The orbit is the cavity of the skull Skull The skull (cranium) is the skeletal structure of the head supporting the face and forming a protective cavity for the brain. The skull consists of 22 bones divided into the viscerocranium (facial skeleton) and the neurocranium. Skull: Anatomy in which the eye and its appendages are situated. The orbit is composed of 7 bones and has a pyramidal shape, with its apex pointed posteromedially. The orbital contents comprise the eye; orbital and retrobulbar fascia Fascia Layers of connective tissue of variable thickness. The superficial fascia is found immediately below the skin; the deep fascia invests muscles, nerves, and other organs. Cellulitis; extraocular muscles; cranial nerves Cranial nerves There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves (CNs), which run from the brain to various parts of the head, neck, and trunk. The CNs can be sensory or motor or both. The CNs are named and numbered in Roman numerals according to their location, from the front to the back of the brain. The 12 Cranial Nerves: Overview and Functions II, III, IV, V, and VI; blood vessels; fat; lacrimal gland with its sac and nasolacrimal duct Nasolacrimal Duct Nasolacrimal duct. Dacryocystitis; eyelids Eyelids Each of the upper and lower folds of skin which cover the eye when closed. Blepharitis; palpebral and suspensory ligaments; ciliary ganglion Ciliary Ganglion Pupil: Physiology and Abnormalities; and short ciliary nerves.
Last updated: Dec 5, 2024
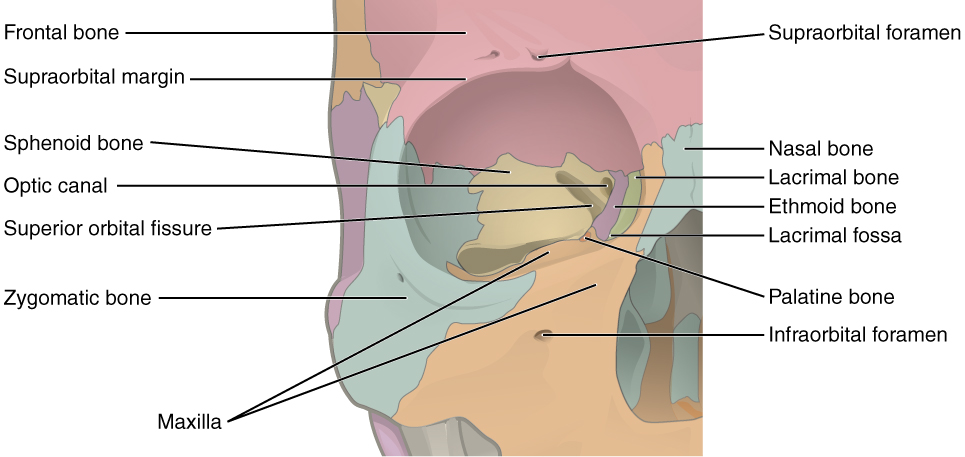
The right orbit and the 7 bones that make up its walls: frontal (red), maxilla (orange), lacrimal (green), ethmoid (purple), sphenoid (yellow), palatine (dark orange), and zygomatic (blue)
Image: “Illustration from Anatomy & Physiology” by OpenStax College. License: CC-BY-3.0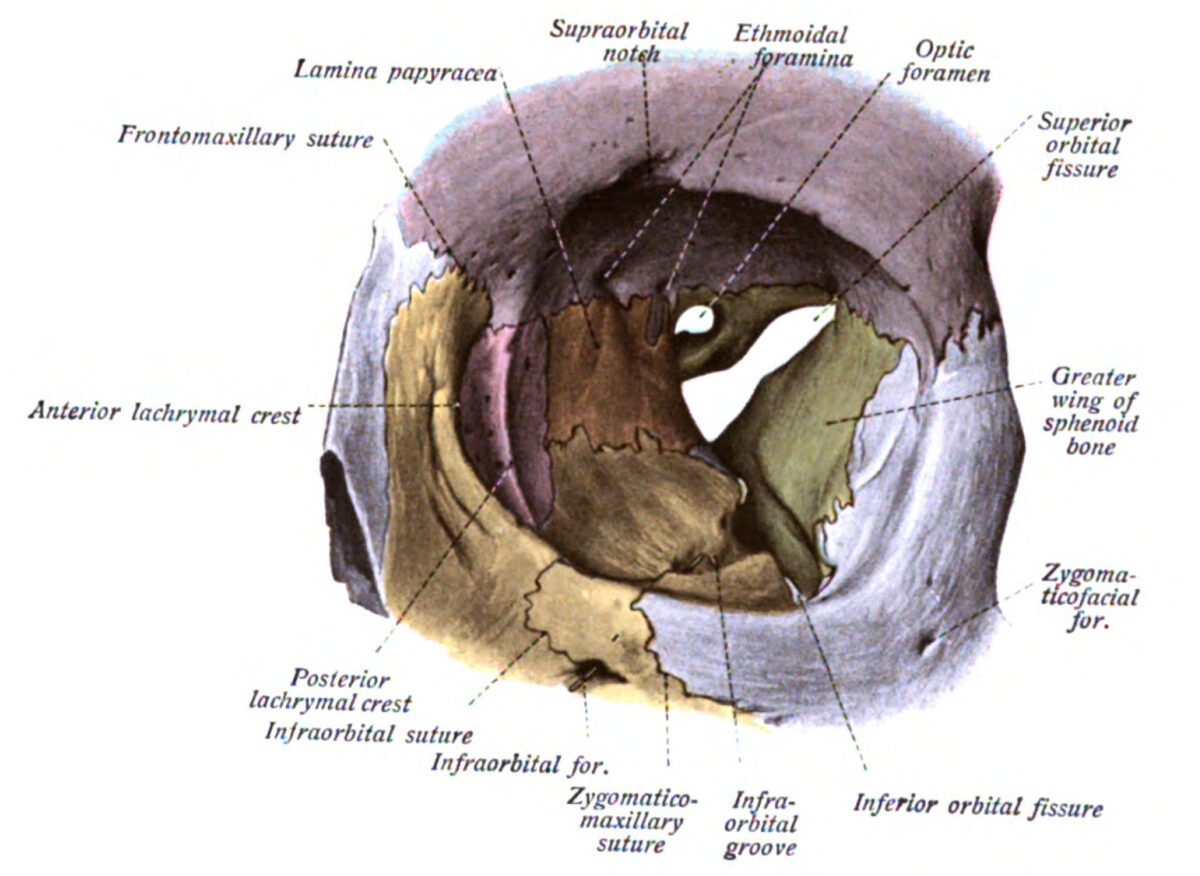
The left orbit, featuring its many openings: optic foramen, ethmoidal foramina, superior and inferior orbital fissures, infraorbital groove, and supraorbital notch
Image: “An illustration from the 1909 American edition of Sobotta’s anatomy” by Dr. Johannes Sobotta. License: Public Domain| Location | Contents | |
|---|---|---|
| Optic foramen or canal | Apex, bordered by the body and lesser wing of the sphenoid |
|
| Ethmoidal foramina |
|
Anterior and posterior ethmoidal veins Veins Veins are tubular collections of cells, which transport deoxygenated blood and waste from the capillary beds back to the heart. Veins are classified into 3 types: small veins/venules, medium veins, and large veins. Each type contains 3 primary layers: tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica adventitia. Veins: Histology, arteries Arteries Arteries are tubular collections of cells that transport oxygenated blood and nutrients from the heart to the tissues of the body. The blood passes through the arteries in order of decreasing luminal diameter, starting in the largest artery (the aorta) and ending in the small arterioles. Arteries are classified into 3 types: large elastic arteries, medium muscular arteries, and small arteries and arterioles. Arteries: Histology, and nerves |
| Superior orbital fissure Fissure A crack or split that extends into the dermis Generalized and Localized Rashes | Between the greater and lesser wings of the sphenoid bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types | Inside the common tendinous ring:
|
| Inferior orbital fissure Fissure A crack or split that extends into the dermis Generalized and Localized Rashes |
|
|
| Infraorbital foramen | Middle of the orbital floor Orbital Floor Orbital Fractures ( maxilla Maxilla One of a pair of irregularly shaped bones that form the upper jaw. A maxillary bone provides tooth sockets for the superior teeth, forms part of the orbit, and contains the maxillary sinus. Skull: Anatomy) | Exit of the infraorbital vein, artery, and nerve |
| Supraorbital notch or foramen | Superior margin of the orbit ( frontal Frontal The bone that forms the frontal aspect of the skull. Its flat part forms the forehead, articulating inferiorly with the nasal bone and the cheek bone on each side of the face. Skull: Anatomy bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types) | Exit of the supraorbital vein, artery, and nerve |
To help memorize the bones that make up the orbit, remember: Many Friendly Zebras Enjoy Lazy Summer Picnics
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Irrigation | Innervation | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medial rectus | Annulus of Zinn (common tendinous ring) | Anterior, medial surface of the eye | Inferior muscular branch of ophthalmic artery Ophthalmic artery Artery originating from the internal carotid artery and distributing to the eye, orbit and adjacent facial structures. Eye: Anatomy | Inferior branch of oculomotor nerve Oculomotor nerve The 3D cranial nerve. The oculomotor nerve sends motor fibers to the levator muscles of the eyelid and to the superior rectus, inferior rectus, and inferior oblique muscles of the eye. It also sends parasympathetic efferents (via the ciliary ganglion) to the muscles controlling pupillary constriction and accommodation. The motor fibers originate in the oculomotor nuclei of the midbrain. The 12 Cranial Nerves: Overview and Functions (CN III) | Adduction Adduction Examination of the Upper Limbs |
| Lateral rectus | Anterior, lateral surface of the eye | Lacrimal artery | Abducens nerve Abducens nerve The 6th cranial nerve which originates in the abducens nucleus of the pons and sends motor fibers to the lateral rectus muscles of the eye. Damage to the nerve or its nucleus disrupts horizontal eye movement control. The 12 Cranial Nerves: Overview and Functions (CN VI) | Abduction Abduction Examination of the Upper Limbs | |
| Inferior rectus | Anterior, inferior surface of the eye | Inferior muscular branch of ophthalmic artery Ophthalmic artery Artery originating from the internal carotid artery and distributing to the eye, orbit and adjacent facial structures. Eye: Anatomy and the infraorbital branch of the maxillary artery | Inferior branch of oculomotor nerve Oculomotor nerve The 3D cranial nerve. The oculomotor nerve sends motor fibers to the levator muscles of the eyelid and to the superior rectus, inferior rectus, and inferior oblique muscles of the eye. It also sends parasympathetic efferents (via the ciliary ganglion) to the muscles controlling pupillary constriction and accommodation. The motor fibers originate in the oculomotor nuclei of the midbrain. The 12 Cranial Nerves: Overview and Functions (CN III) | Depression, extorsion, and adduction Adduction Examination of the Upper Limbs. In abduction Abduction Examination of the Upper Limbs: only depresses | |
| Superior rectus | Anterior, superior surface of the eye | Superior muscular branch of ophthalmic artery Ophthalmic artery Artery originating from the internal carotid artery and distributing to the eye, orbit and adjacent facial structures. Eye: Anatomy | Superior branch of the oculomotor nerve Oculomotor nerve The 3D cranial nerve. The oculomotor nerve sends motor fibers to the levator muscles of the eyelid and to the superior rectus, inferior rectus, and inferior oblique muscles of the eye. It also sends parasympathetic efferents (via the ciliary ganglion) to the muscles controlling pupillary constriction and accommodation. The motor fibers originate in the oculomotor nuclei of the midbrain. The 12 Cranial Nerves: Overview and Functions (CN III) | Elevation, intorsion, and adduction Adduction Examination of the Upper Limbs. In abduction Abduction Examination of the Upper Limbs: only elevates | |
| Superior oblique | Lesser wing of sphenoid, medial to optic canal | Posterior, superior, lateral surface of the eye | Superior muscular branch of the ophthalmic artery Ophthalmic artery Artery originating from the internal carotid artery and distributing to the eye, orbit and adjacent facial structures. Eye: Anatomy | Trochlear nerve Trochlear nerve The 4th cranial nerve. The trochlear nerve carries the motor innervation of the superior oblique muscles of the eye. The 12 Cranial Nerves: Overview and Functions (CN IV) | Intorsion, depression, and abduction Abduction Examination of the Upper Limbs |
| Inferior oblique | Lateral to the lacrimal groove ( maxilla Maxilla One of a pair of irregularly shaped bones that form the upper jaw. A maxillary bone provides tooth sockets for the superior teeth, forms part of the orbit, and contains the maxillary sinus. Skull: Anatomy) | Posterior, inferior, lateral surface of the eye | Inferior branch of the ophthalmic artery Ophthalmic artery Artery originating from the internal carotid artery and distributing to the eye, orbit and adjacent facial structures. Eye: Anatomy and infraorbital artery | Inferior branch of oculomotor nerve Oculomotor nerve The 3D cranial nerve. The oculomotor nerve sends motor fibers to the levator muscles of the eyelid and to the superior rectus, inferior rectus, and inferior oblique muscles of the eye. It also sends parasympathetic efferents (via the ciliary ganglion) to the muscles controlling pupillary constriction and accommodation. The motor fibers originate in the oculomotor nuclei of the midbrain. The 12 Cranial Nerves: Overview and Functions (CN III) | Extorsion, elevation, and abduction Abduction Examination of the Upper Limbs |
| Levator palpebrae superioris | Lesser wing of the sphenoid, above the optic canal | Tarsal plate of upper eyelid | Supraorbital branch of the ophthalmic artery Ophthalmic artery Artery originating from the internal carotid artery and distributing to the eye, orbit and adjacent facial structures. Eye: Anatomy | Superior branch of
oculomotor nerve
Oculomotor nerve
The 3D cranial nerve. The oculomotor nerve sends motor fibers to the levator muscles of the eyelid and to the superior rectus, inferior rectus, and inferior oblique muscles of the eye. It also sends parasympathetic efferents (via the ciliary ganglion) to the muscles controlling pupillary constriction and accommodation. The motor fibers originate in the oculomotor nuclei of the midbrain.
