Blepharitis is an ocular condition characterized by eyelid inflammation. Anterior blepharitis involves the eyelid skin and eyelashes, while the posterior type affects the meibomian glands. Often, these conditions overlap. The typical presentation of blepharitis includes eyelid edema with itching and redness, crusts and scales around the eyelashes, and gritty sensation. Diagnosis is clinical, with a slit-lamp examination providing details of the structural changes affecting the eye. The mainstay of treatment is eyelid hygiene using warm compresses and eyelid scrubs. In moderate-to-severe cases, topical and oral antibiotics are utilized. Topical glucocorticoids also help improve symptoms but require an ophthalmology evaluation due to potentially adverse effects.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
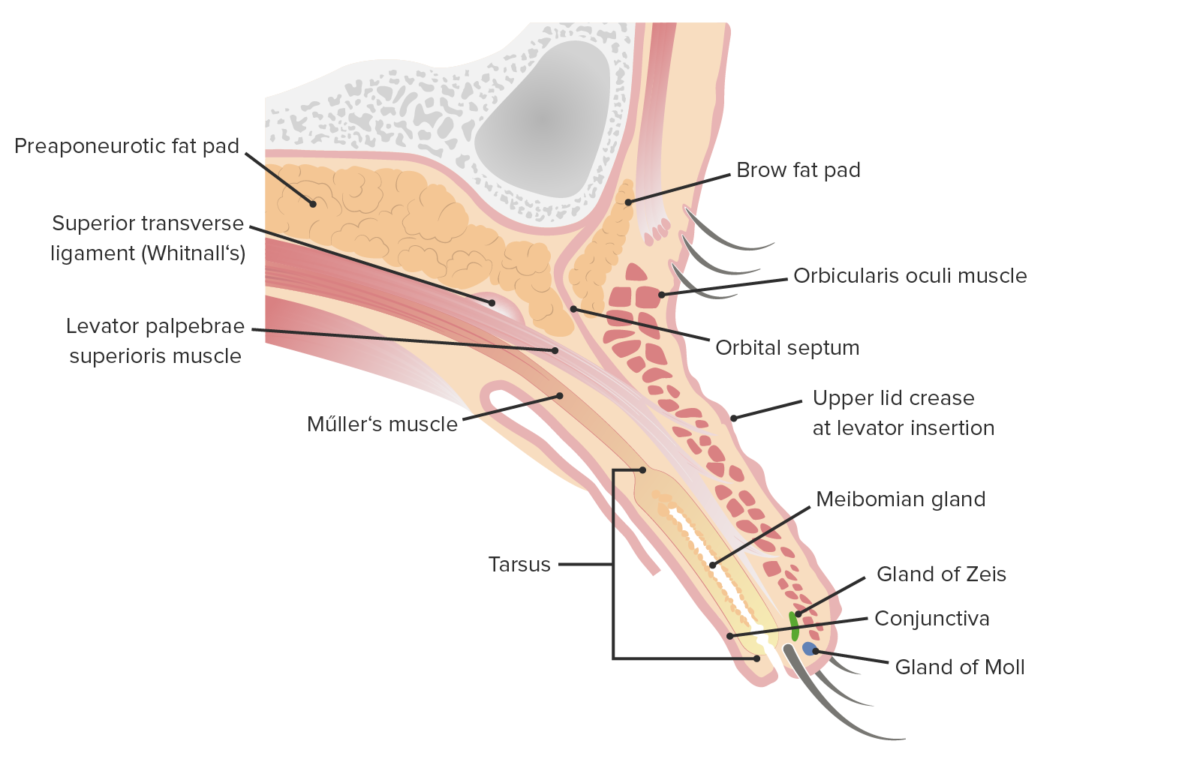
Sagittal cut of the upper lid featuring its internal structures
Image by Lecturio.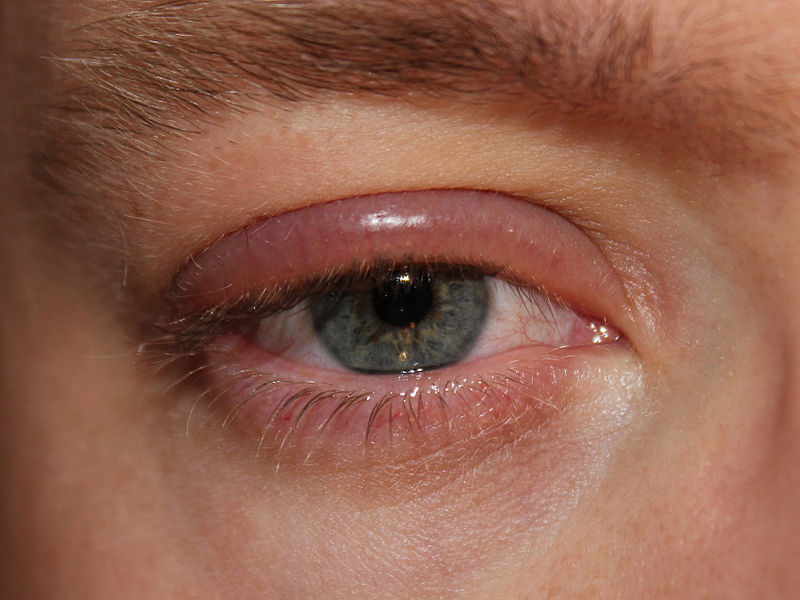
