Methemoglobinemia is a condition characterized by elevated levels of methemoglobin in the blood. Methemoglobin is the oxidized form of hemoglobin, where the heme iron Iron A metallic element with atomic symbol fe, atomic number 26, and atomic weight 55. 85. It is an essential constituent of hemoglobins; cytochromes; and iron-binding proteins. It plays a role in cellular redox reactions and in the transport of oxygen. Trace Elements has been converted from the usual ferrous (Fe2+) to the ferric (Fe3+) form. The Fe3+ form of iron Iron A metallic element with atomic symbol fe, atomic number 26, and atomic weight 55. 85. It is an essential constituent of hemoglobins; cytochromes; and iron-binding proteins. It plays a role in cellular redox reactions and in the transport of oxygen. Trace Elements cannot bind BIND Hyperbilirubinemia of the Newborn O2, and, thus, leads to tissue hypoxia Hypoxia Sub-optimal oxygen levels in the ambient air of living organisms. Ischemic Cell Damage. Methemoglobinemia results from congenital defects or can occur after exposure to oxidizing agents. Symptoms depend on methemoglobin levels and vary from simple cyanosis Cyanosis A bluish or purplish discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes due to an increase in the amount of deoxygenated hemoglobin in the blood or a structural defect in the hemoglobin molecule. Pulmonary Examination to neurologic and cardiac presentations. The condition can be fatal in the case of significant elevation of methemoglobin (> 70%). Diagnosis is established by measuring methemoglobin levels in blood using co-oximetry. Treatment of methemoglobinemia is with methylene blue or ascorbic acid, as they hasten the conversion of methemoglobin to hemoglobin.
Last updated: Jun 21, 2025
Methemoglobinemia occurs when RBCs RBCs Erythrocytes, or red blood cells (RBCs), are the most abundant cells in the blood. While erythrocytes in the fetus are initially produced in the yolk sac then the liver, the bone marrow eventually becomes the main site of production. Erythrocytes: Histology contain elevated methemoglobin levels (normal range in adults is 0%–3%).
Methemoglobin is a form of hemoglobin in which ferrous (Fe2+) heme iron Iron A metallic element with atomic symbol fe, atomic number 26, and atomic weight 55. 85. It is an essential constituent of hemoglobins; cytochromes; and iron-binding proteins. It plays a role in cellular redox reactions and in the transport of oxygen. Trace Elements is oxidized to the ferric (Fe3+) state, which is unable to bind BIND Hyperbilirubinemia of the Newborn O2.
Congenital:
Acquired due to exposure to oxidizing agents:
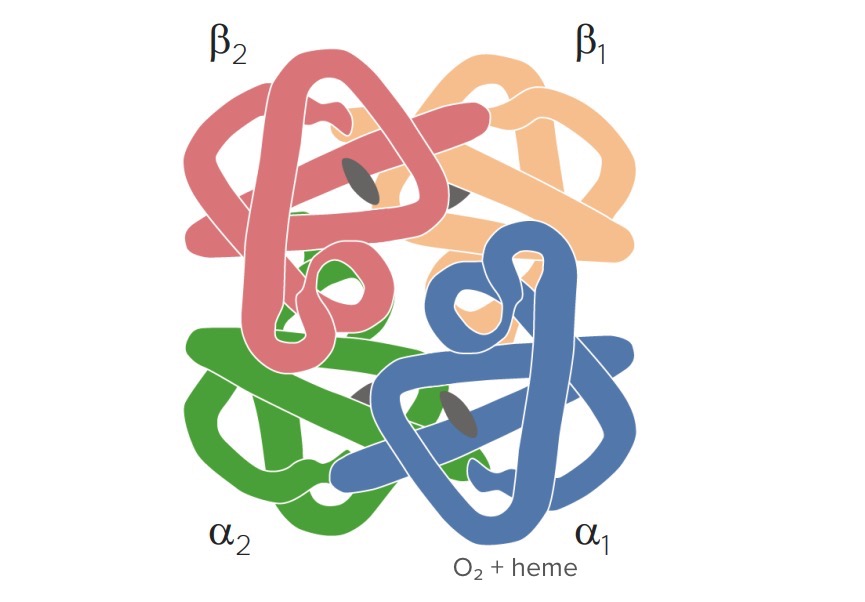
Hemoglobin structure: 4 globin chains (β1, β2, ɑ1, and ɑ2) and 4 heme molecules (with iron in the ferrous state) for binding with O2
Image by Lecturio.Methemoglobin levels are limited through different mechanisms:
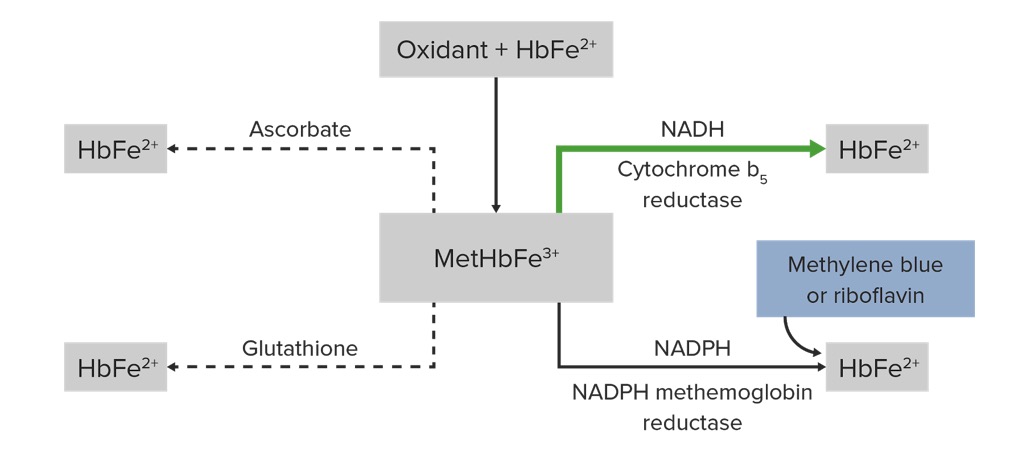
Pathophysiology and management of methemoglobin (HbFe²⁺: hemoglobin, MetHbFe³⁺: methemoglobin, NADPH: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, NADH: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide):
Oxidation of heme iron from ferrous state to ferric state produces MetHbFe³⁺. Cytochrome b5 reductase reduces MetHbFe³⁺ to HbFe²⁺. Methylene blue acts as an electron acceptor for NADPH reductase and also facilitates the reduction of methemoglobin. Other compounds that can promote MetHbFe³⁺ reduction include glutathione and ascorbic acid.
