Valvular disorders can arise from the pulmonary valve Pulmonary valve A valve situated at the entrance to the pulmonary trunk from the right ventricle. Heart: Anatomy, located between the right ventricle (RV) and the pulmonary artery Pulmonary artery The short wide vessel arising from the conus arteriosus of the right ventricle and conveying unaerated blood to the lungs. Lungs: Anatomy (PA). Valvular disorders are diagnosed by echocardiography Echocardiography Ultrasonic recording of the size, motion, and composition of the heart and surrounding tissues. The standard approach is transthoracic. Tricuspid Valve Atresia (TVA). Pulmonary stenosis Stenosis Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS) ( PS PS Invasive Mechanical Ventilation) is valvular narrowing causing RV outflow tract obstruction. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship are often asymptomatic unless they have other congenital cardiac anomalies or severe PS PS Invasive Mechanical Ventilation. Symptoms (exertional dyspnea Dyspnea Dyspnea is the subjective sensation of breathing discomfort. Dyspnea is a normal manifestation of heavy physical or psychological exertion, but also may be caused by underlying conditions (both pulmonary and extrapulmonary). Dyspnea, chest pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways, and syncope Syncope Syncope is a short-term loss of consciousness and loss of postural stability followed by spontaneous return of consciousness to the previous neurologic baseline without the need for resuscitation. The condition is caused by transient interruption of cerebral blood flow that may be benign or related to a underlying life-threatening condition. Syncope) are due to RV failure. Severe PS PS Invasive Mechanical Ventilation is treated surgically.
Last updated: Apr 26, 2025
Pulmonary (or pulmonic) valve:
| Pulmonary stenosis Stenosis Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS) ( PS PS Invasive Mechanical Ventilation) | Pulmonary regurgitation Regurgitation Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) (PR) | |
|---|---|---|
| Etiology | Mostly congenital | Mostly acquired |