Erythematous, swollen eyelids from blepharitis
Image: “Blepharitis” by clubtable. License: Public Domain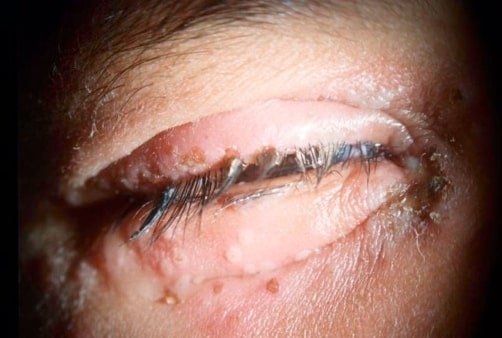
Herpetic blepharitis: swelling and erythema of the eyelids. Erosions and ulcerations of the lid margins can be seen.
Image: “Herpetic blepharitis” by 3501 Champion Lake Boulevard, #1609, Shreveport, LA 71105 USA. License: CC BY 3.0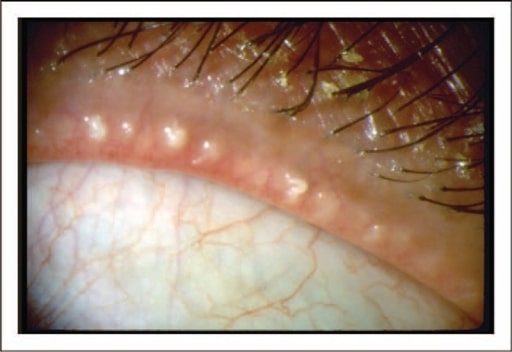
Image of a patient with posterior blepharitis/meibomian gland dysfunction: There is obstruction of the orifices of the meibomian glands with thick crusts around the eyelash follicles.
Image: “Dysfunctional tear syndrome” by American Academy of Ophthalmology. License: CC BY 4.0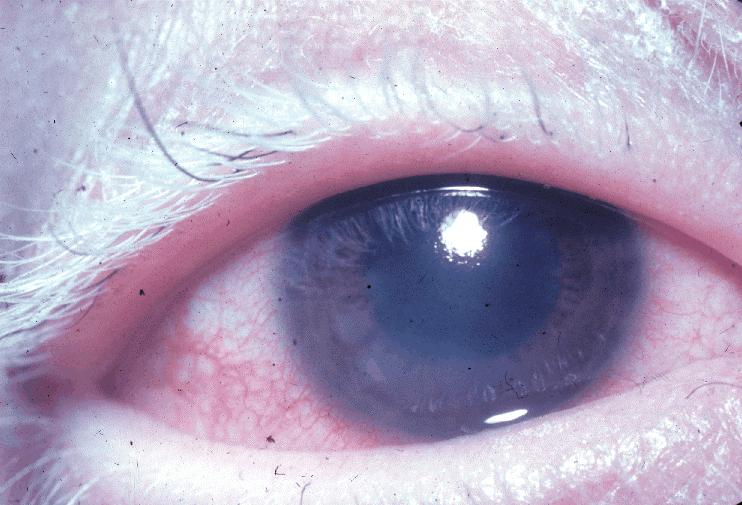
Whitening of eyelashes (poliosis)
Image: “Poliosis VKHS” by National Eye Institute. License: Public DomainManagement may vary based on locale. The following information is based on US and UK guidelines for adult patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship.
