Erythrocytes, or red blood cells (RBCs), are the most abundant cells in the blood. While erythrocytes in the fetus are initially produced in the yolk sac Yolk Sac The first of four extra-embryonic membranes to form during embryogenesis. In reptiles and birds, it arises from endoderm and mesoderm to incorporate the egg yolk into the digestive tract for nourishing the embryo. In placental mammals, its nutritional function is vestigial; however, it is the source of intestinal mucosa; blood cells; and germ cells. It is sometimes called the vitelline sac, which should not be confused with the vitelline membrane of the egg. Embryoblast and Trophoblast Development then the liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy, the bone marrow Bone marrow The soft tissue filling the cavities of bones. Bone marrow exists in two types, yellow and red. Yellow marrow is found in the large cavities of large bones and consists mostly of fat cells and a few primitive blood cells. Red marrow is a hematopoietic tissue and is the site of production of erythrocytes and granular leukocytes. Bone marrow is made up of a framework of connective tissue containing branching fibers with the frame being filled with marrow cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis eventually becomes the main site of production. Erythropoiesis starts with hematopoietic stem cells Hematopoietic stem cells Progenitor cells from which all blood cells derived. They are found primarily in the bone marrow and also in small numbers in the peripheral blood. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis, which develop into lineage-committed progenitors and differentiate into mature RBCs. The process occurs in stages, and extrusion of the nuclei and organelles Organelles A cell is a complex unit that performs several complex functions. An organelle is a specialized subunit within a cell that fulfills a specific role or function. Organelles are enclosed within their own lipid bilayers or are unbound by membranes. The Cell: Organelles occurs prior to maturation. Thus, mature RBCs lack nuclei and have a biconcave shape. RBCs carry hemoglobin, and the shape allows efficient oxygen transport. Billions of RBCs are produced daily, as the life span is 120 days. Senescent or deformed RBCs are removed by macrophages Macrophages The relatively long-lived phagocytic cell of mammalian tissues that are derived from blood monocytes. Main types are peritoneal macrophages; alveolar macrophages; histiocytes; kupffer cells of the liver; and osteoclasts. They may further differentiate within chronic inflammatory lesions to epithelioid cells or may fuse to form foreign body giant cells or langhans giant cells. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation in the spleen Spleen The spleen is the largest lymphoid organ in the body, located in the LUQ of the abdomen, superior to the left kidney and posterior to the stomach at the level of the 9th-11th ribs just below the diaphragm. The spleen is highly vascular and acts as an important blood filter, cleansing the blood of pathogens and damaged erythrocytes. Spleen: Anatomy, liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy, and bone marrow Bone marrow The soft tissue filling the cavities of bones. Bone marrow exists in two types, yellow and red. Yellow marrow is found in the large cavities of large bones and consists mostly of fat cells and a few primitive blood cells. Red marrow is a hematopoietic tissue and is the site of production of erythrocytes and granular leukocytes. Bone marrow is made up of a framework of connective tissue containing branching fibers with the frame being filled with marrow cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis.
Last updated: May 17, 2024
Erythrocytes, also called red blood cells (RBCs), are terminally differentiated structures lacking nuclei but filled with oxygen-carrying hemoglobin. Erythrocytes are the most abundant cells in the blood.
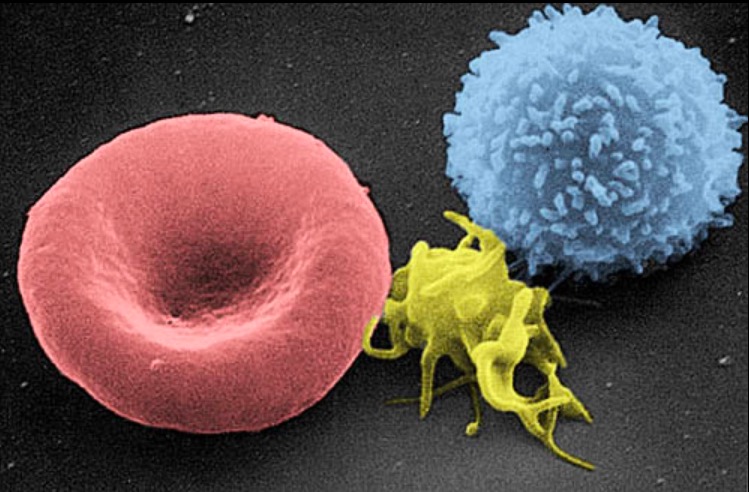
Scanning electron micrograph of a blood cell:
Left to right: human RBC, thrombocyte (platelet), and leukocyte
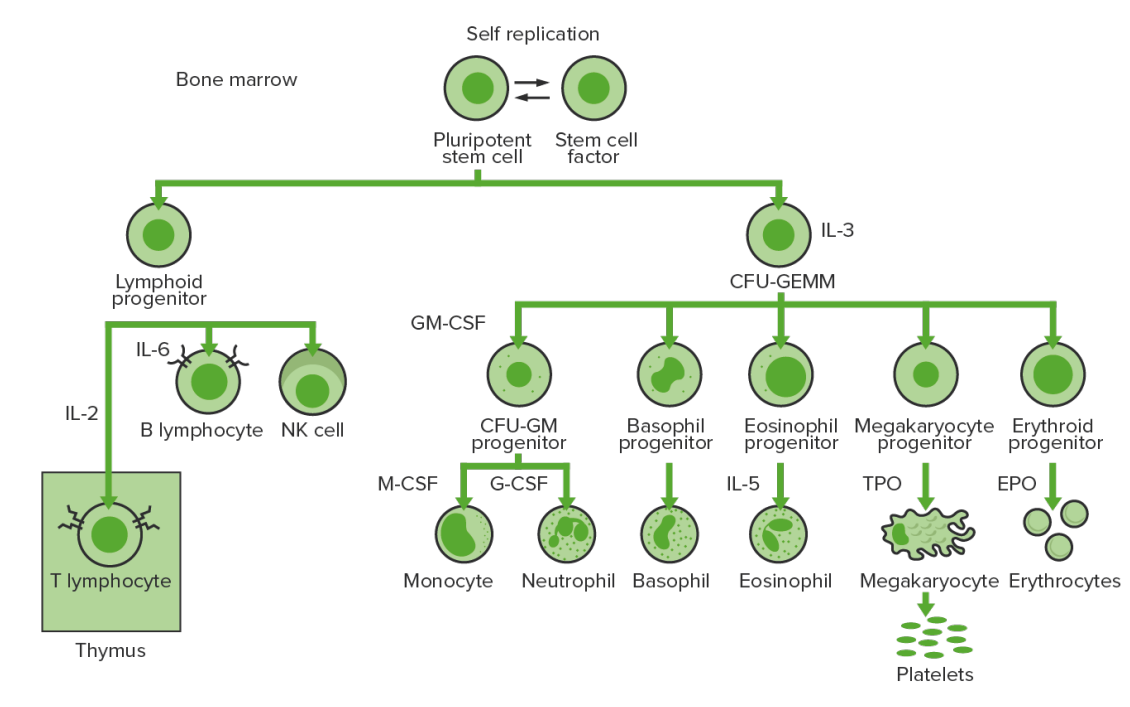
Bone-marrow hematopoiesis: proliferation and differentiation of the formed elements of blood.
CFU-GEMM: colony-forming unit–granulocyte, erythrocyte, monocyte, megakaryocyte
CFU-GM: colony-forming unit–granulocyte-macrophage
GM-CSF: granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor
M-CSF: macrophage colony-stimulating factor
G-CSF: granulocyte colony-stimulating factor
NK: natural killer
TPO: thrombopoietin
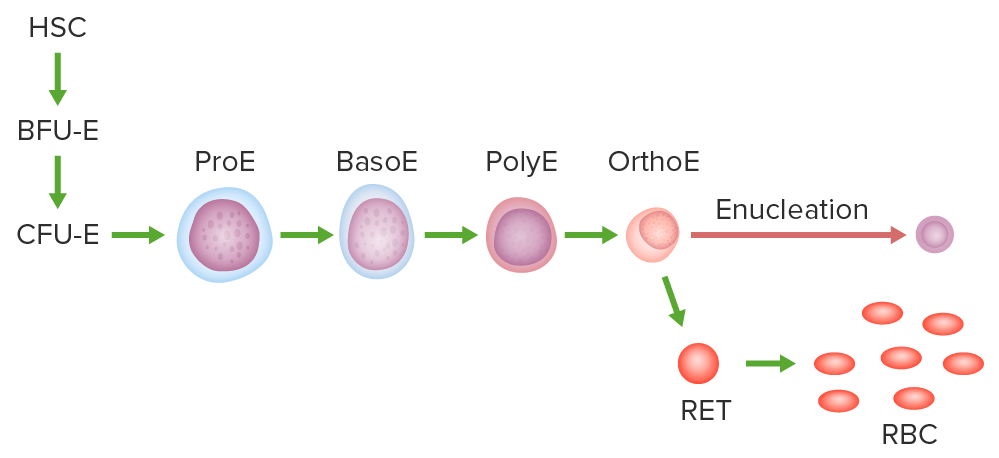
Pathway of erythropoiesis:
Hematopoietic stem cell (HSC), burst-forming unit erythroid (BFU-E) or the earliest committed progenitor, colony-forming unit erythroid (CFU-E), proerythroblast (ProE), basophilic (BasoE), polychromatic (PolyE), and orthochromatic erythroblast (OrthoE).
