Primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD), also known as immotile-cilia syndrome, is an autosomal recessive Autosomal recessive Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal recessive diseases are only expressed when 2 copies of the recessive allele are inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance disorder leading to an impairment that affects mucociliary clearance Mucociliary clearance A nonspecific host defense mechanism that removes mucus and other material from the lungs by ciliary and secretory activity of the tracheobronchial submucosal glands. It is measured in vivo as mucus transfer, ciliary beat frequency, and clearance of radioactive tracers. Acute Bronchitis. Primary ciliary dyskinesia is caused by defective ciliary function in the airways and is characterized by the loss of oscillation (immotility), abnormal oscillation (dyskinesia), or absence of cilia ( aplasia Aplasia Cranial Nerve Palsies). In most cases, PCD commonly presents with recurrent infections Recurrent infections Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID) of the upper and lower respiratory tract. Clinical features include bronchiectasis Bronchiectasis Bronchiectasis is a chronic disease of the airways that results from permanent bronchial distortion. This results from a continuous cycle of inflammation, bronchial damage and dilation, impaired clearance of secretions, and recurrent infections. Bronchiectasis, chronic rhinosinusitis, and situs inversus. There is no gold standard diagnostic test for PCD, as several tests are used in the diagnosis. Treatment is individualized, and the primary goal is to remove trapped mucus and treat infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with PCD usually have a regular Regular Insulin lifespan.
Last updated: Dec 28, 2024
Primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD) is a genetic condition in which cilia in the respiratory tract have defective functionality that leads to ineffective mucociliary clearance Mucociliary clearance A nonspecific host defense mechanism that removes mucus and other material from the lungs by ciliary and secretory activity of the tracheobronchial submucosal glands. It is measured in vivo as mucus transfer, ciliary beat frequency, and clearance of radioactive tracers. Acute Bronchitis.
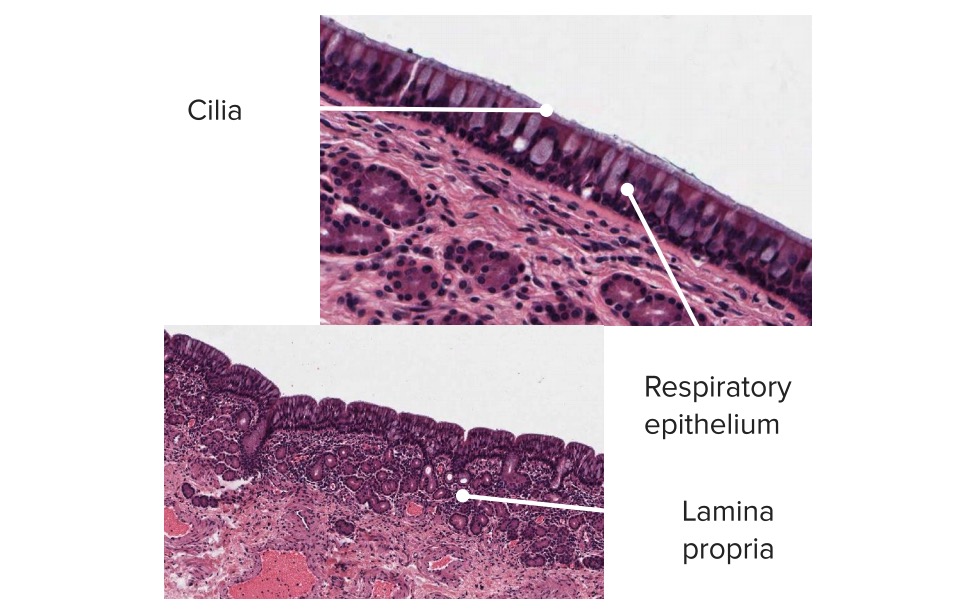
A histological slide of the respiratory mucosa composed of ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium, which covers the lamina propria of the nasal conchae:
The mucus produced by this epithelium serves as a filter by trapping airborne particles larger than 2–3 micrometers.
