Valvular disorders can arise from the pulmonary valve Pulmonary valve A valve situated at the entrance to the pulmonary trunk from the right ventricle. Heart: Anatomy, located between the right ventricle (RV) and the pulmonary artery Pulmonary artery The short wide vessel arising from the conus arteriosus of the right ventricle and conveying unaerated blood to the lungs. Lungs: Anatomy (PA). Valvular disorders are diagnosed by echocardiography Echocardiography Ultrasonic recording of the size, motion, and composition of the heart and surrounding tissues. The standard approach is transthoracic. Tricuspid Valve Atresia (TVA). Pulmonic regurgitation Regurgitation Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) (PR) is the backflow of blood through the valve. Prior cardiac surgeries can lead to PR. Graham-Steell murmur, a high-pitched decrescendo murmur at the left sternal border, is a hallmark finding. Pulmonic regurgitation Regurgitation Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) results in RV volume overload, from which RV failure eventually develops. Severe PR is also treated with surgical valve replacement.
Last updated: Feb 28, 2025
Pulmonary or pulmonic valve:
| Pulmonary stenosis Stenosis Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS) | Pulmonary regurgitation Regurgitation Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) | |
|---|---|---|
| Etiology | Mostly congenital | Mostly acquired |
| Murmur | Systolic murmur, left upper sternal border (preceded by a systolic click that decreases with inspiration Inspiration Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing) | Diastolic murmur, left upper sternal border, increases with inspiration Inspiration Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing |
| S2 S2 Heart Sounds | Split S2 S2 Heart Sounds with soft and delayed P2 | Split S2 S2 Heart Sounds with a loud P2 |
| Echocardiographic findings | Thick and domed leaflets, with increased systolic velocity across the valve, right ventricular hypertrophy Right Ventricular Hypertrophy Tetralogy of Fallot (RVH) | Valvular abnormalities (depending on etiology), RV enlargement, and regurgitant jet in the right ventricular outflow tract |
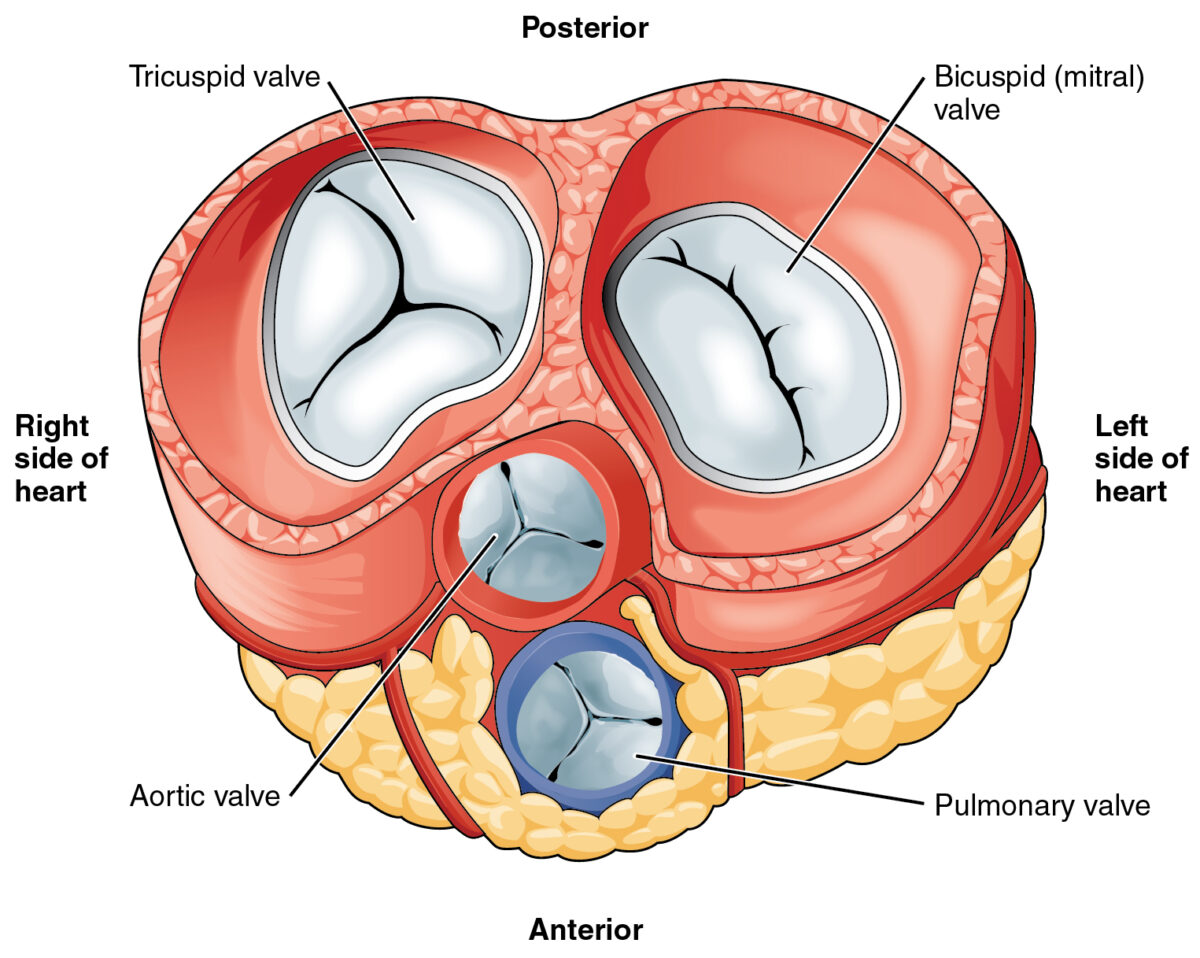
Heart valves:
The pulmonary valve is the lower middle valve.