The 12 Cranial Nerves: Overview and Functions (CN III). Sympathetic fibers innervate the smooth muscle fibers on the inferior surface of this muscle. |
Retracting and elevating the eyelid |
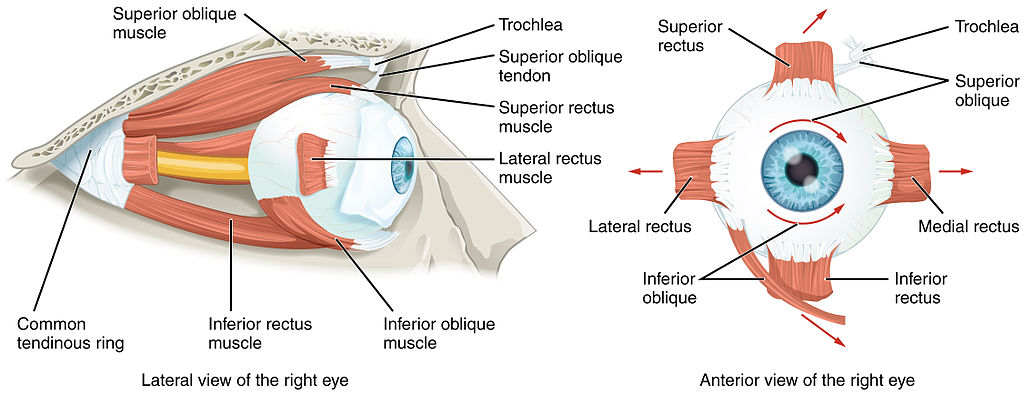
Origin and insertions of the extraocular muscles. Note that the four rectus muscles originate from a common tendinous ring (the obliques do not) and the location of the trochlea for the superior oblique.
Image: “Extraocular Muscles” by OpenStax College. License: CC BY 3.0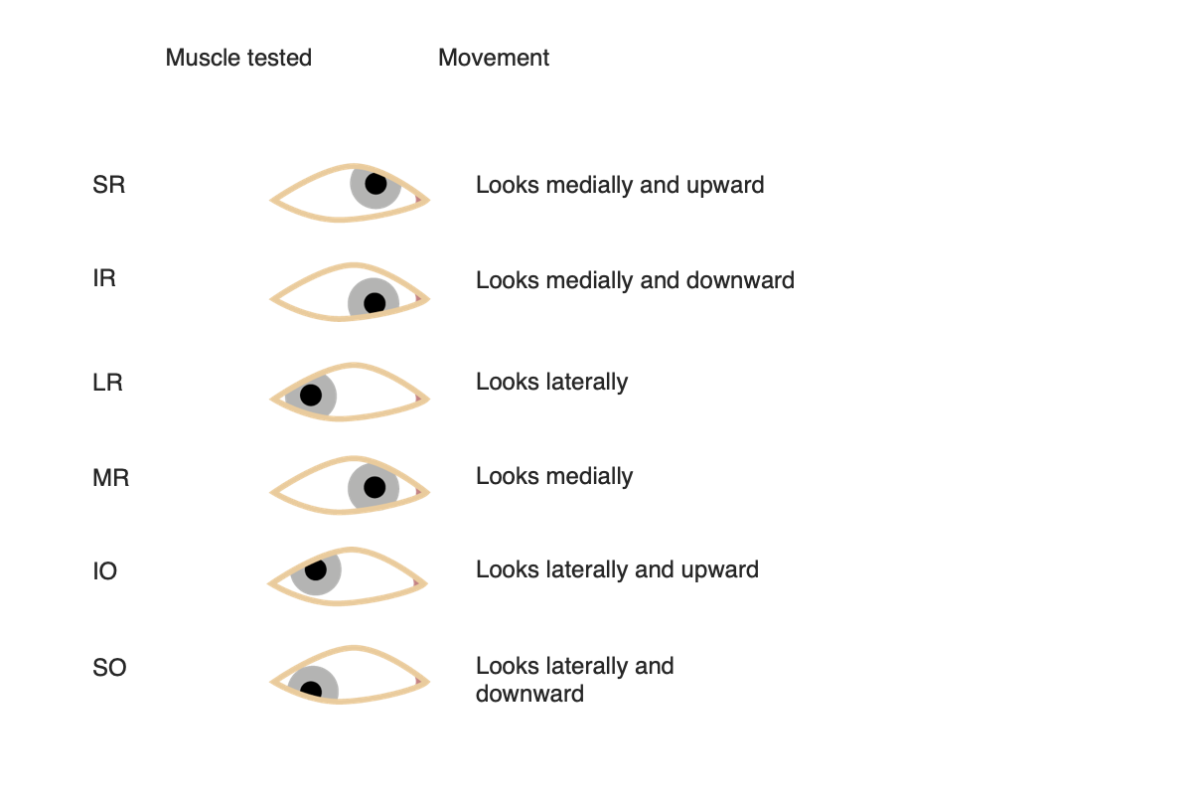
Eye movements for each extraocular muscle
Image by Lecturio.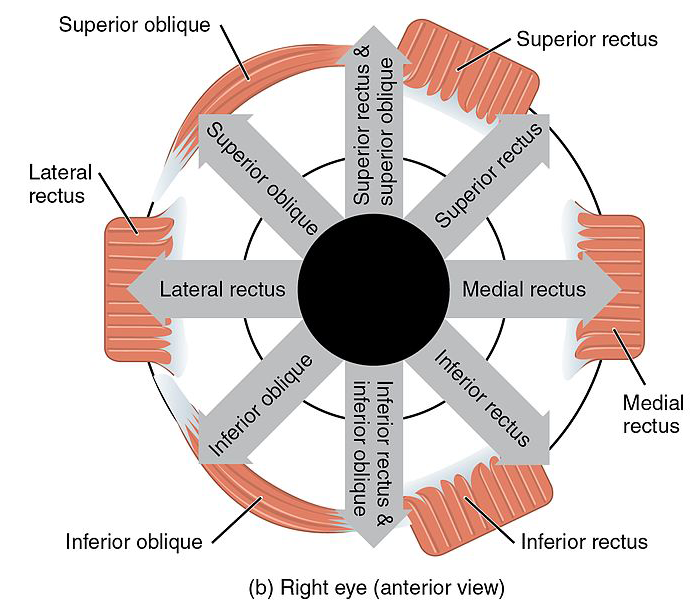
Eye movements for each extraocular muscle. Note the synergistic movements of the superior rectus and oblique, as well as the inferior rectus and oblique muscles.
Image: “Version 8.25” by OpenStax. License: CC BY 4.0, edited by Lecturio.To help memorize the innervation of the extraocular muscles, remember: LR6, SO4, 3