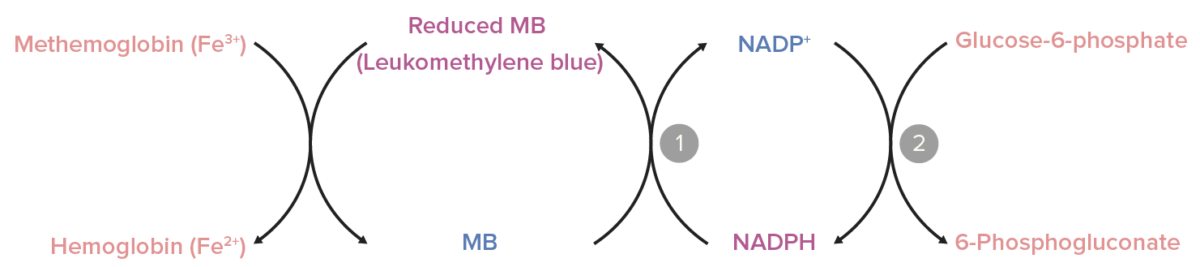
Role of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) methemoglobin reductase:
NADPH is generated in the glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase reaction (2). NADPH-methemoglobin reductase converts methylene blue (MB) to leukomethylene blue (the active form) using NADPH as an electron donor (1). Leukomethylene blue, in turn, reduces methemoglobin to hemoglobin.
Symptoms depend on the etiology, chronicity, and level of methemoglobin.
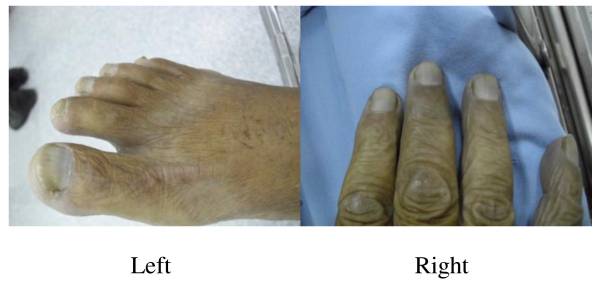
Cyanosis in methemoglobinemia:
The individual’s foot and hand show a bluish color and cyanotic nail beds.
History:
Physical exam findings:

Color code suggestive of methemoglobin:
Blood with methemoglobin concentration > 15% of total hemoglobin levels appears brownish, as seen in the image (right side).
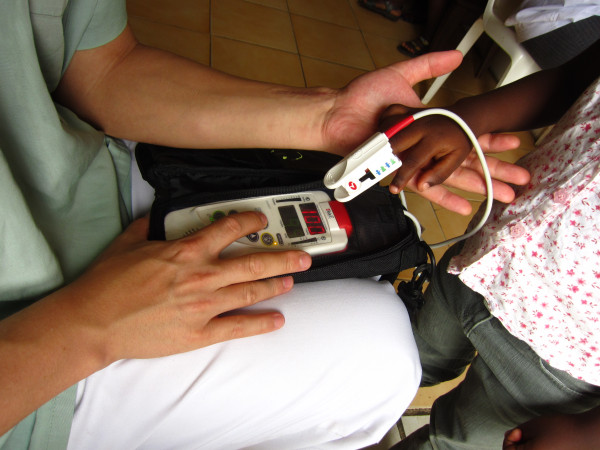
Methemoglobin measurement:
Use of co-oximetry (multiple-wavelength oximetry). Pictured above is a Rad-57 pulse oximeter applied to the finger of a child. Instead of just 2 wavelengths, co-oximetry utilizes 8 wavelengths.
Management of methemoglobinemia depends on the severity and chronicity.
Methemoglobin levels > 30% and associated with tissue hypoxia Hypoxia Sub-optimal oxygen levels in the ambient air of living organisms. Ischemic Cell Damage is a medical emergency:
In congenital methemoglobinemia: