The development of the embryonic cardiovascular system begins during the 3rd week of gestation. The process begins with a straight tube, which will eventually differentiate to form a functional heart after several events. Disturbances of any events in the development of the heart, such as cardiac looping, can result in severe congenital disorders. The major clinical presentation of these abnormalities will be cyanosis Cyanosis A bluish or purplish discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes due to an increase in the amount of deoxygenated hemoglobin in the blood or a structural defect in the hemoglobin molecule. Pulmonary Examination.
Last updated: Apr 25, 2025
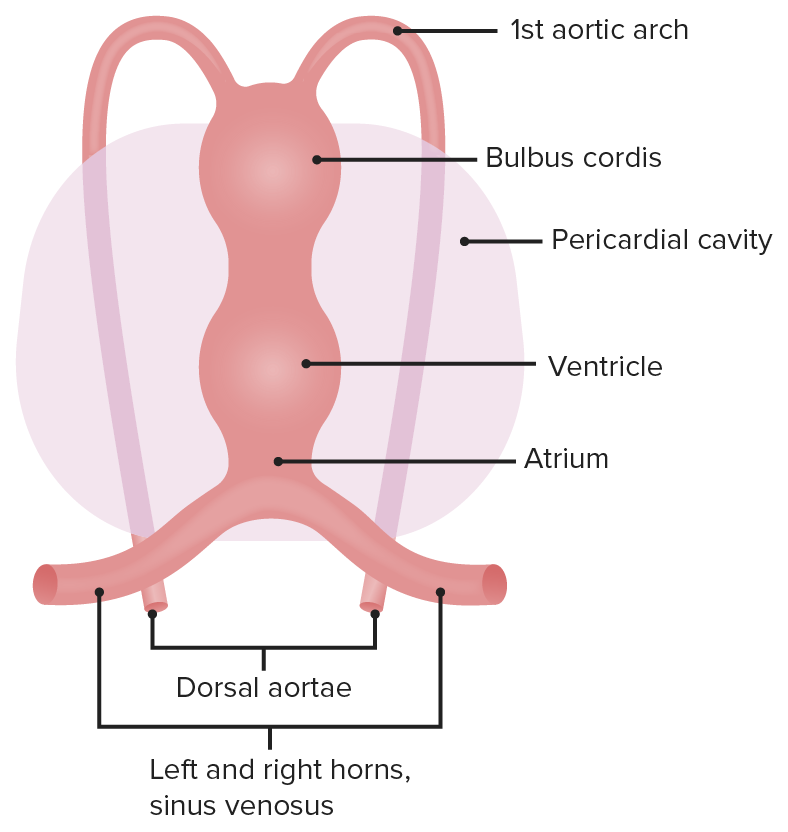
The early heart is divided into five regions, each of which gives rise to different structures.
Image by Lecturio.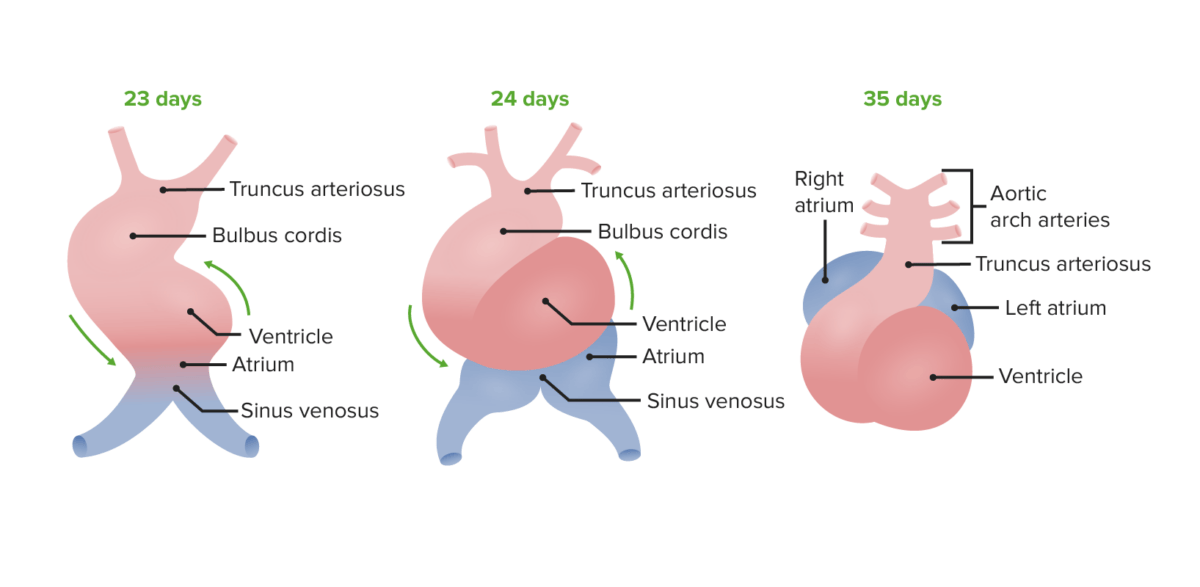
During the looping, the cranial end will bend ventrally and caudally, and then rotate over to the right (24 days). The atrial end will then shift dorso-cranially (posteriorly and cranially) and will move to the left (35 days).
