Aortic stenosis Stenosis Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS) (AS), or the narrowing of the aortic valve Aortic valve The valve between the left ventricle and the ascending aorta which prevents backflow into the left ventricle. Heart: Anatomy aperture, is the most common valvular heart disease in high-income countries. While rheumatic heart disease Rheumatic Heart Disease Cardiac manifestation of systemic rheumatological conditions, such as rheumatic fever. Rheumatic heart disease can involve any part the heart, most often the heart valves and the endocardium. Rheumatic Fever remains the most frequent etiology worldwide, degenerative AS and congenital bicuspid aortic valve Aortic valve The valve between the left ventricle and the ascending aorta which prevents backflow into the left ventricle. Heart: Anatomy are the 2 usual causes in developed countries. Aortic stenosis Stenosis Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS) gradually progresses to heart failure Heart Failure A heterogeneous condition in which the heart is unable to pump out sufficient blood to meet the metabolic need of the body. Heart failure can be caused by structural defects, functional abnormalities (ventricular dysfunction), or a sudden overload beyond its capacity. Chronic heart failure is more common than acute heart failure which results from sudden insult to cardiac function, such as myocardial infarction. Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return (TAPVR), producing exertional dyspnea Dyspnea Dyspnea is the subjective sensation of breathing discomfort. Dyspnea is a normal manifestation of heavy physical or psychological exertion, but also may be caused by underlying conditions (both pulmonary and extrapulmonary). Dyspnea, angina, and/or syncope Syncope Syncope is a short-term loss of consciousness and loss of postural stability followed by spontaneous return of consciousness to the previous neurologic baseline without the need for resuscitation. The condition is caused by transient interruption of cerebral blood flow that may be benign or related to a underlying life-threatening condition. Syncope. A crescendo-decrescendo systolic murmur is audible in the right upper sternal border. Doppler Doppler Ultrasonography applying the doppler effect, with frequency-shifted ultrasound reflections produced by moving targets (usually red blood cells) in the bloodstream along the ultrasound axis in direct proportion to the velocity of movement of the targets, to determine both direction and velocity of blood flow. Ultrasound (Sonography) echocardiography Echocardiography Ultrasonic recording of the size, motion, and composition of the heart and surrounding tissues. The standard approach is transthoracic. Tricuspid Valve Atresia (TVA) is the imaging of choice, showing structural and flow Flow Blood flows through the heart, arteries, capillaries, and veins in a closed, continuous circuit. Flow is the movement of volume per unit of time. Flow is affected by the pressure gradient and the resistance fluid encounters between 2 points. Vascular resistance is the opposition to flow, which is caused primarily by blood friction against vessel walls. Vascular Resistance, Flow, and Mean Arterial Pressure changes in the valvular area. Valve replacement is the only effective treatment for symptomatic severe AS. Indications for the procedure depend on the patient's symptoms, degree of AS severity, exercise tolerance Tolerance Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics, concurrent cardiac abnormalities, surgical risk, and life expectancy Life expectancy Based on known statistical data, the number of years which any person of a given age may reasonably expected to live. Population Pyramids.
Last updated: May 16, 2024
Aortic stenosis Stenosis Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS) (AS) is the narrowing of the aortic valve Aortic valve The valve between the left ventricle and the ascending aorta which prevents backflow into the left ventricle. Heart: Anatomy aperture.

Short-axis view of the aortic valve of the heart (echocardiogram and image of anatomy).
Image: “Aortic valve sa” by Patrick J. Lynch and C. Carl Jaffe. License: CC BY 2.5.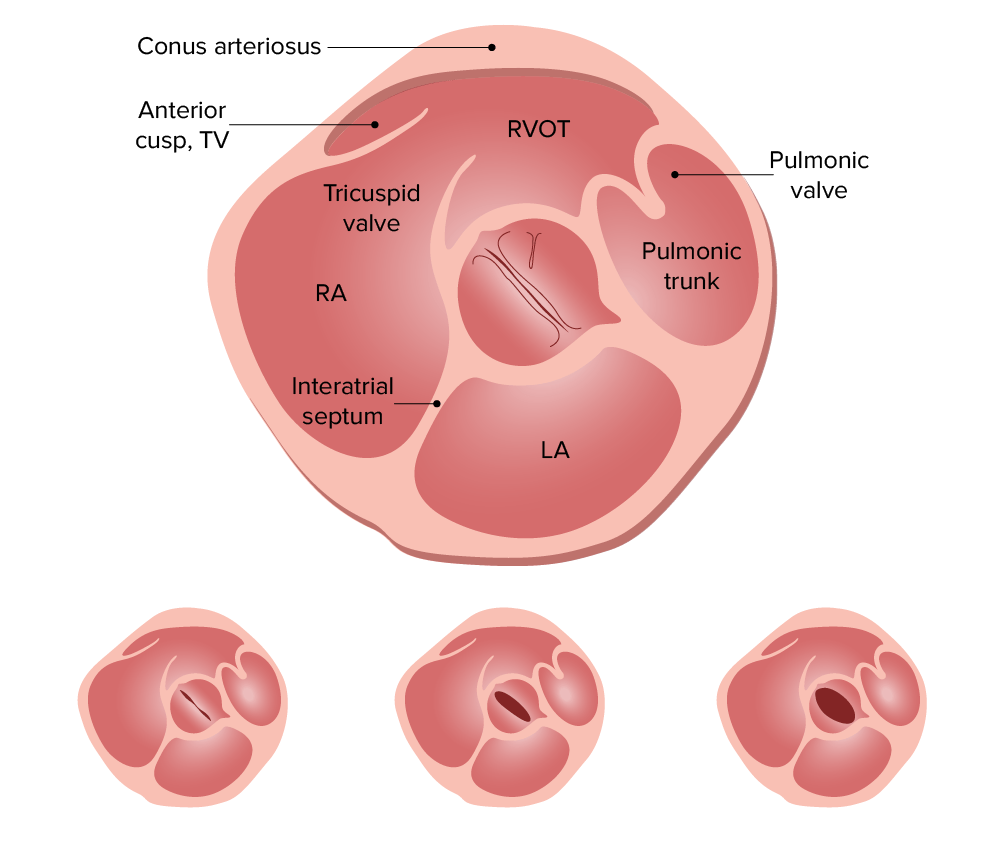
Bicuspid valve:
Short axis views of bicuspid aortic valves show a clam-shell like systolic opening pattern. A normal valve appears pie shaped with peeling back.
