Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase Pentose Phosphate Pathway ( G6PD G6PD Pentose Phosphate Pathway) deficiency is a type of intravascular hemolytic anemia Hemolytic Anemia Hemolytic anemia (HA) is the term given to a large group of anemias that are caused by the premature destruction/hemolysis of circulating red blood cells (RBCs). Hemolysis can occur within (intravascular hemolysis) or outside the blood vessels (extravascular hemolysis). Hemolytic Anemia. The condition is inherited in an X-linked recessive X-Linked Recessive Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy manner. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship have episodic hemolysis due to an oxidative stressor that causes damage to red blood cells Red blood cells Erythrocytes, or red blood cells (RBCs), are the most abundant cells in the blood. While erythrocytes in the fetus are initially produced in the yolk sac then the liver, the bone marrow eventually becomes the main site of production. Erythrocytes: Histology, which lack sufficient NADPH NADPH Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate. A coenzyme composed of ribosylnicotinamide 5'-phosphate (nmn) coupled by pyrophosphate linkage to the 5'-phosphate adenosine 2. Pentose Phosphate Pathway to protect them from oxidative injury.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
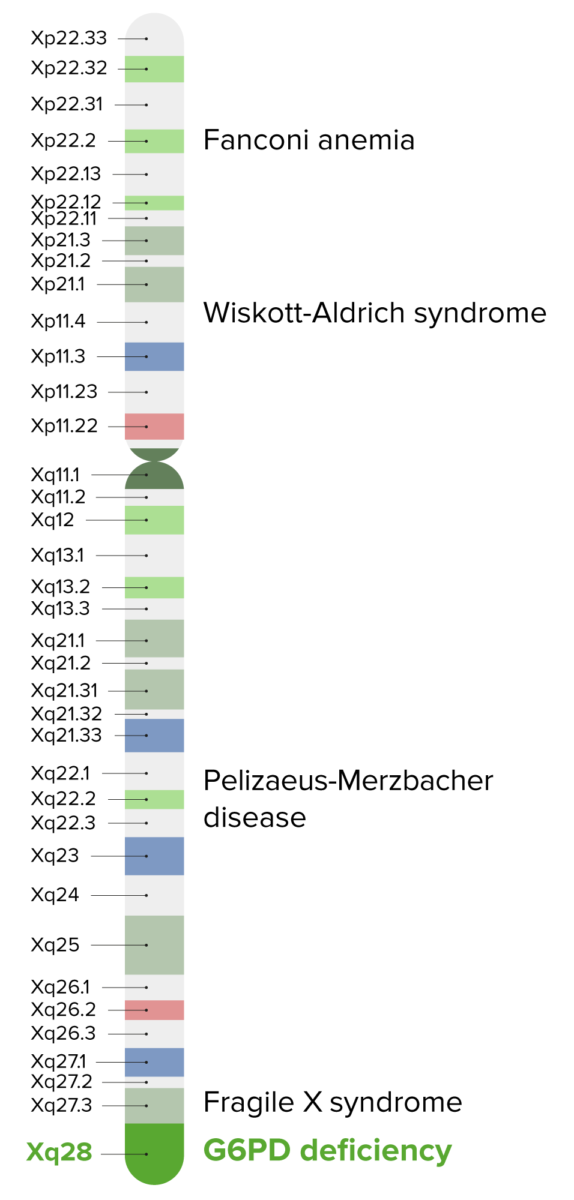
G6PD deficiency is an X-linked disorder found on band Xq28.