Image by Lecturio.The atrial septum begins with endocardial cushions at the base of the atrial chamber and septum primum.
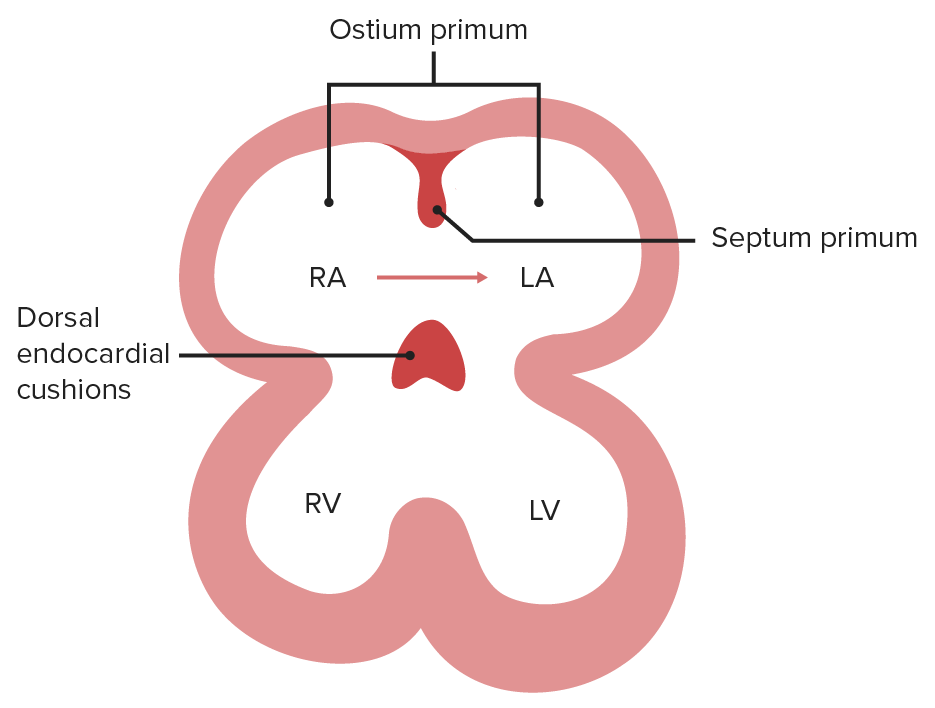
The foramen (ostium) primum is the opening between the 2 embryonic atria.
Image by Lecturio.
Endocardial cushions are derived from the neural crest. As the septum primum approaches the dorsal endocardial cushions, cells in the septum undergo apoptosis, which creates the foramen (ostium) secundum.