TV: tricuspid valve
RVOT: right ventricular outflow tract
RA: right atrium
LA: left atrium
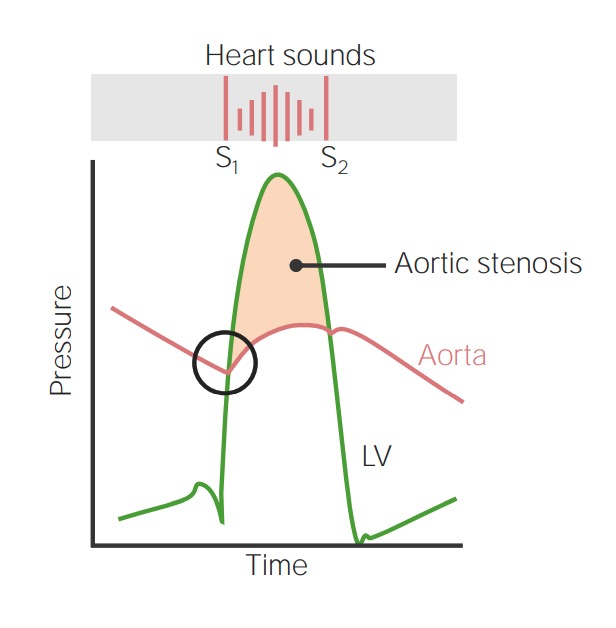
Image demonstrates the relationship between left ventricular pressure (green line) and aortic pressure (red line) throughout the cardiac cycle. The circle corresponds with the point at which the aortic valve would normally open, beginning the ventricular ejection phase. In aortic stenosis, left ventricular pressure exceeds the aortic pressure to overcome the stenotic valve. This leads to a systolic ejection murmur.
Image by Lecturio.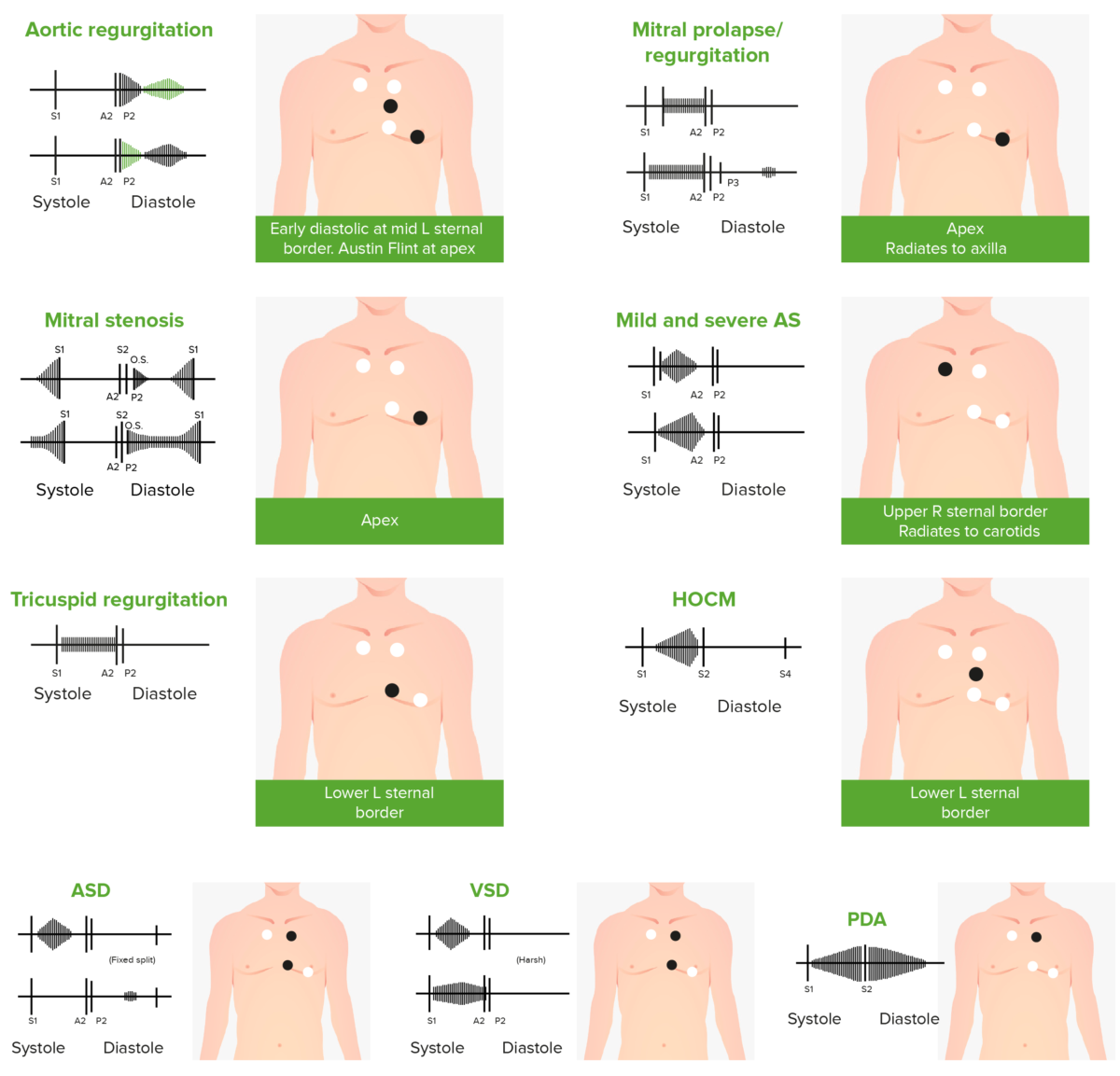
Phonocardiograms of abnormal heart sounds caused by the following cardiac defects:
aortic regurgitation, mitral valve prolapse, mitral stenosis (MS), aortic stenosis (AS), tricuspid regurgitation, hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (HOCM), atrial septal defect (ASD), ventricular septal defect (VSD), and patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