| Murmur | Systolic murmur, left upper sternal border (preceded by a systolic click that decreases with inspiration Inspiration Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing) | Diastolic murmur, left upper sternal border, increases with inspiration Inspiration Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing |
| S2 S2 Heart Sounds | Split S2 S2 Heart Sounds with soft and delayed P2 | Split S2 S2 Heart Sounds with a loud P2 |
| Echocardiographic findings | Thick and domed leaflets, with increased systolic velocity across the valve, RVH | Valvular abnormalities (depending on etiology), RV enlargement, and a regurgitant jet in the right ventricular outflow tract |
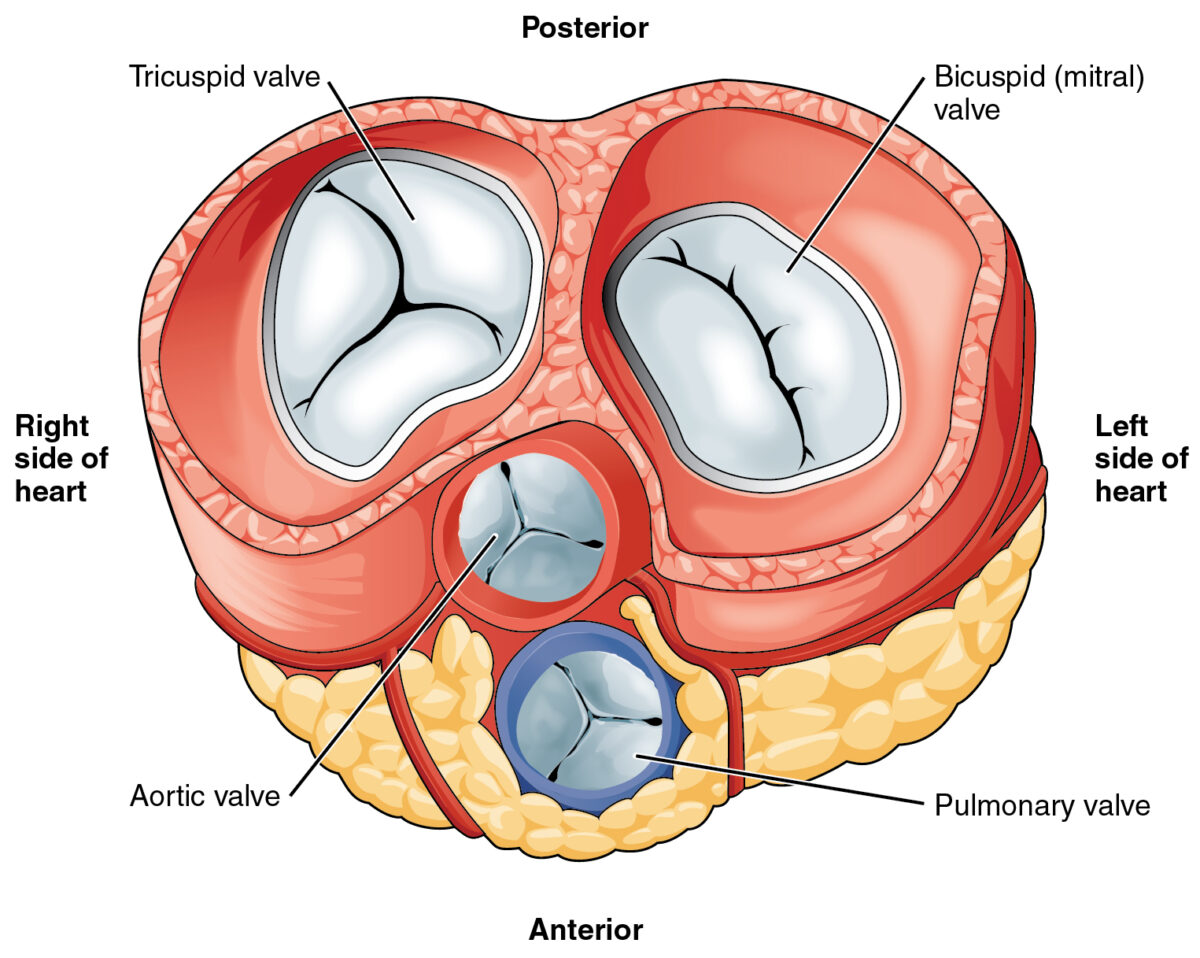
Heart valves:
The pulmonary valve is the lower middle valve.
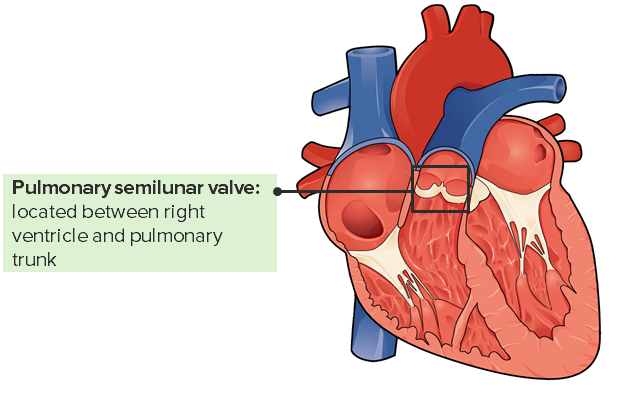
The pulmonary valve and its location in the heart
Image: “Internal Anatomy of the Heart” by Philschatz. License: CC BY 4.0, edited by Lecturio.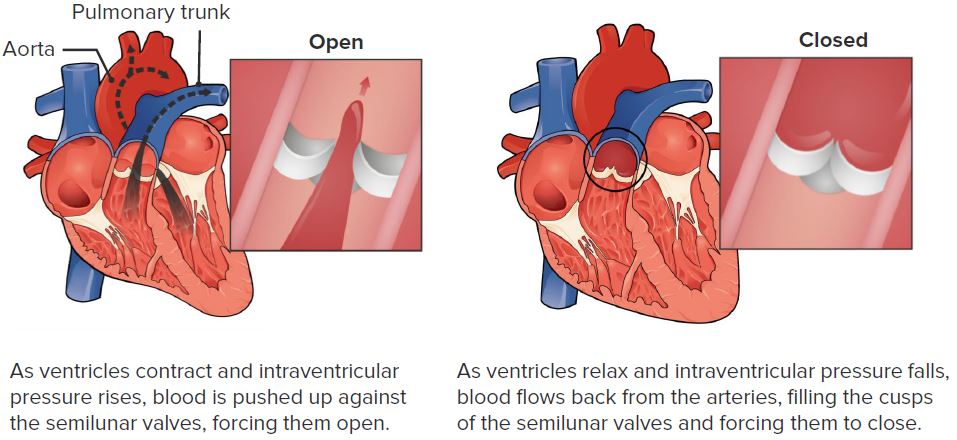
The function of the pulmonary valve
