The hepatitis A virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology (HAV) is a nonenveloped virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology of the Picornaviridae Picornaviridae A family of small RNA viruses comprising some important pathogens of humans and animals. Transmission usually occurs mechanically. There are nine genera: aphthovirus; cardiovirus; enterovirus; erbovirus; hepatovirus; kobuvirus; parechovirus; rhinovirus; and teschovirus. Coxsackievirus family with single-stranded RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure. The virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology replicates in the liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy, is excreted in the bile Bile An emulsifying agent produced in the liver and secreted into the duodenum. Its composition includes bile acids and salts; cholesterol; and electrolytes. It aids digestion of fats in the duodenum. Gallbladder and Biliary Tract: Anatomy, and is found in high concentrations in the stool of acutely infected individuals. The 2 main routes of infection are consumption of contaminated food or water and direct contact with an infected person. HAV causes an acute, highly contagious hepatitis with unspecific prodromal symptoms such as fever Fever Fever is defined as a measured body temperature of at least 38°C (100.4°F). Fever is caused by circulating endogenous and/or exogenous pyrogens that increase levels of prostaglandin E2 in the hypothalamus. Fever is commonly associated with chills, rigors, sweating, and flushing of the skin. Fever and malaise Malaise Tick-borne Encephalitis Virus followed by jaundice Jaundice Jaundice is the abnormal yellowing of the skin and/or sclera caused by the accumulation of bilirubin. Hyperbilirubinemia is caused by either an increase in bilirubin production or a decrease in the hepatic uptake, conjugation, or excretion of bilirubin. Jaundice and elevated liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy transaminases Transaminases A subclass of enzymes of the transferase class that catalyze the transfer of an amino group from a donor (generally an amino acid) to an acceptor (generally a 2-keto acid). Most of these enzymes are pyridoxyl phosphate proteins. Autoimmune Hepatitis. Most individuals recover fully within a few months, and the immunity resulting from HAV infection is lifelong. Unlike hepatitis B Hepatitis B Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, which belongs to the Orthohepadnavirus genus and the Hepadnaviridae family. Most individuals with acute HBV infection are asymptomatic or have mild, self-limiting symptoms. Chronic infection can be asymptomatic or create hepatic inflammation, leading to liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis B Virus and C, HAV infection does not result in chronic infection or chronic liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy disease. Preventive vaccination Vaccination Vaccination is the administration of a substance to induce the immune system to develop protection against a disease. Unlike passive immunization, which involves the administration of pre-performed antibodies, active immunization constitutes the administration of a vaccine to stimulate the body to produce its own antibodies. Vaccination is available for HAV and is recommended for individuals with increased risk of exposure and, in some countries such as the United States, for all children > 12 months of age.
Last updated: May 16, 2024

RNA virus identification:
Viruses can be classified in many ways. Most viruses, however, will have a genome formed by either DNA or RNA. RNA genome viruses can be further characterized by either a single- or double-stranded RNA. “Enveloped” viruses are covered by a thin coat of cell membrane (usually taken from the host cell). If the coat is absent, the viruses are called “naked” viruses. Viruses with single-stranded genomes are “positive-sense” viruses if the genome is directly employed as messenger RNA (mRNA), which is translated into proteins. “Negative-sense,” single-stranded viruses employ RNA dependent RNA polymerase, a viral enzyme, to transcribe their genome into messenger RNA.
