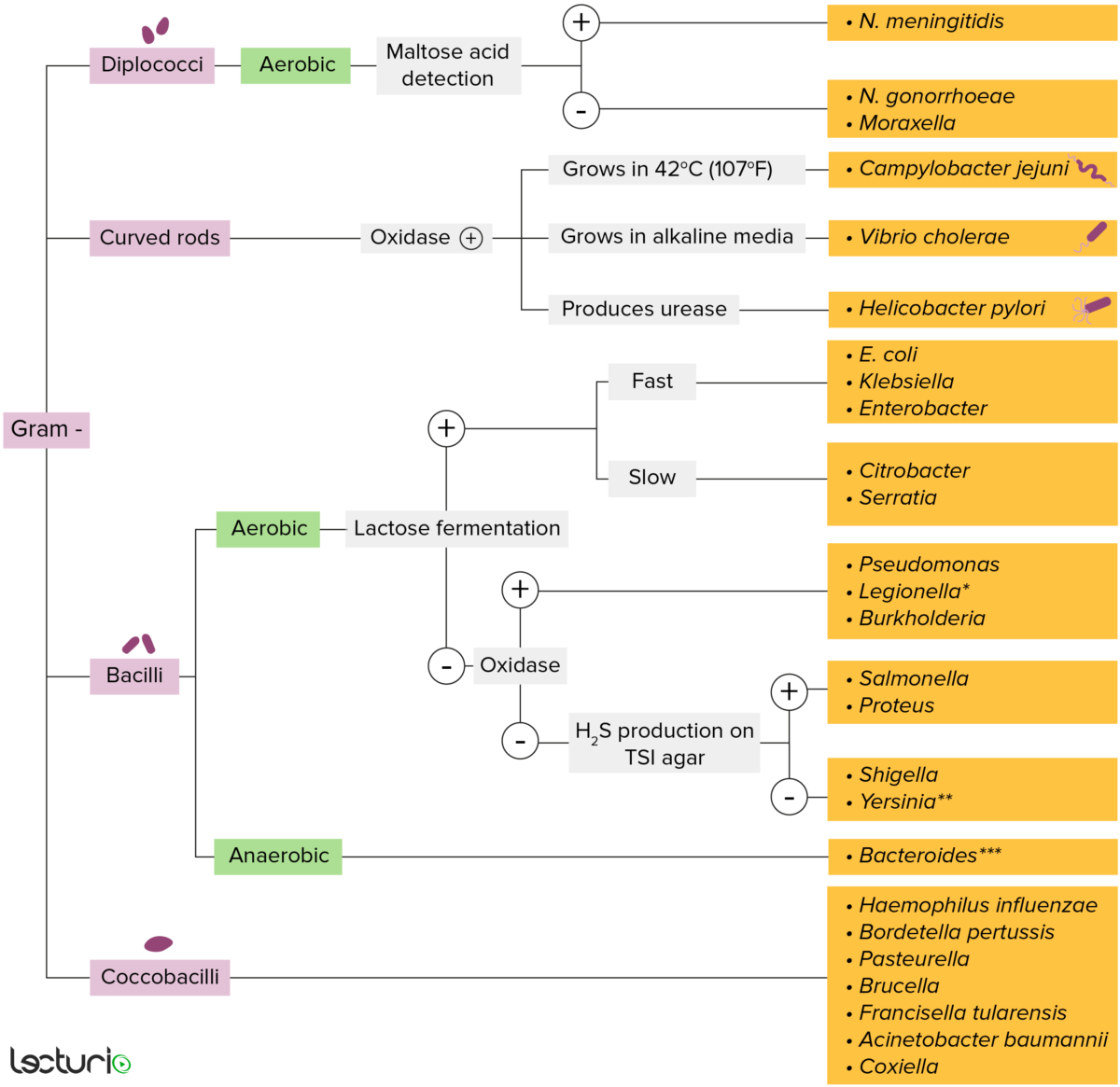
Gram-negative bacteria:
Most bacteria can be classified according to a lab procedure called Gram staining.
Bacteria with cell walls that have a thin layer of peptidoglycan do not retain the crystal violet stain utilized in Gram staining. These bacteria do, however, retain the safranin counterstain and thus appear as pinkish-red on the stain, making them gram negative. These bacteria can be further classified according to morphology (diplococci, curved rods, bacilli, and coccobacilli) and their ability to grow in the presence of oxygen (aerobic versus anaerobic). The bacteria can be more narrowly identified by growing them on specific media (triple sugar iron (TSI) agar) where their enzymes can be identified (urease, oxidase) and their ability to ferment lactose can be tested.
* Stains poorly on Gram stain
** Pleomorphic rod/coccobacillus
*** Require special transport media
Burkholderia:
Clinically significant species:
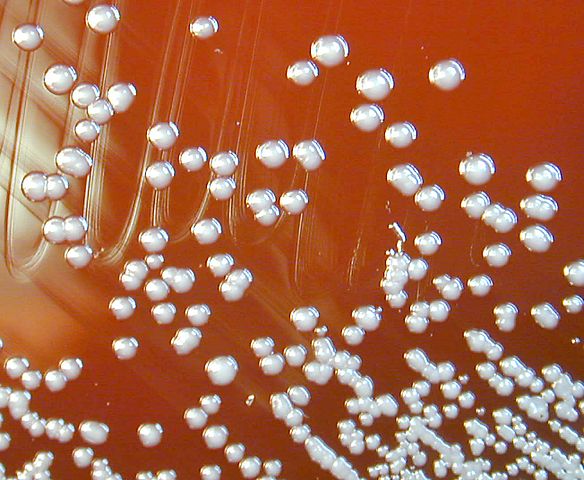

Burkholderia pseudomallei colonies on a blood agar plate
Image: “Burkholderia pseudomallei 01” by CDC. License: Public DomainTransmission:
Host risk factors include:
Symptoms can present in various systems:
Diagnostic tests Diagnostic tests Diagnostic tests are important aspects in making a diagnosis. Some of the most important epidemiological values of diagnostic tests include sensitivity and specificity, false positives and false negatives, positive and negative predictive values, likelihood ratios, and pre-test and post-test probabilities. Epidemiological Values of Diagnostic Tests:
Additional tests:
Resistant to:
Initial regimen(s) depends on severity of illness and system(s) affected:
Eradication treatment:
Prevention:
BCC:
Epidemiology:
Transmission:
Medical devices that can be contaminated and produce infection:
Host risk factors:
Most infected people have no symptoms. Those with symptoms can have:
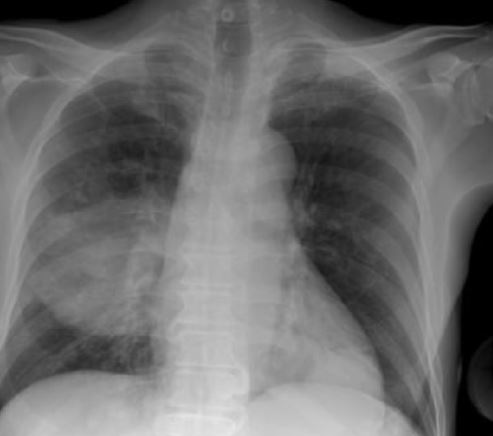
B. cepacia complex infection:
Chest X-ray of a patient showing right-sided pneumonia. Tracheal aspirate and blood cultures grew B. cepacia.