Image: “Pulmonary Valve” by Philschatz. License: CC BY 4.0, edited by Lecturio.Pulmonary stenosis Stenosis Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS) is the narrowing of the pulmonary valve Pulmonary valve A valve situated at the entrance to the pulmonary trunk from the right ventricle. Heart: Anatomy causing:
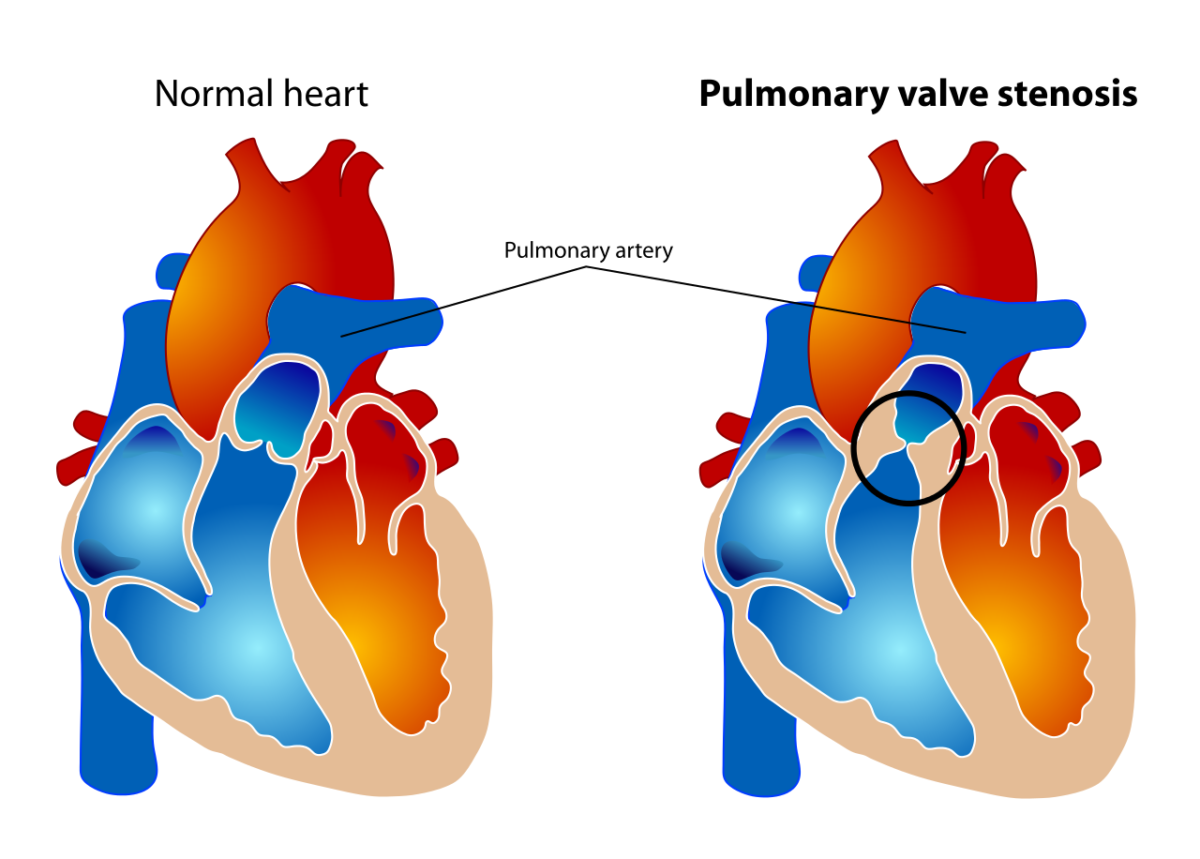
Differentiation of the normal heart with a normal pulmonary valve and a heart with pulmonary valve stenosis
Image: “Pulmonary valve stenosis” by LadyofHats. License: Public domain.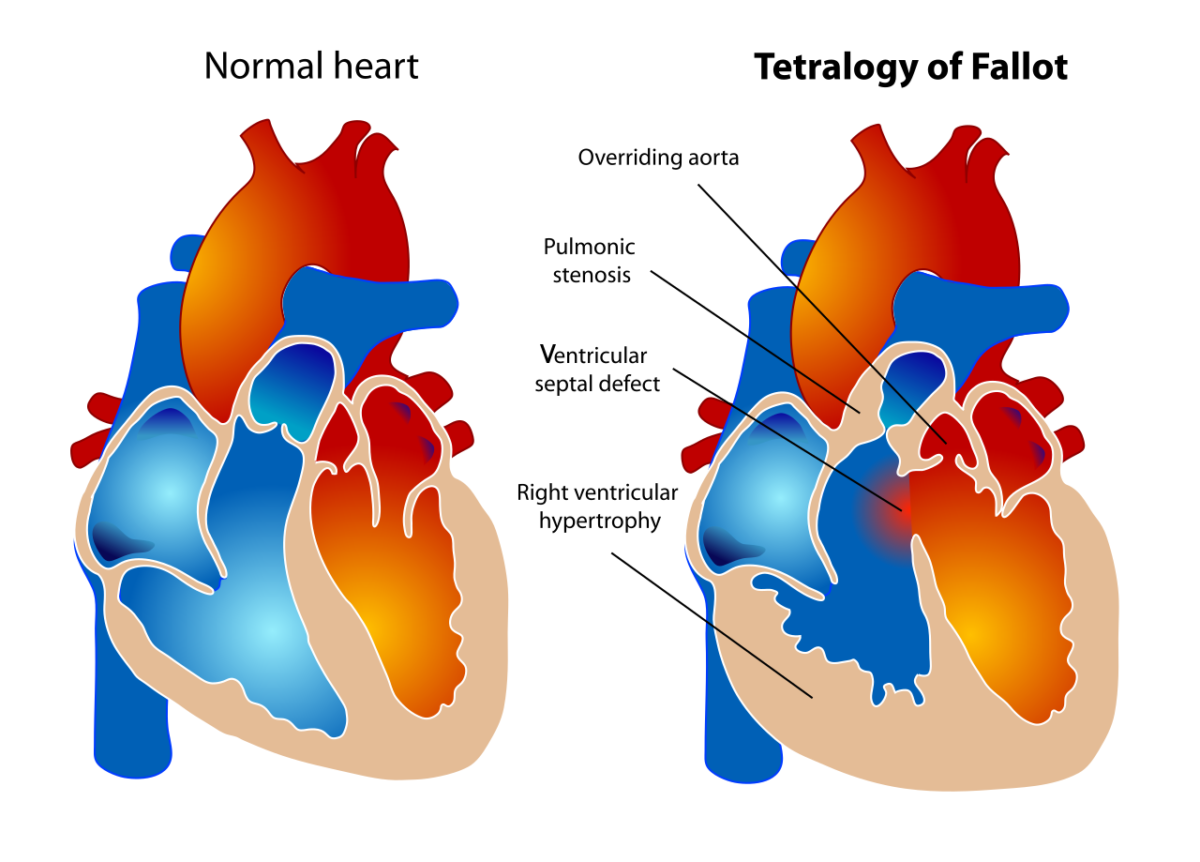
Comparison of the normal heart and a heart with TOF: pulmonary valve stenosis, overriding aorta, RVH, VSD
Image: “Tetralogy of Fallot” by LadyofHats. License: Public domain.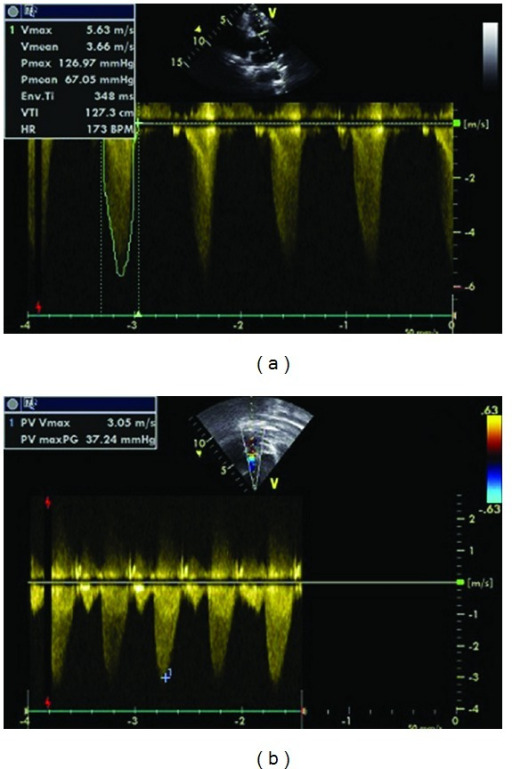
Echocardiography. A: pulmonary valve stenosis with a maximum gradient of 126 mm Hg before pulmonary balloon valvuloplasty; B: mild pulmonary valve stenosis after balloon valvuloplasty (maximum gradient of 37 mm Hg)
Image: “Pulmonary Balloon Valvuloplasty” by Oylumlu M, Aykent K, Soydinc HE, Oylumlu M, Ertas F, Ozer HO, Sari I. License: CC By 3.0.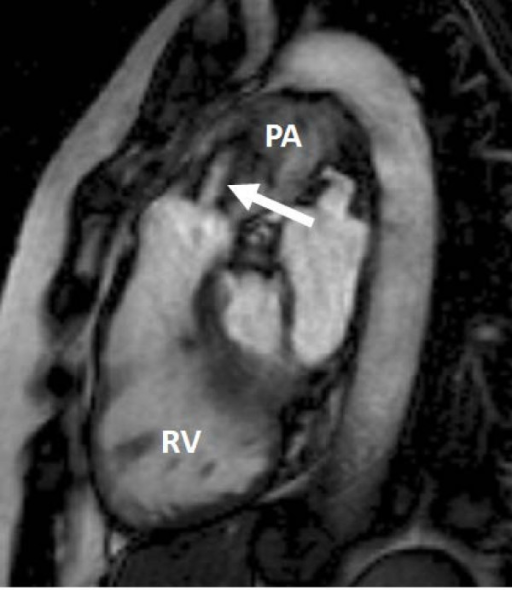