Image by Lecturio.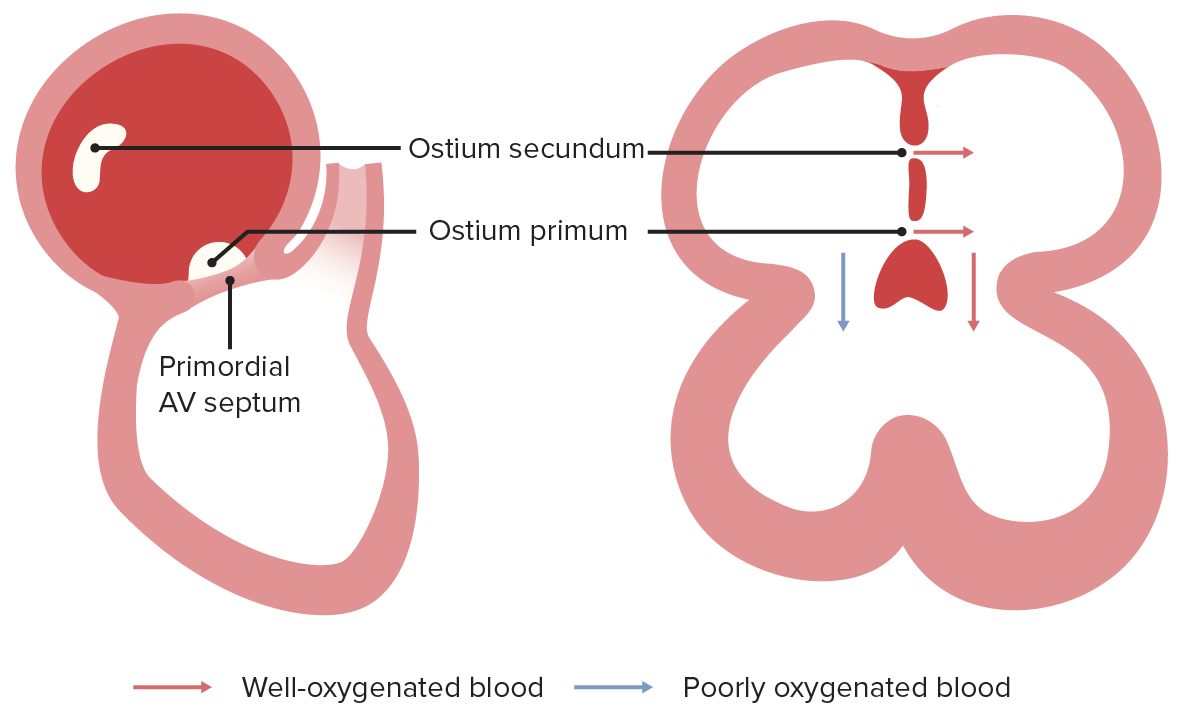
The foramen (ostium) primum and secundum function together to deliver oxygenated blood to the left atrium, which will then flow to the left ventricle, whereas, poorly oxygenated blood delivered from the SVC will flow to the right ventricle.
Image by Lecturio.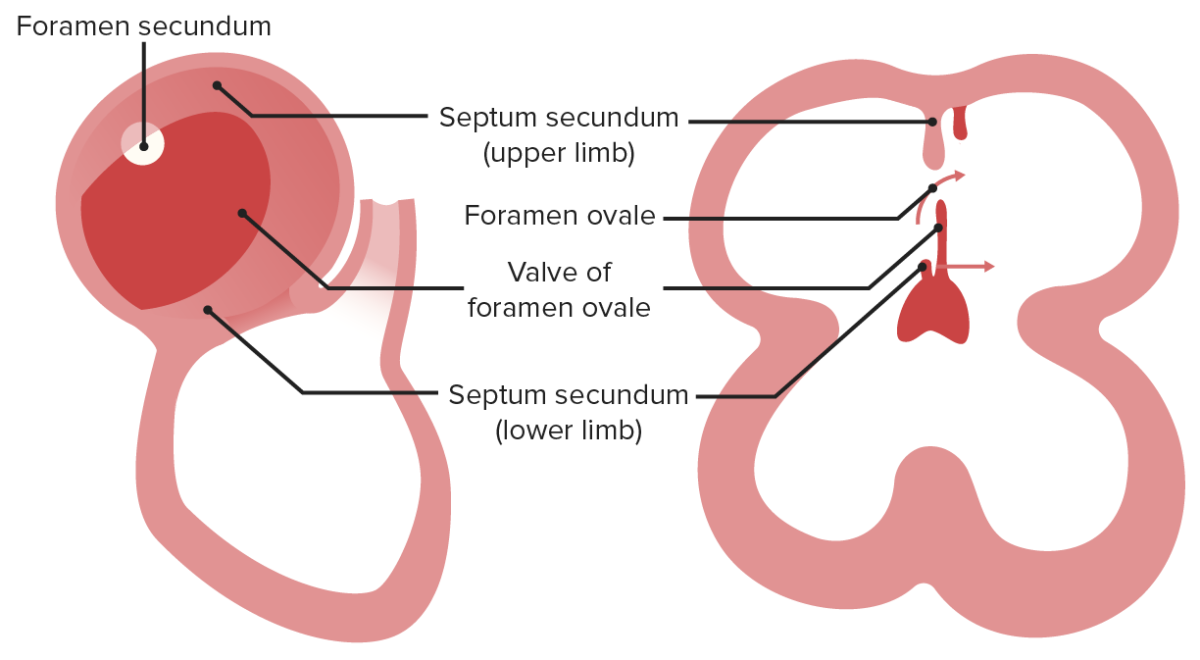
The secundum will grow to narrow the foramen (ostium) secundum and form foramen ovale. In this case, the septum primum will function as a valve.
Image by Lecturio.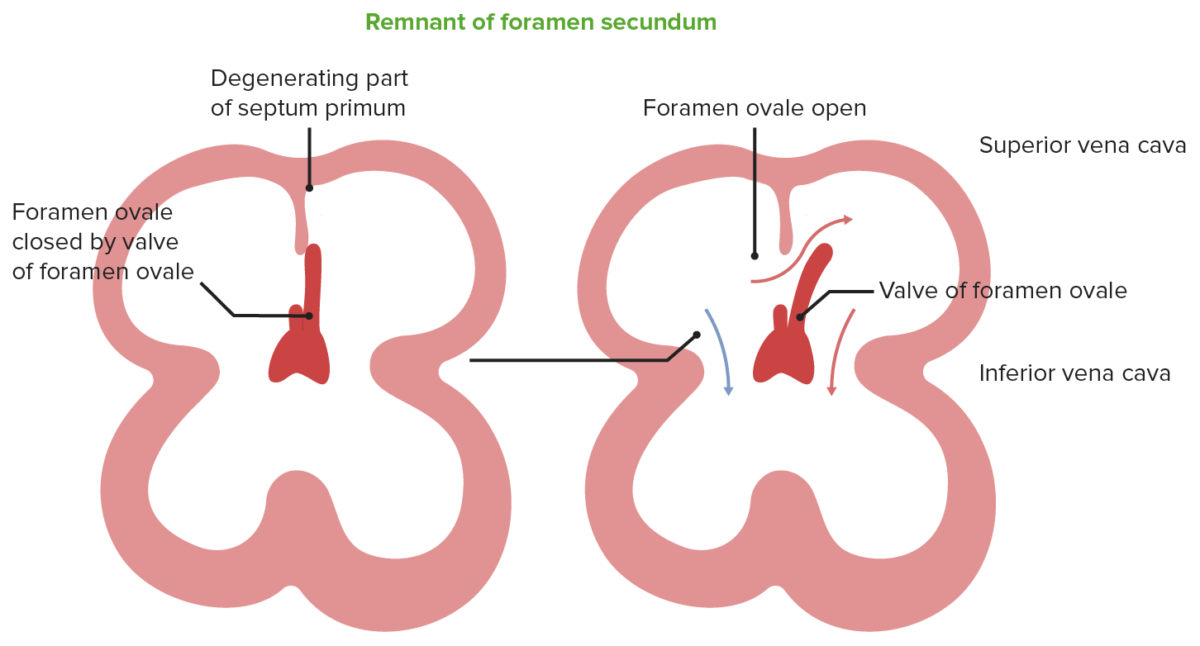
Blood from the IVC pushes the septum primum (valve of foramen ovale) to move blood from the RA to the LA, after which blood will flow to the left ventricle. At birth, the pressure in the LA will increase, which will shut the foramen ovale.