Audio:
This audio clip is an example of severe aortic stenosis Stenosis Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS). This is a harsh, crescendo-decrescendo murmur occurring between S1 S1 Heart Sounds and S2 S2 Heart Sounds. Due to the severity of the aortic stenosis Stenosis Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS), the S2 S2 Heart Sounds heart sound is inaudible.
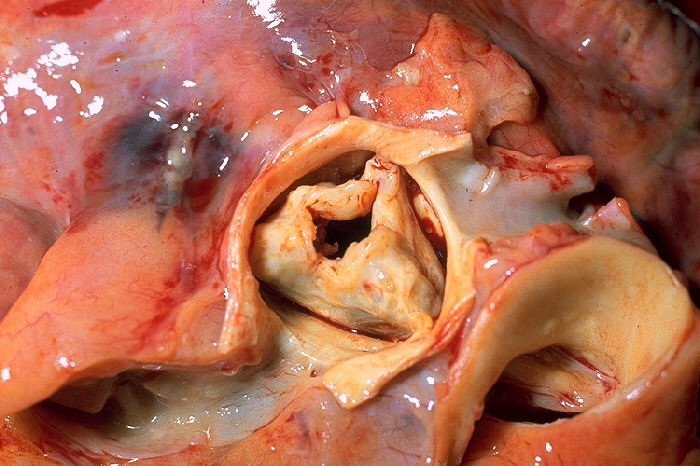
Gross pathology of rheumatic heart disease: AS.
Image: “Aortic stenosis rheumatic” by CDC/Dr. Edwin P. Ewing, Jr. License: Public domain.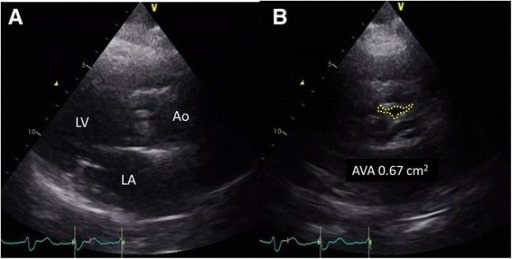
Pre-procedure transthoracic echocardiogram. A: parasternal long-axis view of severe AS. B: parasternal short-axis view of 0.67-cm² aortic valve, consistent with severe stenosis.
Image: “Pre-procedure transthoracic echocardiogram” by Department of Cardiology, Hokkaido Cardiovascular Hospital, 1-30, West 13, South 27, Chuou-ku, Sapporo, 064-8622, Japan. License: CC BY 4.0.