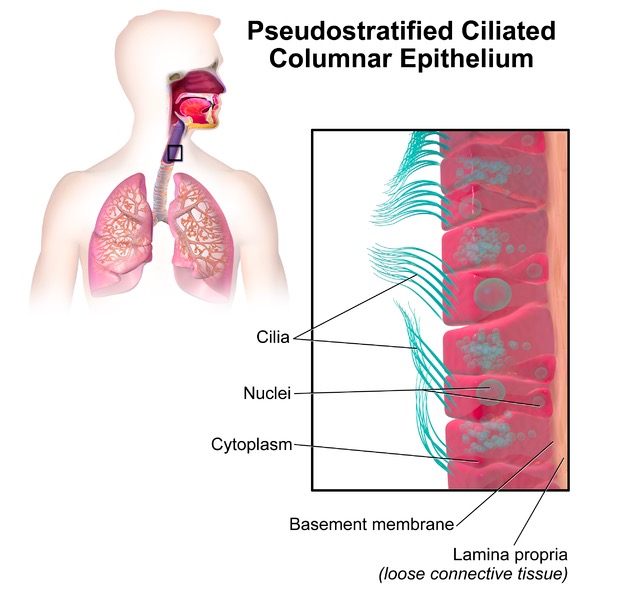
Illustration of a ciliated epithelium found in the respiratory tract
Image: “Pseudostratified ciliated columnar” by BruceBlaus. License: Public Domain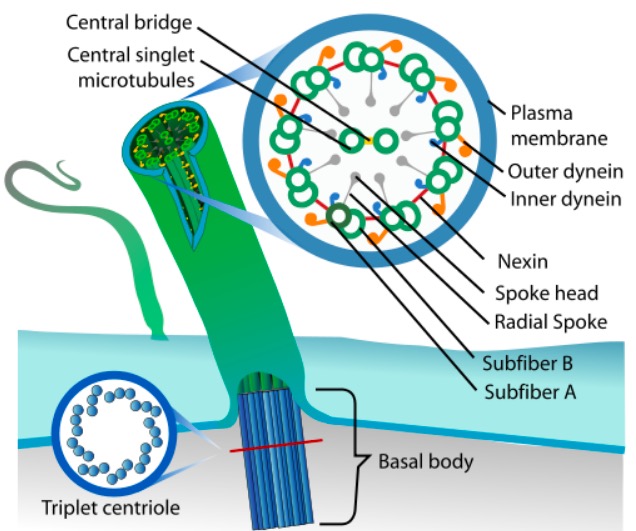
Inner structure of a cilium (singular of cilia)
Image: “Eukaryotic cilium diagram” by LadyofHats. License: Public DomainThere is no gold standard diagnostic test for PCD, but the following evaluations aid in the diagnosis:
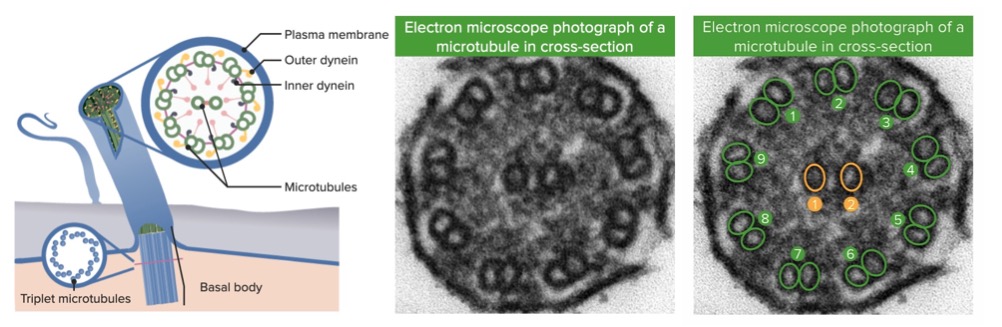
Electron microscope photograph of the ciliary structure in a bronchiole:
Left: diagram of the ciliary internal structures
Middle: cross-section image obtained using electron microscopy
Right: The microtubules are labeled.