To help memorize the actions of the muscles, remember: RAD
Recti are Ad AD The term advance directive (AD) refers to treatment preferences and/or the designation of a surrogate decision-maker in the event that a person becomes unable to make medical decisions on their own behalf. Advance directives represent the ethical principle of autonomy and may take the form of a living will, health care proxy, durable power of attorney for health care, and/or a physician’s order for life-sustaining treatment. Advance Directivesductors, except the lateral rectus.
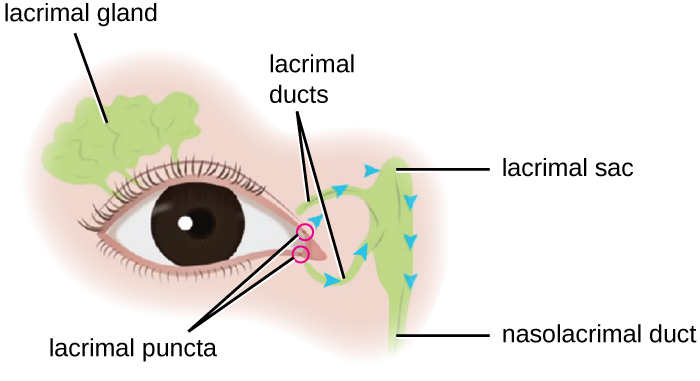
Schematic diagram of the location of the lacrimal gland and apparatus
Image: “Microbiology” by CNX OpenStax. License: CC BY 4.0| Nerve palsy Palsy paralysis of an area of the body, thus incapable of voluntary movement Cranial Nerve Palsies | Causes | Symptoms involving affected eye |
|---|---|---|
| Oculomotor (CN III) |
|
|
| Trochlear (CN IV) |
|
Eye is up and in |
| Abducens (CN VI) |
|
Eye directed medially |