Cardiac magnetic resonance image: right ventricular outflow tract view showing foreshortened RV and a pulmonary valve with moderate-to-severe stenosis. The high-velocity jet of the stenosis can be seen (arrow). PA = main pulmonary artery.
Image: “Heart valve disease” by Myerson SG, John Radcliffe Hospital. License: CC BY 2.0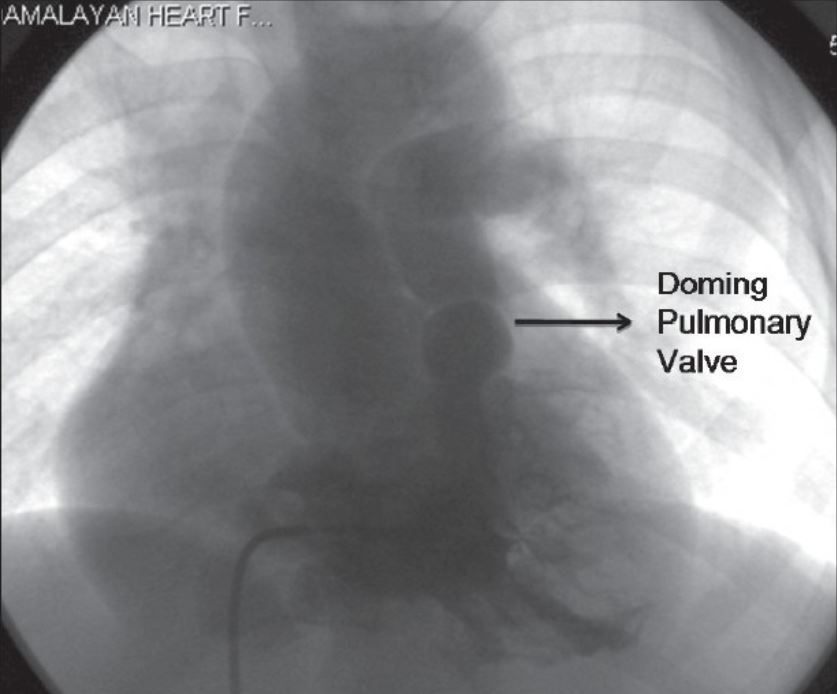
Right ventricular angiogram done in postero-anterior view showing infundibular narrowing and doming pulmonary valve
Image: “Tetralogy of fallot” by Kannan BR. License: CC BY 2.0.
Chest X-ray of an adult woman with severe pulmonary valvular stenosis. The patient underwent percutaneous pulmonary balloon valvuloplasty (PBV). Left image: A chest X-ray revealed marked enlargement of the main pulmonary trunk from PS. Right image: The lateral view shows a complication of the procedure, with the catheter entrapped across the fossa ovalis.
Image: “Entrapped Catheter across the Fossa Ovalis” by Betigeri VM, Gopinathan G, Malik I, Sanwal MK, Datt V, Satsangi DK. License: CC BY 3.0.