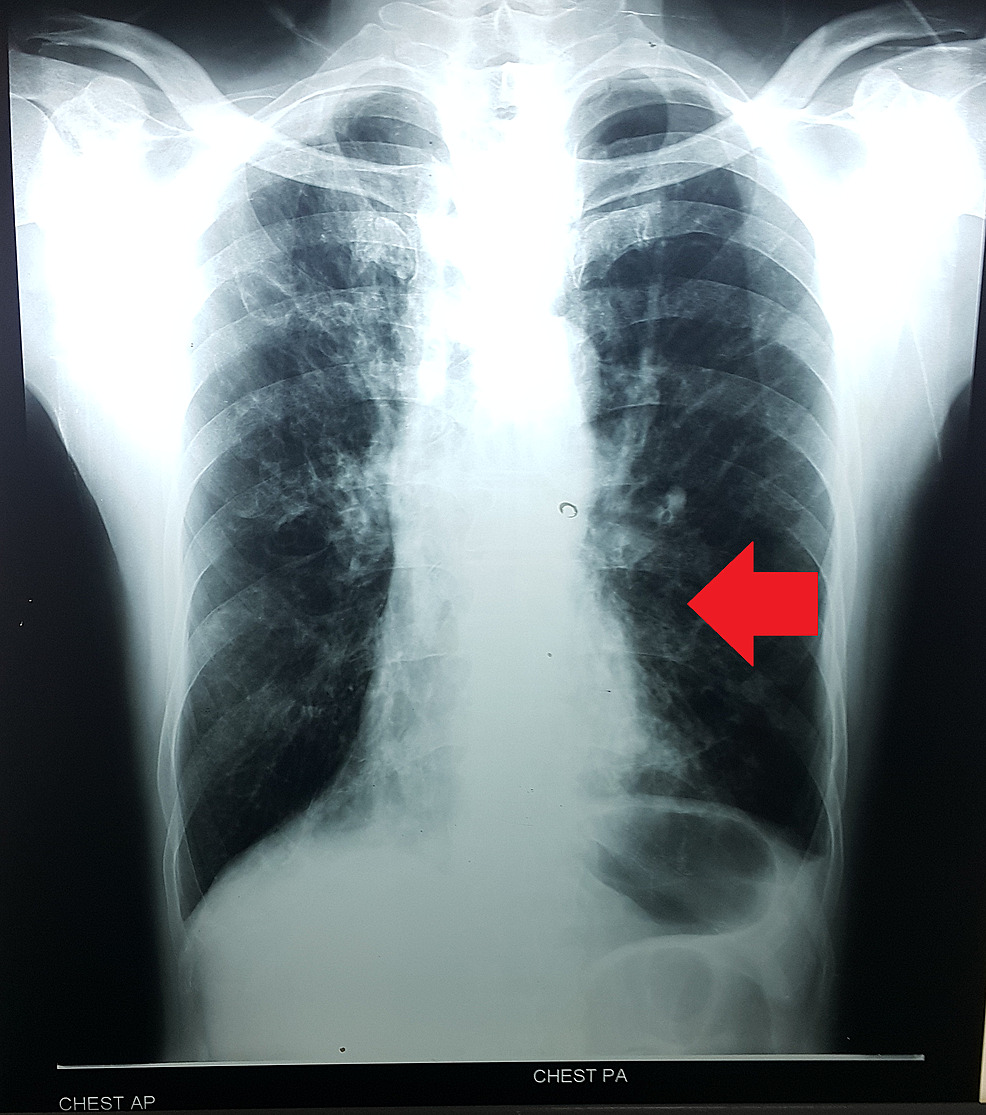
Chest X-ray diagnosing Kartagener syndrome:
Mild cardiomegaly with pulmonary congestion and dextrocardia (arrow) noted in a patient with a form of primary ciliary dyskinesia. Kartagener syndrome (primary ciliary dyskinesia: situs inversus, chronic sinusitis, and bronchiectasis)
Treatment is individualized and guided by the clinical presentation of the patient.