A patent foramen ovale (PFO) is an abnormal communication Communication The exchange or transmission of ideas, attitudes, or beliefs between individuals or groups. Decision-making Capacity and Legal Competence between the atria that persists after birth. The condition results from incomplete closure of the foramen ovale. Small, isolated, and asymptomatic PFOs are a common incidental finding on echocardiography Echocardiography Ultrasonic recording of the size, motion, and composition of the heart and surrounding tissues. The standard approach is transthoracic. Tricuspid Valve Atresia (TVA) and require no treatment. Larger PFOs and PFOs associated with paradoxical thromboembolic stroke or other cardiac anomalies may require treatment with anticoagulation Anticoagulation Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs. Surgical or percutaneous closure may be indicated in select cases.
Last updated: Dec 28, 2024
Patent foramen ovale (PFO) is a persistent, post-natal communication Communication The exchange or transmission of ideas, attitudes, or beliefs between individuals or groups. Decision-making Capacity and Legal Competence between the atria due to the failure of the closure of the foramen ovale during the transition from in-utero to ex-utero neonatal circulation Circulation The movement of the blood as it is pumped through the cardiovascular system. ABCDE Assessment.
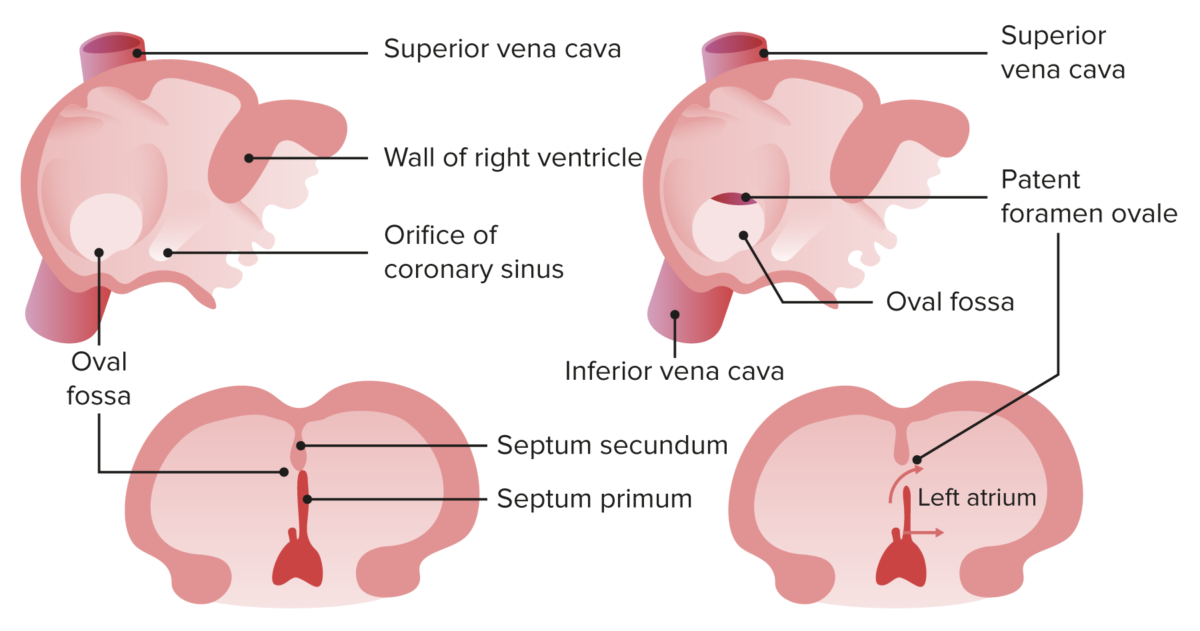
Normal closure of the foramen ovale, and a patent foramen ovale
Image by Lecturio.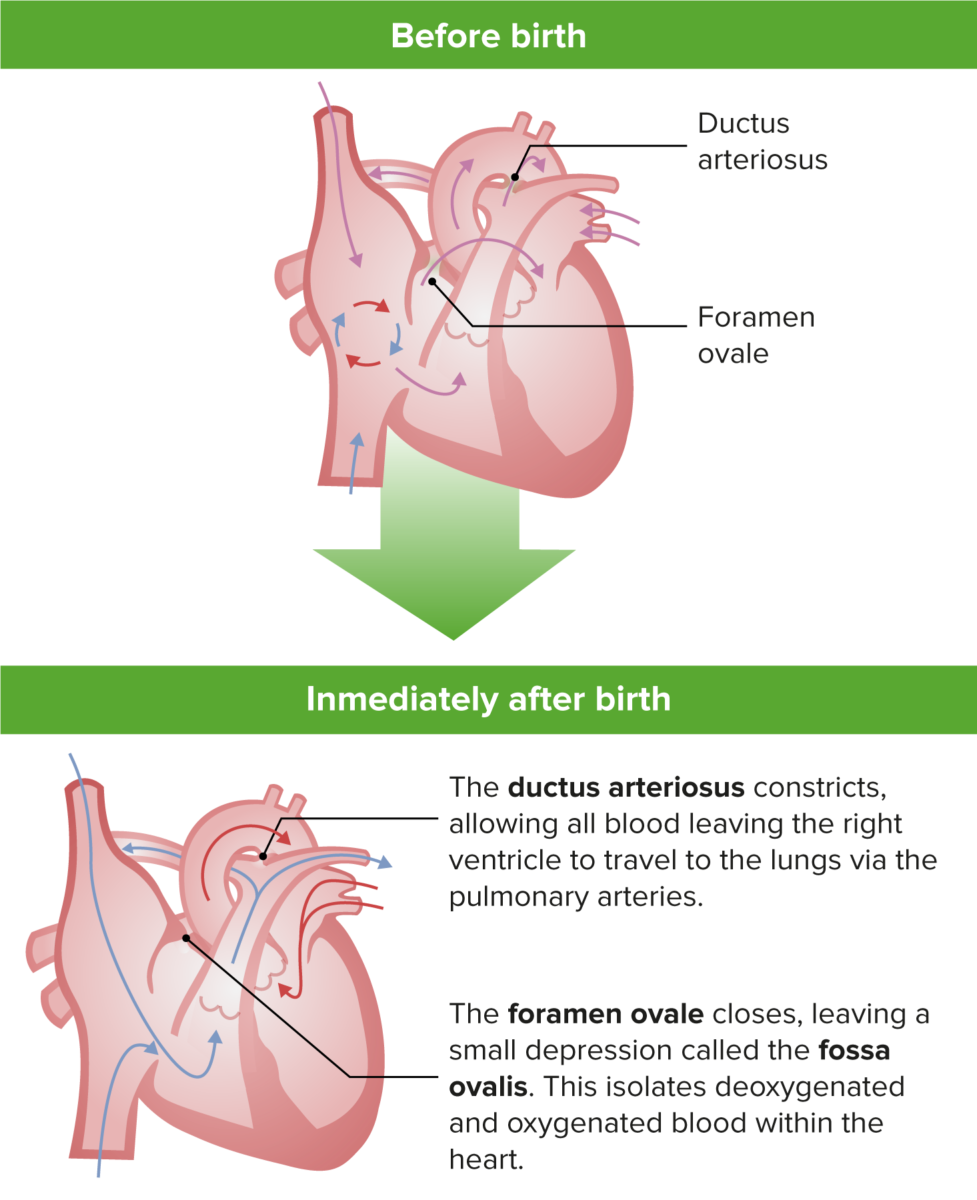
Normal transition from in-utero cardiac circulation to ex-utero cardiac circulation
Image by Lecturio.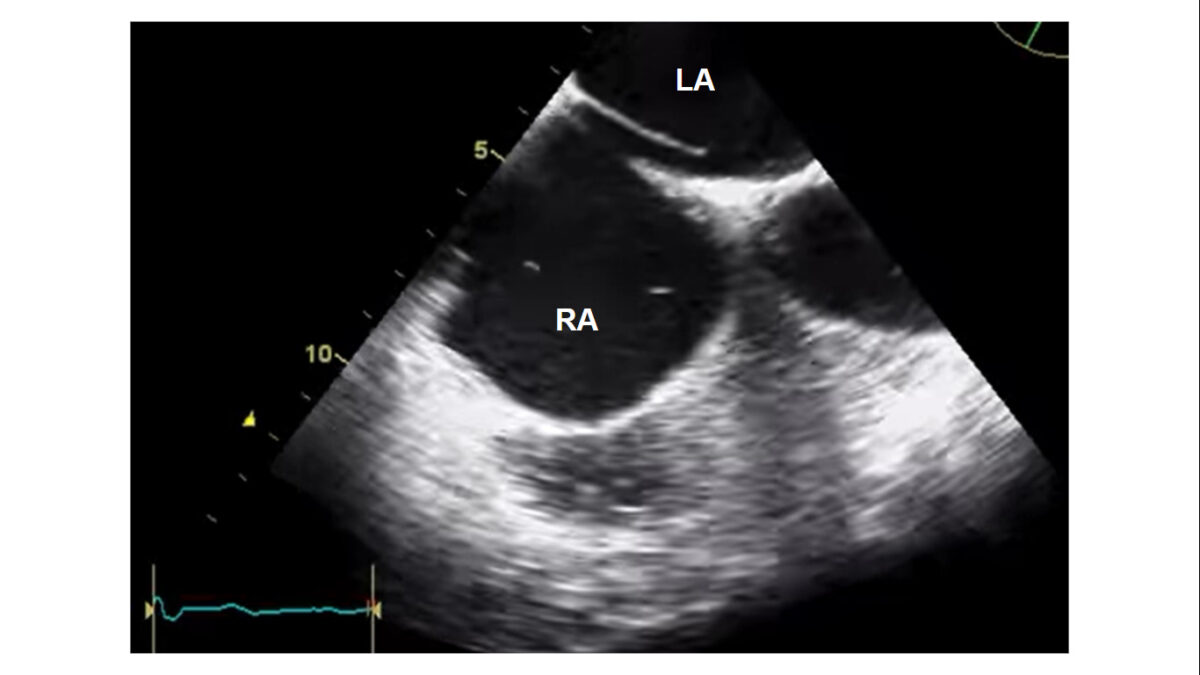
Transesophageal echocardiogram showing a patent foramen ovale in a patient who presented with cryptogenic ischemic stroke. The patent foramen is observed in the septum between the right atrium (RA) and left atrium (LA).
Image: “TEE showing a PFO in 62°” by Knebel, F. at al. License: CC BY 2.0, screenshot edited by Lecturio.