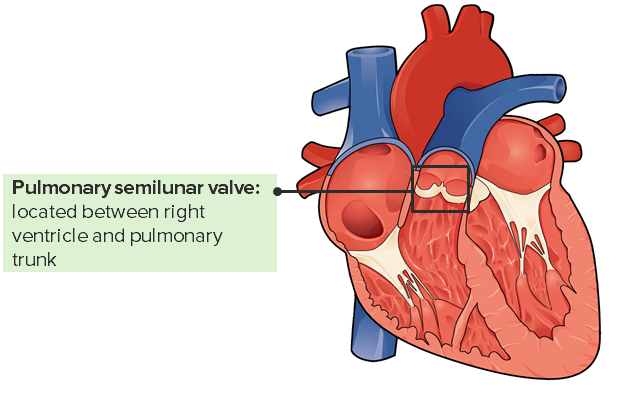
The pulmonary valve and its location in the heart
Image: “Internal Anatomy of the Heart” by Philschatz. License: CC BY 4.0, edited by Lecturio.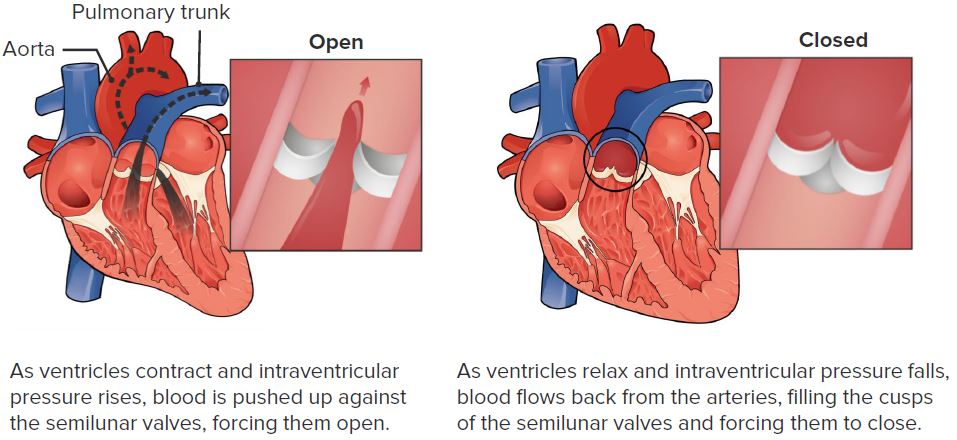
The function of the pulmonary valve
Image: “Pulmonary Valve” by Philschatz. License: CC BY 4.0, edited by Lecturio.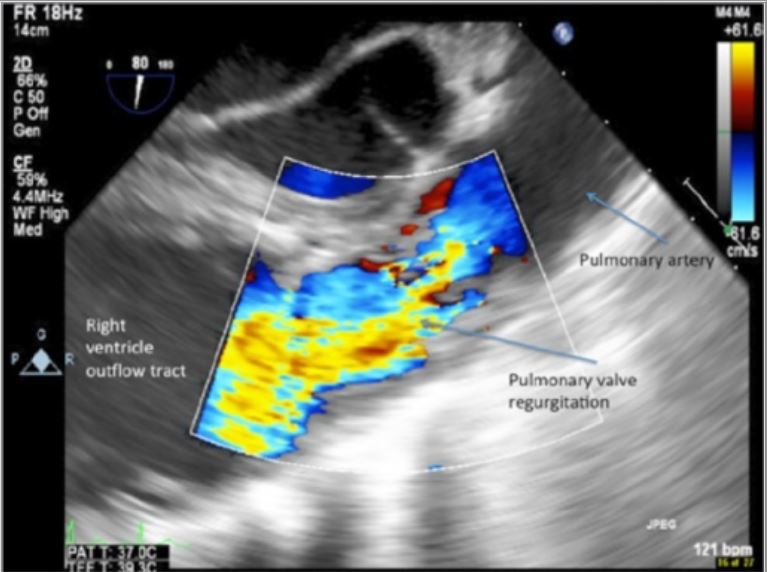
Transesophageal echocardiogram pulmonary outflow view showing severe pulmonary insufficiency
Image: “Isolated Pulmonary Valve Endocarditis” by Swaminath D, Yaqub Y, Narayanan R, Paone RF, Nugent K, Arvandi A. License: CC BY 3.0.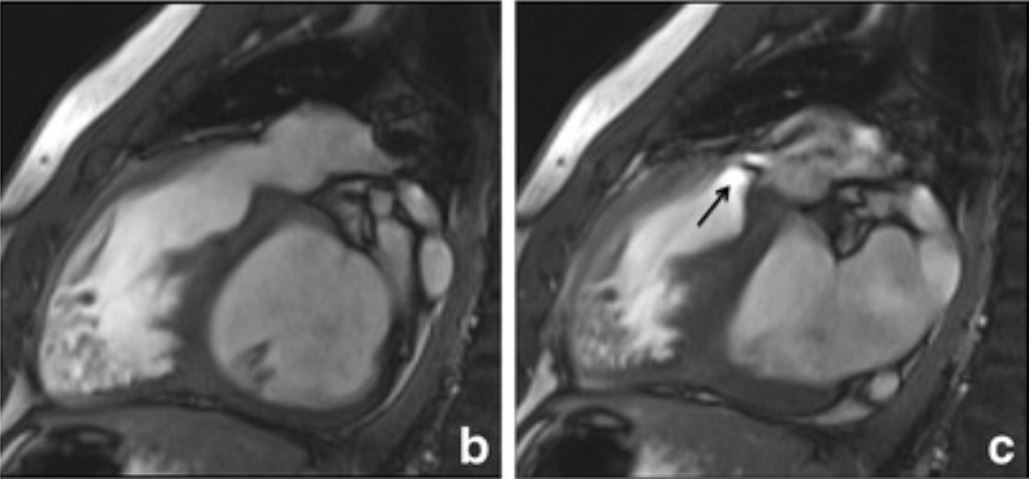
Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (using steady-state free precession imaging). A: A patient with pulmonary hypertension, with images showing. B: A dilated PA with valvular regurgitation (white arrow). C: Severe eccentric RV enlargement at a 4-chamber view.
Image: “Right ventricular cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging” by Galea N, Carbone I, Cannata D, Cannavale G, Conti B, Galea R, Frustaci A, Catalano C, Francone M. License: Public domain.