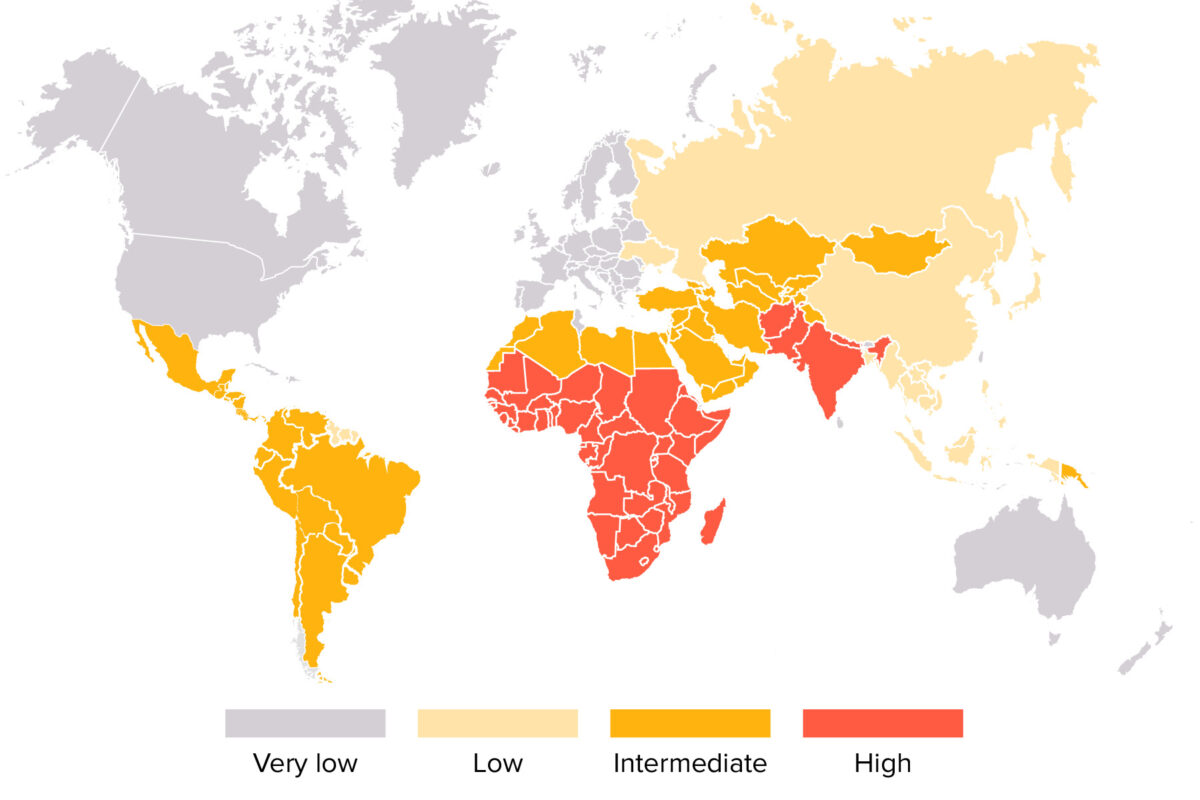
World map showing distribution of the hepatitis A virus
Image by Lecturio. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0The presence of 1 of the following symptoms is a reason to suspect hepatitis A infection, especially in the presence of risk factors:
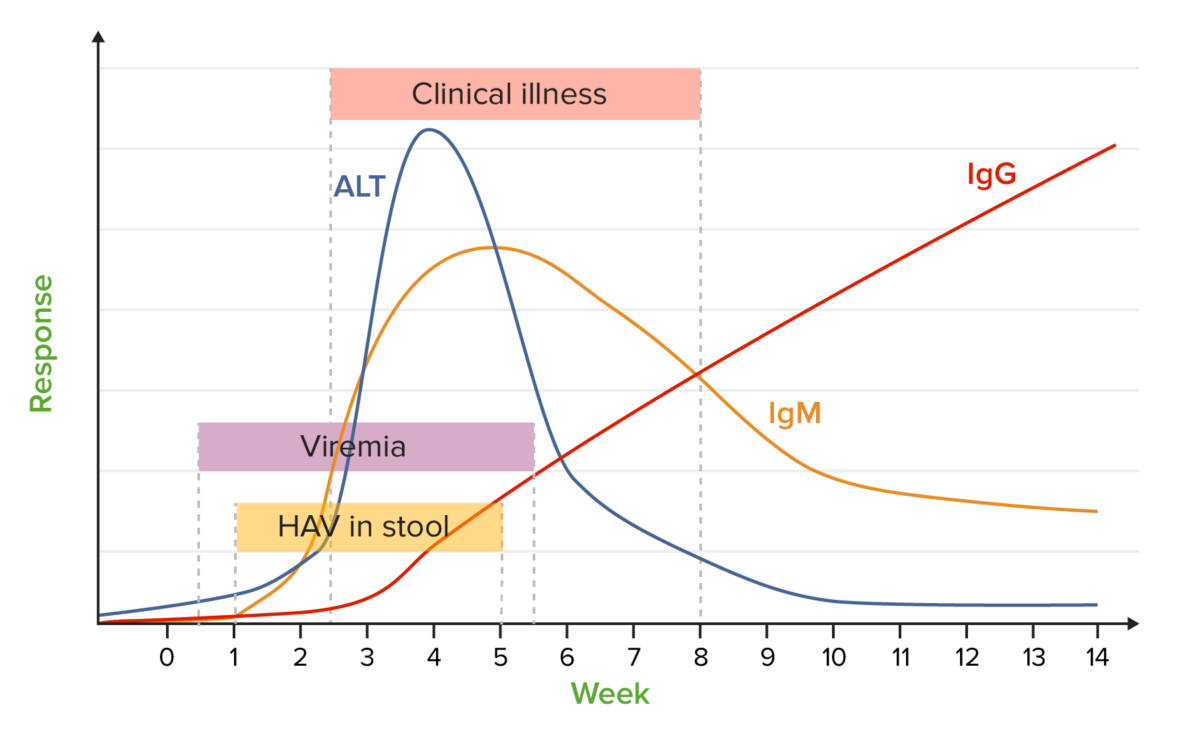
Hepatitis A markers:
chart showing a typical course of the most important laboratory parameters with respect to the time after infection