Image by Lecturio.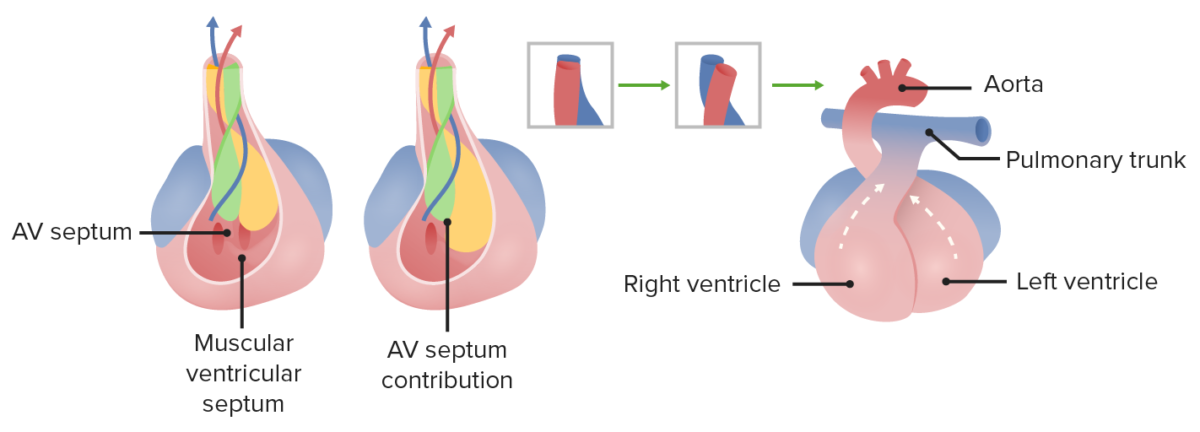
Membranous portion of the interventricular septum grows upward to fuse with conotruncal ridges. Right and left ventricles, as well as the aorta and pulmonary tract, become separated from each other.
Image by Lecturio.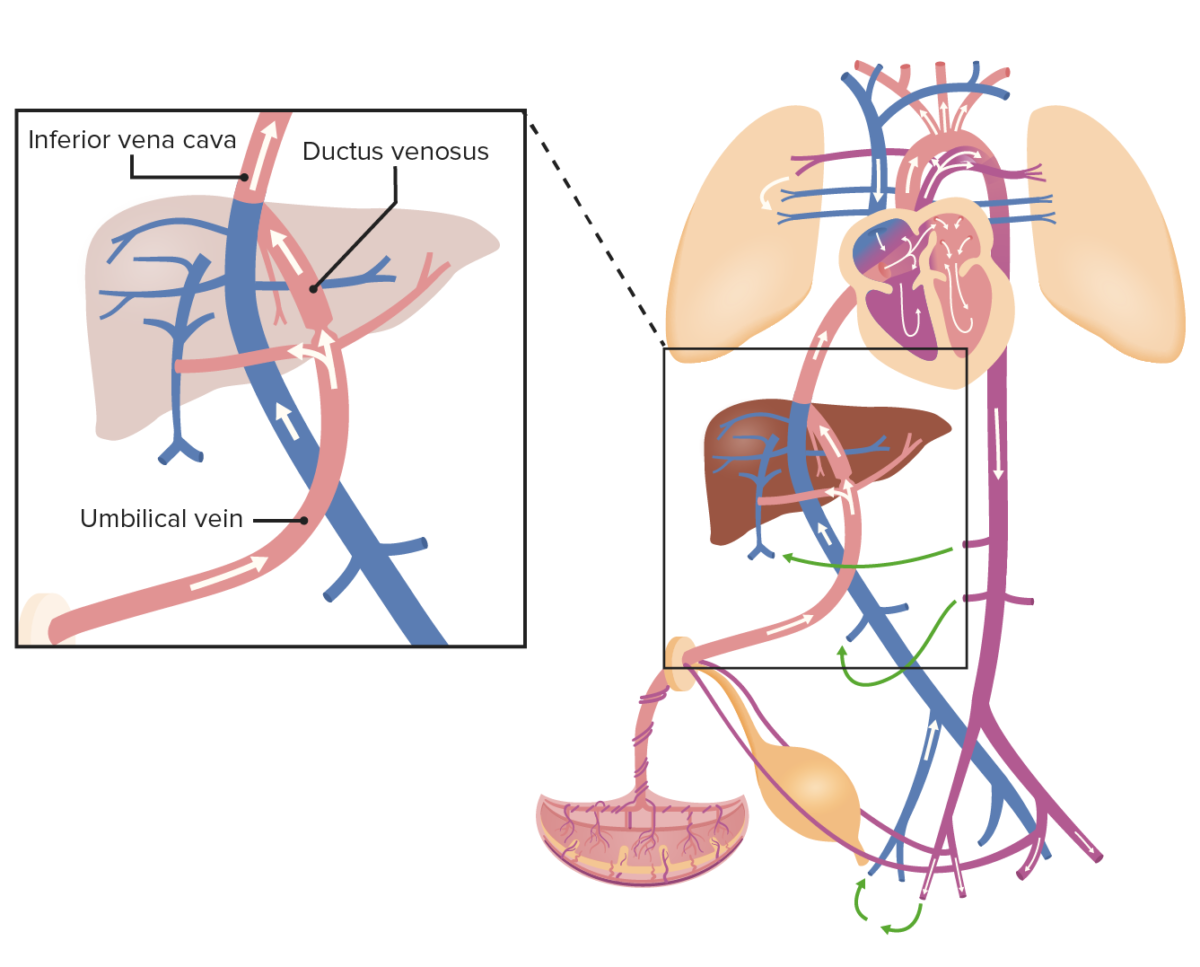
Oxygenated blood from the umbilical vein drains into the IVC, which also collects the blood from the organs and lower