Genu valgum is a deformation of the knee joint Knee joint The knee joint is made up of the articulations between the femur, tibia, and patella bones, and is one of the largest and most complex joints of the human body. The knee is classified as a synovial hinge joint, which primarily allows for flexion and extension with a more limited degree of translation and rotation. Knee Joint: Anatomy(s) that creates angulation Angulation Buckle or Torus Fracture of the lower limb(s) toward the midline in the coronal Coronal Computed Tomography (CT) plane. Children ages 2–6 years are commonly affected. Many cases of genu valgum are physiologic and will resolve with further growth. However, it is critical to differentiate between normal physiologic changes and pathologic disorders, as pathologic cases can have serious long-term consequences if not corrected. Clinical presentation includes characteristic inward bowing of the lower limbs accompanied by gait Gait Manner or style of walking. Neurological Examination disturbances. Diagnosis is clinical but may require support with diagnostic imaging. Management is often supportive but may require surgical intervention.
Last updated: Mar 28, 2025
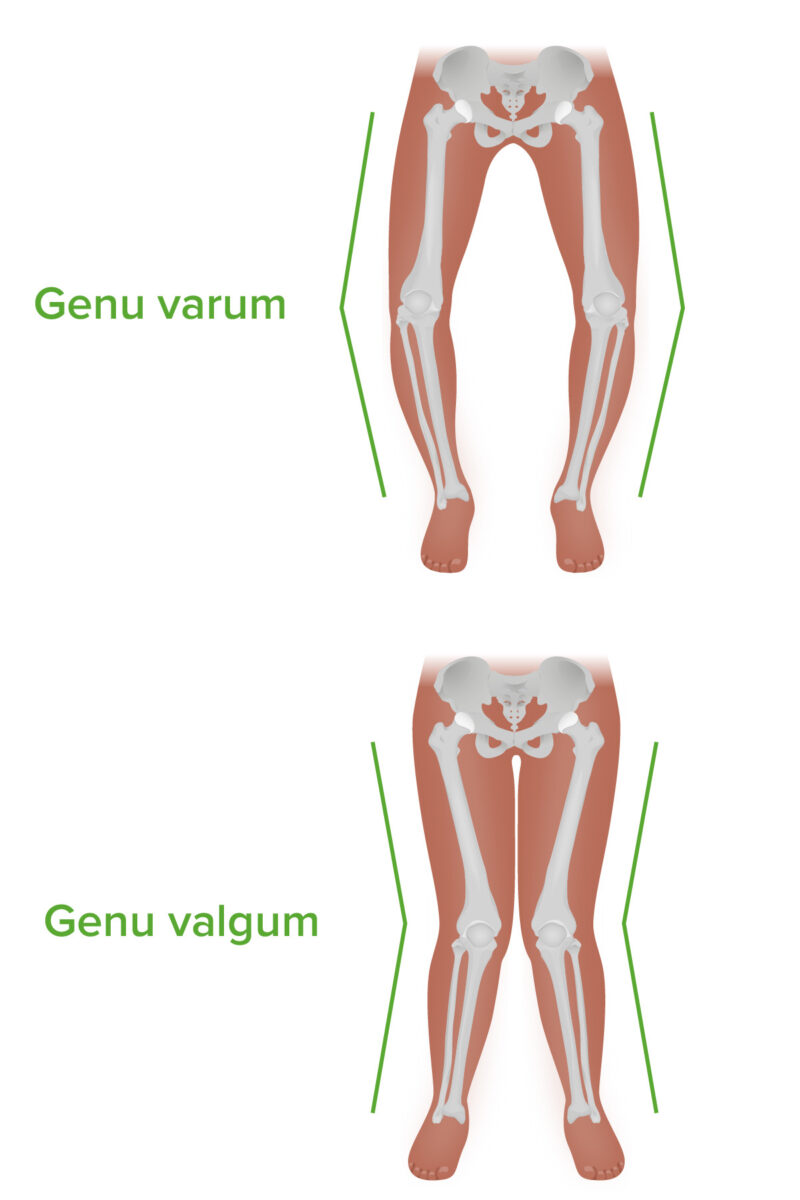
Genu varum and genu valgum: note the difference in angulation in the coronal plane.
Image by Lecturio. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0Bilateral genu valgum:
Unilateral genu valgum:

Pathologic genu valgum:
This child with rickets has developed genu valgum, most notably in the right knee.
Diagnosis is primary based on clinical examination. It is critical to differentiate between normal physiologic genu valgum and a pathologic process.
X-ray X-ray Penetrating electromagnetic radiation emitted when the inner orbital electrons of an atom are excited and release radiant energy. X-ray wavelengths range from 1 pm to 10 nm. Hard x-rays are the higher energy, shorter wavelength x-rays. Soft x-rays or grenz rays are less energetic and longer in wavelength. The short wavelength end of the x-ray spectrum overlaps the gamma rays wavelength range. The distinction between gamma rays and x-rays is based on their radiation source. Pulmonary Function Tests:
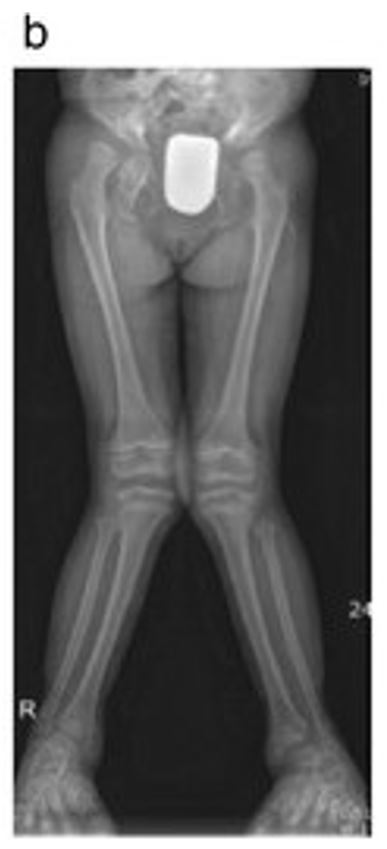
X-ray of a child with genu valgum
Image: “Mutation study for a six-year-old girl with genu valgum” by Kaustuv Bhattacharya, et al. License: CC BY 4.0, cropped by Lecturio.The majority of cases of genu valgum are physiologic and should resolve spontaneously; thus, they require only observation and expectant management.
Observation:
1st-line treatment, appropriate if:
Medical management:
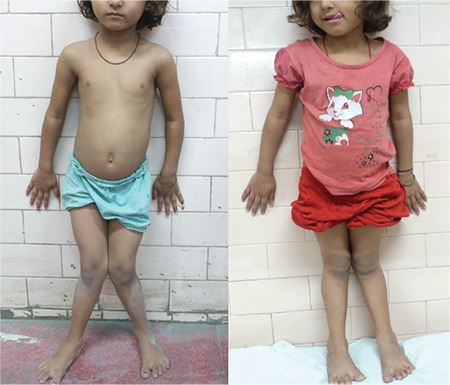
Reduction in genu valgum:
Improved valgus deformity in a 9-year-old child with rickets at 1-year follow-up after vitamin D therapy.