Endometrial polyps are pedunculated or sessile projections of the endometrium that result from overgrowth of endometrial glands and stroma around a central vascular stalk. Endometrial polyps are a few millimeters to a few centimeters in size, can occur anywhere within the uterine cavity, and, while usually benign, can be malignant, particularly in postmenopausal women. Endometrial polyps present with abnormal uterine or postmenopausal bleeding, although many are asymptomatic and discovered incidentally. Endometrial polyps are optimally diagnosed and treated with hysteroscopy.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Endometrial polyps result from the usually benign Benign Fibroadenoma overgrowth of endometrial glands and stroma around a central vascular stalk forming a pedunculated or sessile projection from the endometrium Endometrium The mucous membrane lining of the uterine cavity that is hormonally responsive during the menstrual cycle and pregnancy. The endometrium undergoes cyclic changes that characterize menstruation. After successful fertilization, it serves to sustain the developing embryo. Embryoblast and Trophoblast Development that can develop anywhere in the uterine cavity.
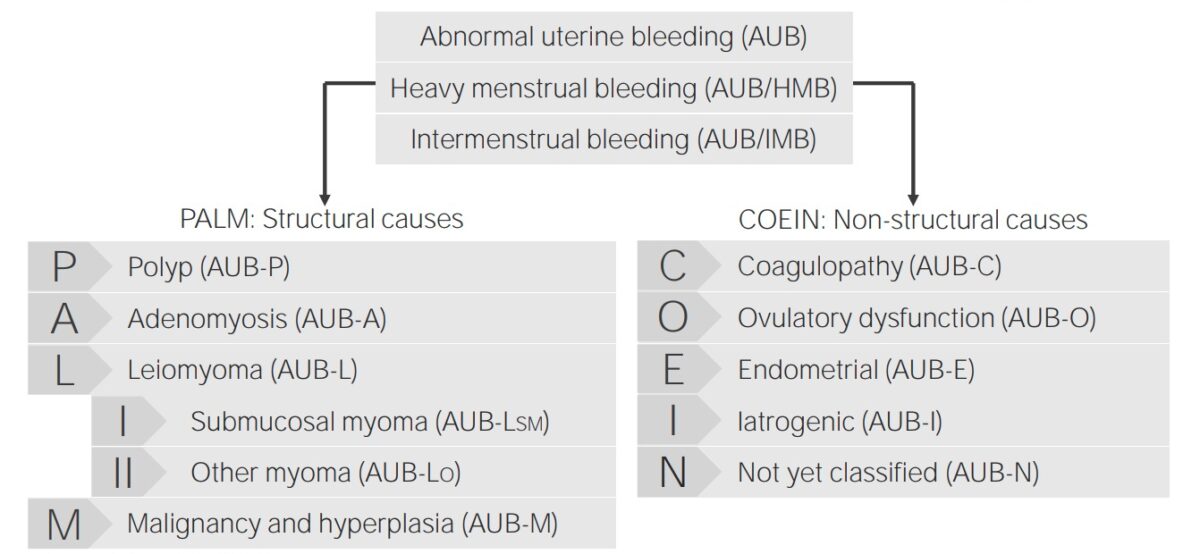
Classification of abnormal uterine bleeding and its causes
Image by Lecturio.The exact mechanisms for pathogenesis are unknown, but estrogen Estrogen Compounds that interact with estrogen receptors in target tissues to bring about the effects similar to those of estradiol. Estrogens stimulate the female reproductive organs, and the development of secondary female sex characteristics. Estrogenic chemicals include natural, synthetic, steroidal, or non-steroidal compounds. Ovaries: Anatomy seems to play an important stimulating role.
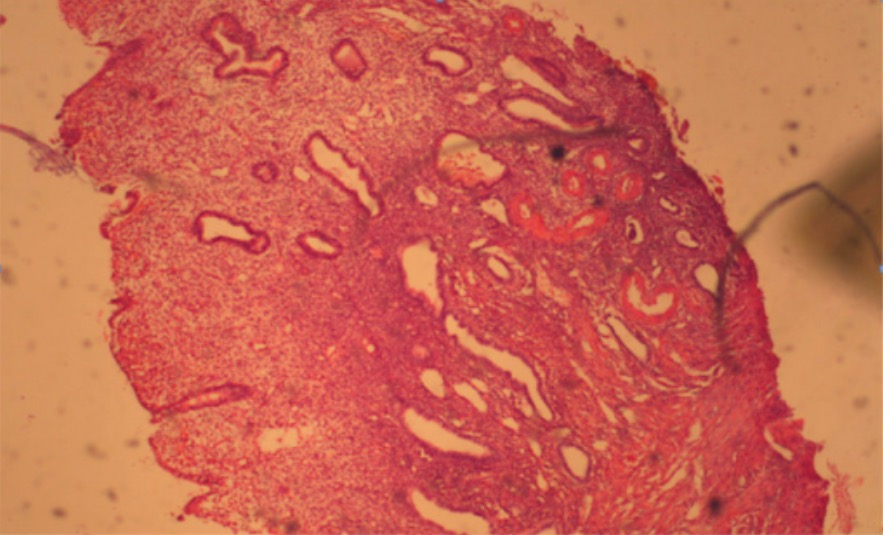
Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stain of a glandular cystic endometrial polyp
Image: “Glandular cystic endometrial polyp” by Clinical Hospital ‘Pheophania’ of State Affairs Department, Zabolotny str,, 21, Kyiv 03680, Ukraine. License: CC BY 2.0Most common presentation of symptomatic polyps involves bleeding:
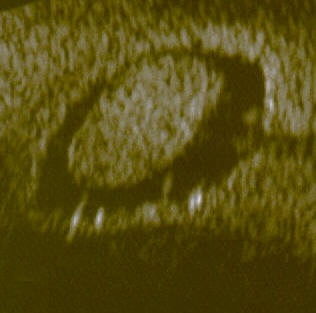
Uterine polyp by sonography
Image: “Uterine polyp by sonography” by Ekem. License: Public Domain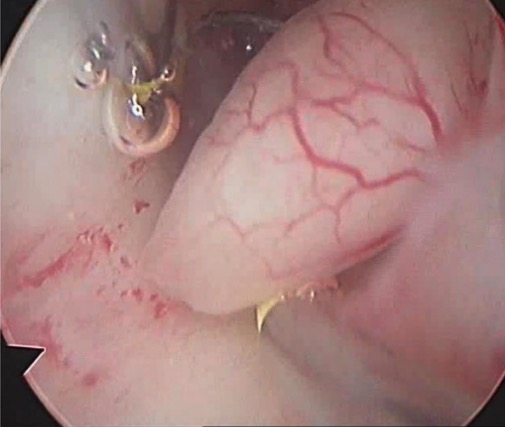
Hysteroscopy showing fibrous endometrial polyp
Image: “Hysteroscopy of intrauterine lesions” by Clinical Hospital ‘Pheophania’ of State Affairs Department, Zabolotny str,, 21, Kyiv 03680, Ukraine. License: CC BY 2.0, edited by Lecturio.Tissue sampling is required to rule out malignancy Malignancy Hemothorax within polyps.