portion of the body; thus, the blood becomes slightly deoxygenated.
Image by Lecturio.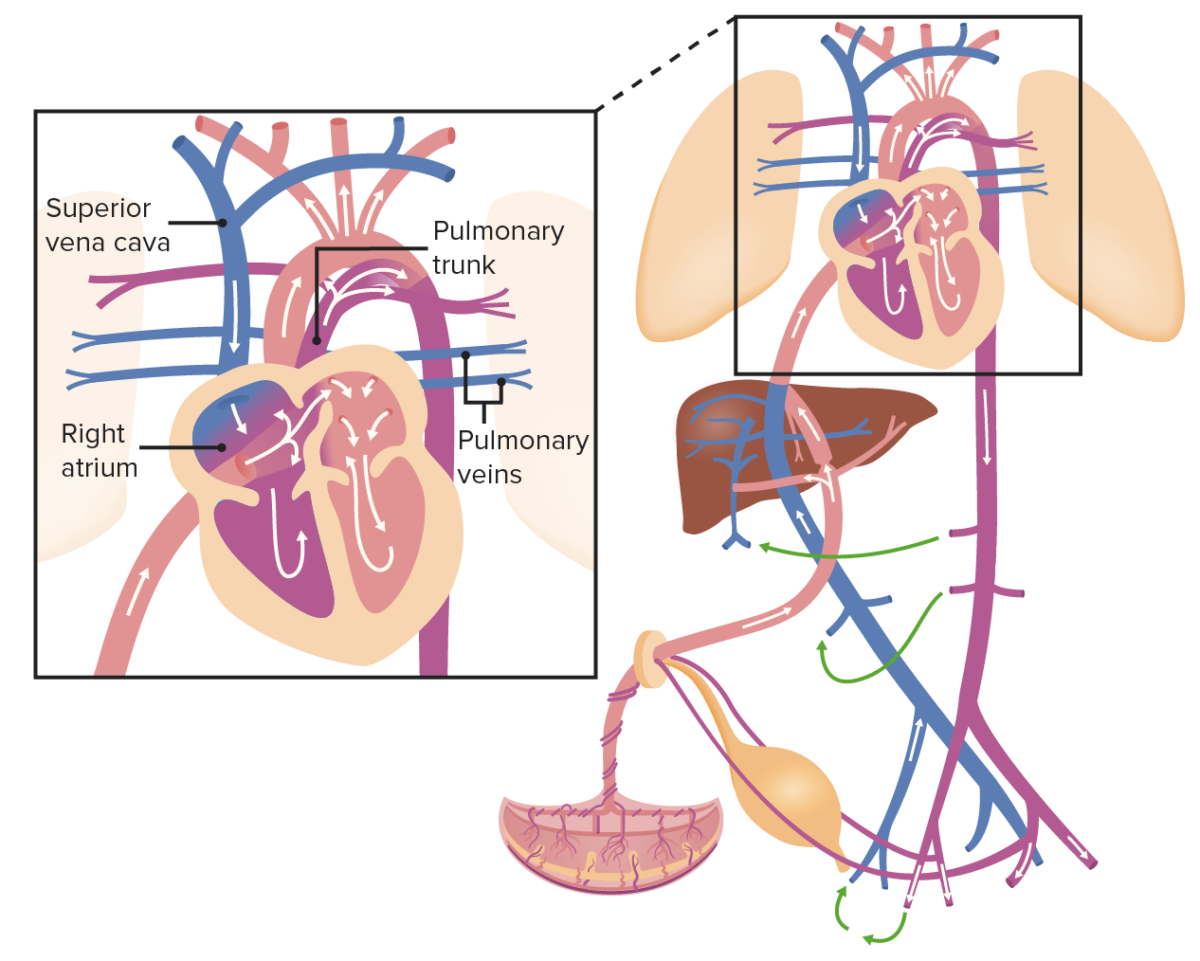
Blood from the IVC pushes the valve of foramen ovale and flows into the left side of the heart, where it mixes in the LA with deoxygenated blood from the pulmonary veins. Blood then leaves the heart through the aorta and flows to the iliac arteries, which are connected to the placenta by the umbilical