Image by Lecturio.| Drugs | Foods | Other |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
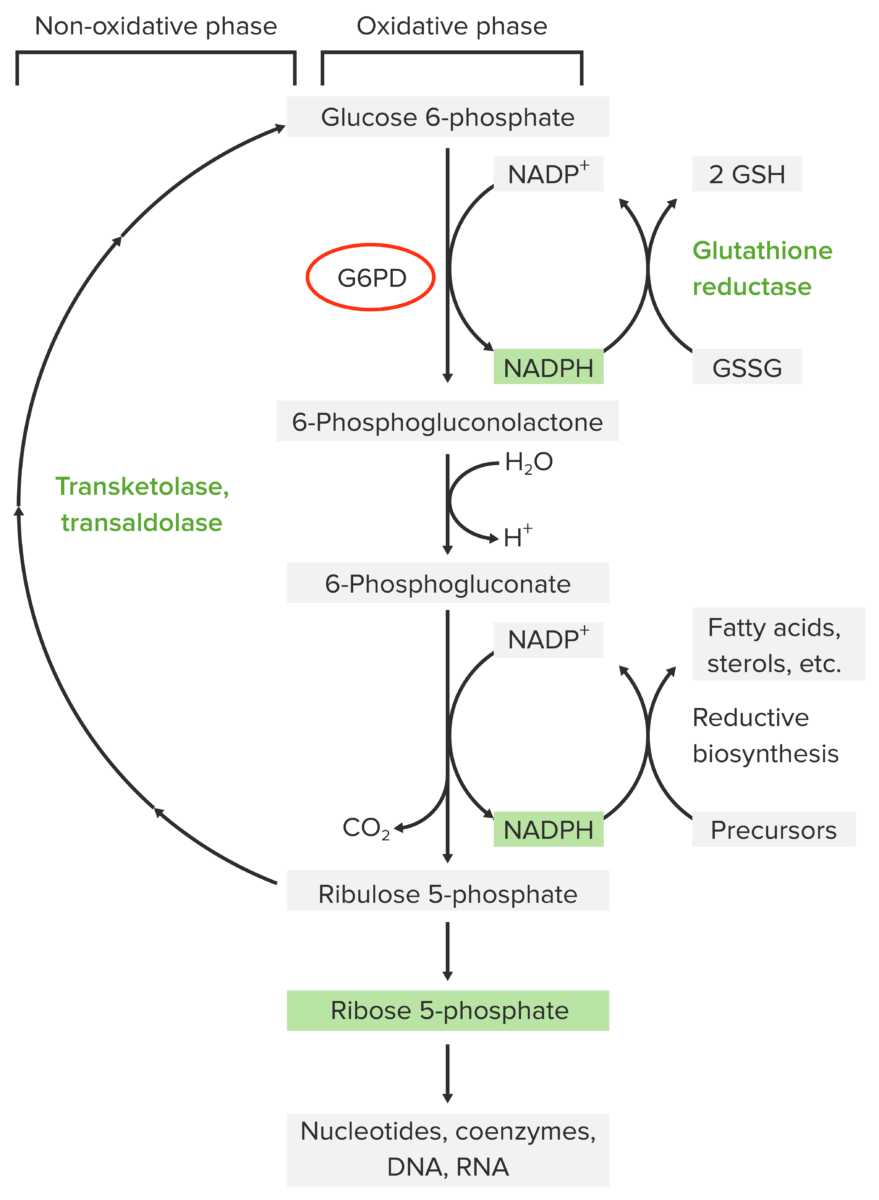
Pathophysiology of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency:
The pentose phosphate pathway contains 2 phases: oxidative and non-oxidative. The oxidative pathway yields NADPH, which is necessary for glutathione reduction in red blood cells (which is needed for neutralizing oxidative metabolites). The 1st step of the oxidative pathway is catalyzed by glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD). Without this enzyme, NADPH is not produced. Thus, red blood cells are not protected from oxidative stressors, resulting in damage and hemolysis.
GSH: reduced glutathione
GSSG: oxidized glutathione

Urinary sample with hematuria
Image: “hematuria” by omicsonline.org. License: CC BY 4.0Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase Pentose Phosphate Pathway deficiency is suspected in cases of episodic hemolytic symptoms. Diagnostic testing should include the following:

G6PD fluorescent spot test under ultraviolet light (365 nm) (Beutler test)
Image: “Figure 1” by Leslie, T., Moiz, B., Mohammad, N., Amanzai, O., Rasheed, H.U., Jan, S., Siddiqi, A.M., Nasir, A., Beg, M.A., & Vink, M. (2013). Prevalence and molecular basis of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency in Afghan populations: implications for treatment policy in the region. Malaria Journal, 12, 230 – 230.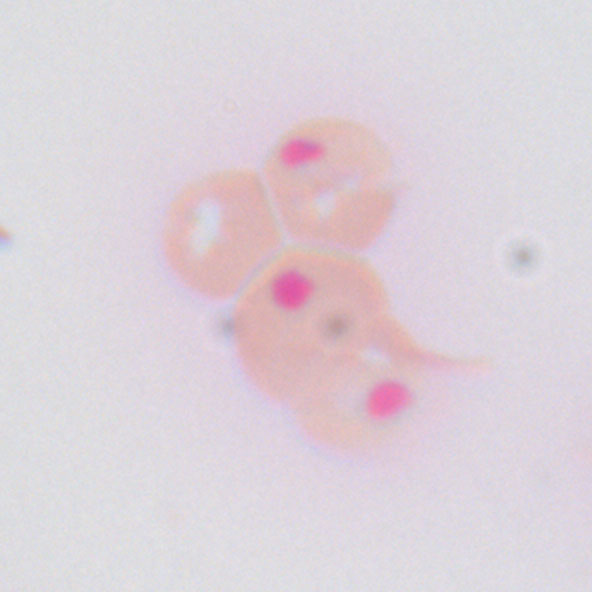
Heinz bodies (inclusions within the RBC) as seen on peripheral smear (seen with supravital stain).
Heinz bodies are precipitates of denatured hemoglobin and are not seen on routine stains, only with supravital stains (rarely performed today).