Ventricular fibrillation (VF or V-fib) is a type of ventricular tachyarrhythmia (> 300/min) often preceded by ventricular tachycardia. In patients with VF, the ventricular contraction is uncoordinated, leading to severely decreased cardiac output and immediate hemodynamic collapse. This medical emergency is most commonly caused by underlying ischemic heart disease.VF leads to death within minutes unless advanced cardiac life support (ACLS) measures are started immediately.
Last updated: May 16, 2024
Ventricular fibrillation (VF) secondary to myocardial infarction Myocardial infarction MI is ischemia and death of an area of myocardial tissue due to insufficient blood flow and oxygenation, usually from thrombus formation on a ruptured atherosclerotic plaque in the epicardial arteries. Clinical presentation is most commonly with chest pain, but women and patients with diabetes may have atypical symptoms. Myocardial Infarction ( MI MI MI is ischemia and death of an area of myocardial tissue due to insufficient blood flow and oxygenation, usually from thrombus formation on a ruptured atherosclerotic plaque in the epicardial arteries. Clinical presentation is most commonly with chest pain, but women and patients with diabetes may have atypical symptoms. Myocardial Infarction) is the most common cause of sudden cardiac death Sudden cardiac death Cardiac arrest is the sudden, complete cessation of cardiac output with hemodynamic collapse. Patients present as pulseless, unresponsive, and apneic. Rhythms associated with cardiac arrest are ventricular fibrillation/tachycardia, asystole, or pulseless electrical activity. Cardiac Arrest (leading cause of death in developed countries).
Ventricular tachyarrhythmias are caused by abnormal ectopic contractions in the ventricle.
Detailed process
Mnemonic
Sustained VF after an MI MI MI is ischemia and death of an area of myocardial tissue due to insufficient blood flow and oxygenation, usually from thrombus formation on a ruptured atherosclerotic plaque in the epicardial arteries. Clinical presentation is most commonly with chest pain, but women and patients with diabetes may have atypical symptoms. Myocardial Infarction results from: Myocardial ischemia Ischemia A hypoperfusion of the blood through an organ or tissue caused by a pathologic constriction or obstruction of its blood vessels, or an absence of blood circulation. Ischemic Cell Damage → Necrosis → Reperfusion → Healing → Scar formation → Autonomic changes (mnemonic device: My Nephew Really Hates Scary Aliens!)
Electrocardiogram Electrocardiogram An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphic representation of the electrical activity of the heart plotted against time. Adhesive electrodes are affixed to the skin surface allowing measurement of cardiac impulses from many angles. The ECG provides 3-dimensional information about the conduction system of the heart, the myocardium, and other cardiac structures. Electrocardiogram (ECG) ( ECG ECG An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphic representation of the electrical activity of the heart plotted against time. Adhesive electrodes are affixed to the skin surface allowing measurement of cardiac impulses from many angles. The ECG provides 3-dimensional information about the conduction system of the heart, the myocardium, and other cardiac structures. Electrocardiogram (ECG)) confirms the diagnosis.
Evaluation of underlying conditions:
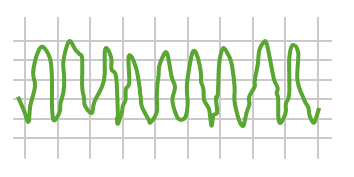
Example of an ECG tracing showing erratic fibrillatory waves in ventricular fibrillation
Image by Lecturio.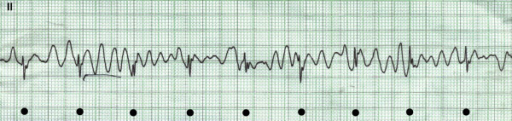
ECG tracing showing ventricular fibrillation, in which black dots mark the QRS complexes “marching through” the artifact in the background
Image: “Ventricular fibrillation” by Department of Medicine, Section of Cardiology, Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi, Pakistan. License: CC BY 2.0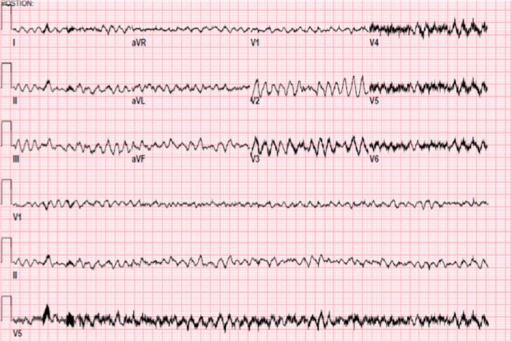
ECG tracing showing ventricular fibrillation
Image: “Electrocardiogram demonstrating ventricular fibrillation” by Oregon Health & Science University, Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine. License: CC BY 3.0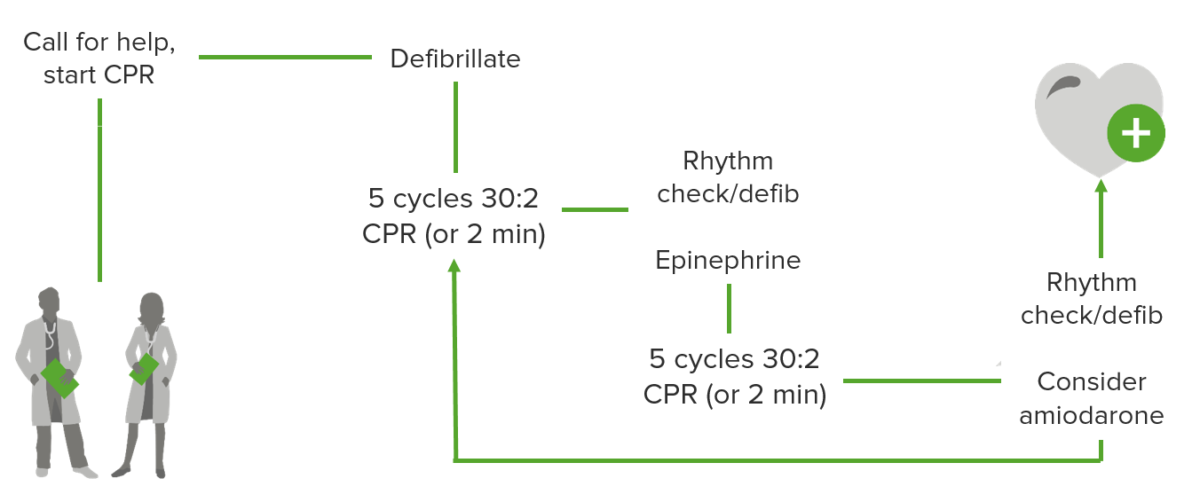
Ventricular fibrillation/tachycardia management algorithm
Image by Lecturio.