arteries. However, blood from the SVC flows directly into the RV and then to the pulmonary trunk, which is connected to the descending aorta through the ductus arteriosus.
Image by Lecturio.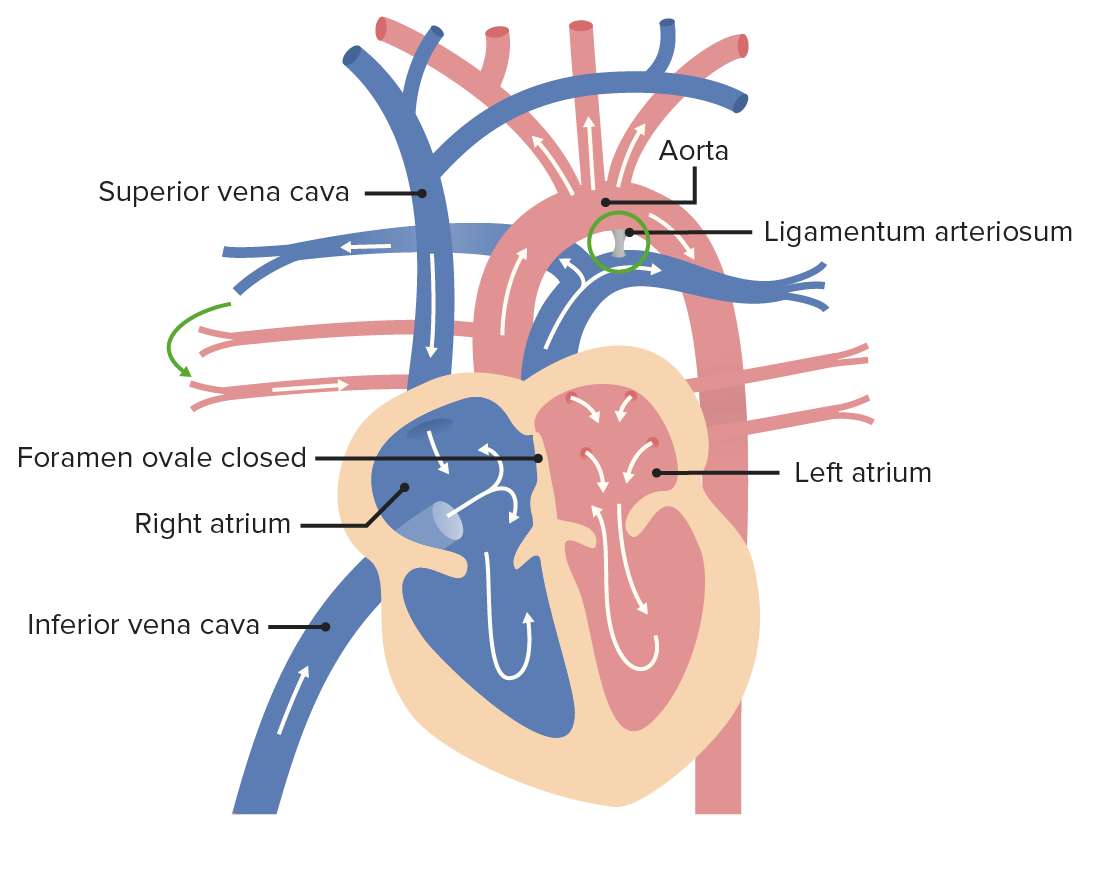
After birth, the ductus arteriosus becomes the ligamentum arteriosum, as blood is able to enter the lungs to be oxygenated. The foramen ovale closes and becomes the fossa ovalis due to increased pressure in the LA.