Nonpharmacologic[6-8]
Pharmacologic[6-8]
| Medication | Typical dose (adult) |
|---|---|
| Doxycycline | 100 mg twice daily |
| Minocycline Minocycline A tetracycline analog, having a 7-dimethylamino and lacking the 5 methyl and hydroxyl groups, which is effective against tetracycline-resistant staphylococcus infections. Tetracyclines | 100 mg twice daily |
| Tetracycline Tetracycline A naphthacene antibiotic that inhibits amino Acyl tRNA binding during protein synthesis. Drug-Induced Liver Injury | 500 mg twice daily |
| Azithromycin Azithromycin A semi-synthetic macrolide antibiotic structurally related to erythromycin. It has been used in the treatment of Mycobacterium avium intracellulare infections, toxoplasmosis, and cryptosporidiosis. Macrolides and Ketolides | 500 mg daily for 3 days in 3 cycles with 7-day intervals |
Office-based procedures[6,7]
Diagnosis Codes:
This code is used to diagnose
blepharitis
Blepharitis
Blepharitis is an ocular condition characterized by eyelid inflammation. Anterior blepharitis involves the eyelid skin and eyelashes, while the posterior type affects the meibomian glands. Often, these conditions overlap.
Blepharitis, a common condition involving
inflammation
Inflammation
Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body’s defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function.
Inflammation of the eyelid margins. It can be anterior (at the base of the eyelashes) or posterior (involving the meibomian glands).
| Coding System | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ICD-10-CM | H01.00- | Unspecified blepharitis Blepharitis Blepharitis is an ocular condition characterized by eyelid inflammation. Anterior blepharitis involves the eyelid skin and eyelashes, while the posterior type affects the meibomian glands. Often, these conditions overlap. Blepharitis |
| ICD-10-CM | H01.01- | Ulcerative blepharitis Blepharitis Blepharitis is an ocular condition characterized by eyelid inflammation. Anterior blepharitis involves the eyelid skin and eyelashes, while the posterior type affects the meibomian glands. Often, these conditions overlap. Blepharitis |
| SNOMED CT | 41445000 | Blepharitis Blepharitis Blepharitis is an ocular condition characterized by eyelid inflammation. Anterior blepharitis involves the eyelid skin and eyelashes, while the posterior type affects the meibomian glands. Often, these conditions overlap. Blepharitis (disorder) |
Medications:
The mainstay of treatment is eyelid hygiene. This code is for a topical antibiotic ointment like
erythromycin
Erythromycin
A bacteriostatic antibiotic macrolide produced by streptomyces erythreus. Erythromycin a is considered its major active component. In sensitive organisms, it inhibits protein synthesis by binding to 50s ribosomal subunits. This binding process inhibits peptidyl transferase activity and interferes with translocation of amino acids during translation and assembly of proteins.
Macrolides and Ketolides or bacitracin, which can be used to manage the bacterial component of
anterior blepharitis
Anterior Blepharitis
Blepharitis.
| Coding System | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| RxNorm | 4053 | Erythromycin Erythromycin A bacteriostatic antibiotic macrolide produced by streptomyces erythreus. Erythromycin a is considered its major active component. In sensitive organisms, it inhibits protein synthesis by binding to 50s ribosomal subunits. This binding process inhibits peptidyl transferase activity and interferes with translocation of amino acids during translation and assembly of proteins. Macrolides and Ketolides (ingredient) |
| RxNorm | 1256 | Bacitracin (ingredient) |