ALT: alanine transaminase
HAV: hepatitis A virus
Ig: immunoglobulin
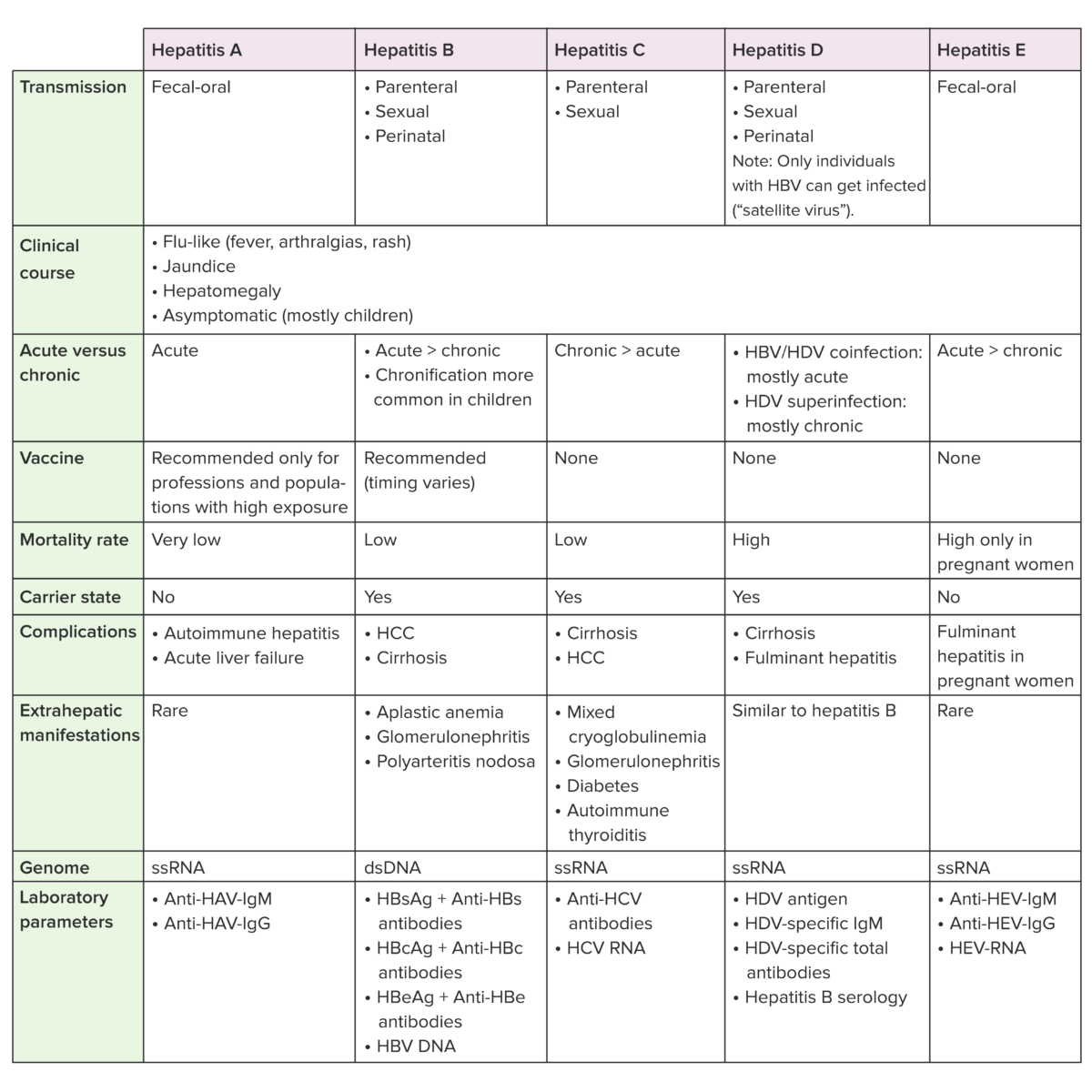
Anti-HBc: hepatitis B core antibody
Anti-HBs: hepatitis B surface antibody
HBcAg: hepatitis B core antigen
HBsAg: hepatitis B surface antigen
HBV: hepatitis B virus
HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma
HAV: hepatitis A virus
HCV: hepatitis C virus
HDV: hepatitis D virus