Image by Lecturio.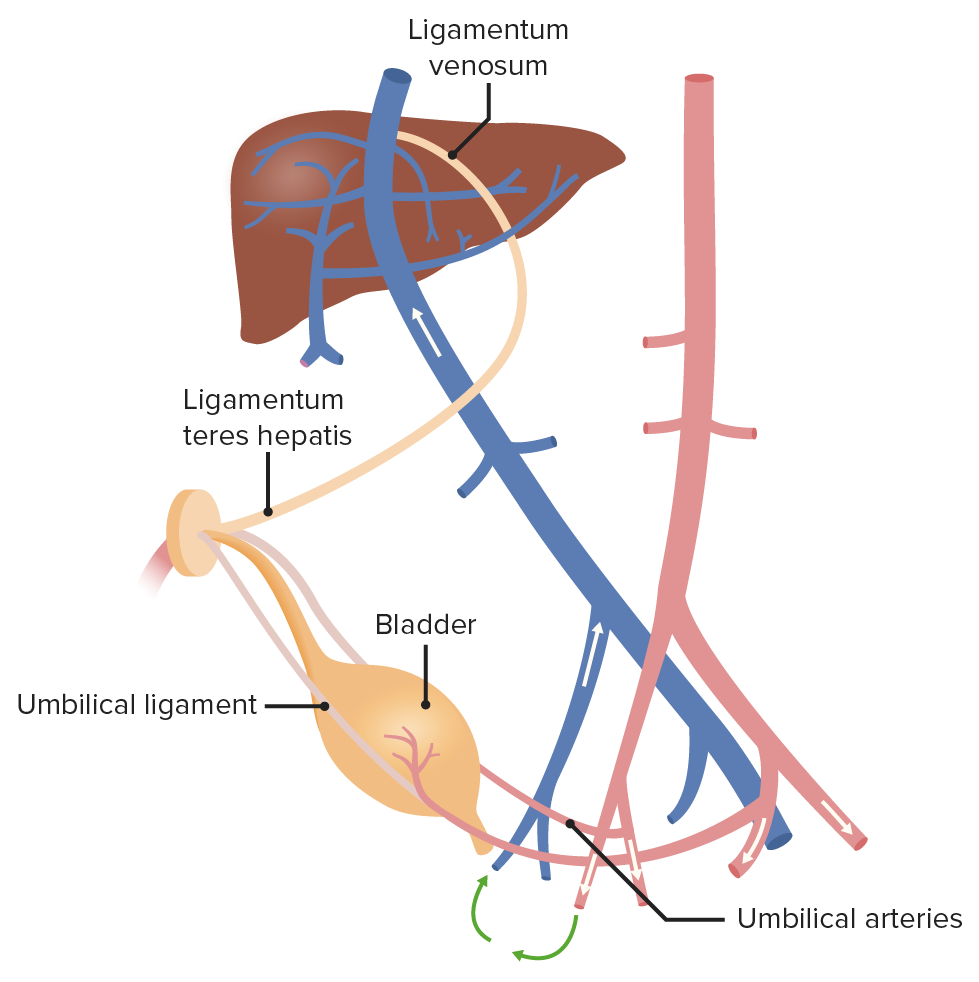
After birth, the umbilical artery becomes the ligamentum teres hepatis, whereas the umbilical vein becomes the medial umbilical ligament.
Image by Lecturio.Mnemonic: right-to-left shunts (cyanotic lesions) (the 5 Ts):