The OrthoE undergoes enucleation and becomes a reticulocyte (RET). After organelles are expelled or digested, the mature RBC is formed.
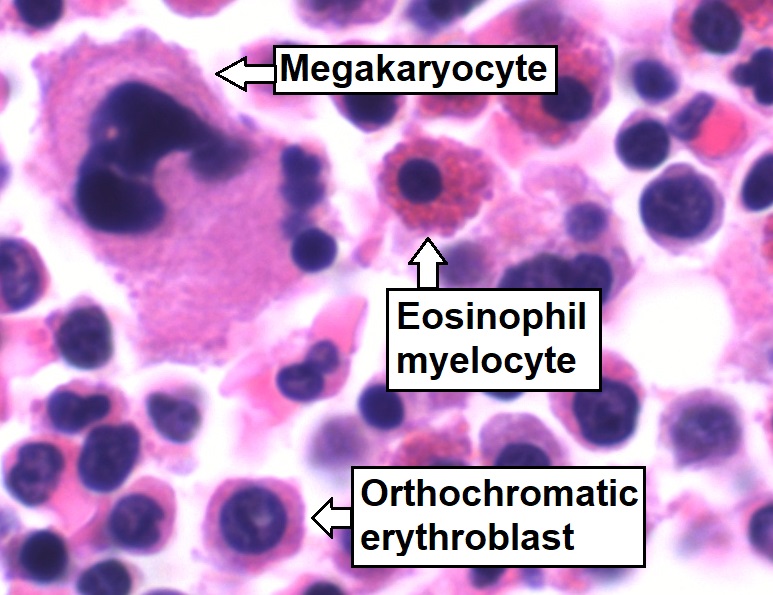
Bone marrow aspirate showing normal trilineage hematopoiesis:
Myelomonocytic cells (labeled Eosinophil myelocyte), erythroid cells (labeled Orthochromatic erythroblast), and megakaryocytic cells
| Cytokines Cytokines Non-antibody proteins secreted by inflammatory leukocytes and some non-leukocytic cells, that act as intercellular mediators. They differ from classical hormones in that they are produced by a number of tissue or cell types rather than by specialized glands. They generally act locally in a paracrine or autocrine rather than endocrine manner. Adaptive Immune Response and growth factors | Activities | Source |
|---|---|---|
| SCF | Stimulates all hematopoietic progenitor cells | Bone marrow Bone marrow The soft tissue filling the cavities of bones. Bone marrow exists in two types, yellow and red. Yellow marrow is found in the large cavities of large bones and consists mostly of fat cells and a few primitive blood cells. Red marrow is a hematopoietic tissue and is the site of production of erythrocytes and granular leukocytes. Bone marrow is made up of a framework of connective tissue containing branching fibers with the frame being filled with marrow cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis stromal cells |
| GM-CSF GM-CSF An acidic glycoprotein of mw 23 kda with internal disulfide bonds. The protein is produced in response to a number of inflammatory mediators by mesenchymal cells present in the hemopoietic environment and at peripheral sites of inflammation. GM-CSF is able to stimulate the production of neutrophilic granulocytes, macrophages, and mixed granulocyte-macrophage colonies from bone marrow cells and can stimulate the formation of eosinophil colonies from fetal liver progenitor cells. GM-CSF can also stimulate some functional activities in mature granulocytes and macrophages. White Myeloid Cells: Histology | Stimulates myeloid progenitor cells Myeloid progenitor cells Stem cells derived from hematopoietic stem cells. Derived from these myeloid progenitor cells are the megakaryocytes; erythroid cells; myeloid cells; and some dendritic cells. Acute Myeloid Leukemia | Endothelial cells, T cells T cells Lymphocytes responsible for cell-mediated immunity. Two types have been identified – cytotoxic (t-lymphocytes, cytotoxic) and helper T-lymphocytes (t-lymphocytes, helper-inducer). They are formed when lymphocytes circulate through the thymus gland and differentiate to thymocytes. When exposed to an antigen, they divide rapidly and produce large numbers of new T cells sensitized to that antigen. T cells: Types and Functions |
| EPO | Stimulates erythropoiesis, including differentiation | Kidney, liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy |
| IL-3 | Mitogen for all granulocyte and megakaryocyte Megakaryocyte Very large bone marrow cells which release mature blood platelets. Platelets: Histology/erythrocyte progenitor cells | T helper cells |
Other factors: