Drowning occurs due to respiratory impairment from submersion or immersion in a liquid medium. Aspiration of water leads to hypoxemia Hypoxemia Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome, which affects all organ systems, resulting in respiratory insufficiency and acute respiratory distress syndrome Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Acute respiratory distress syndrome is characterized by the sudden onset of hypoxemia and bilateral pulmonary edema without cardiac failure. Sepsis is the most common cause of ARDS. The underlying mechanism and histologic correlate is diffuse alveolar damage (DAD). Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) (ARDS), cardiac arrhythmias, and neuronal damage. The management of drowning focuses initially on ventilatory support followed by cardiopulmonary resuscitation Resuscitation The restoration to life or consciousness of one apparently dead. . Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome. As drowning is most often preventable, prevention is the focus of most interventions.
Last updated: Apr 13, 2025
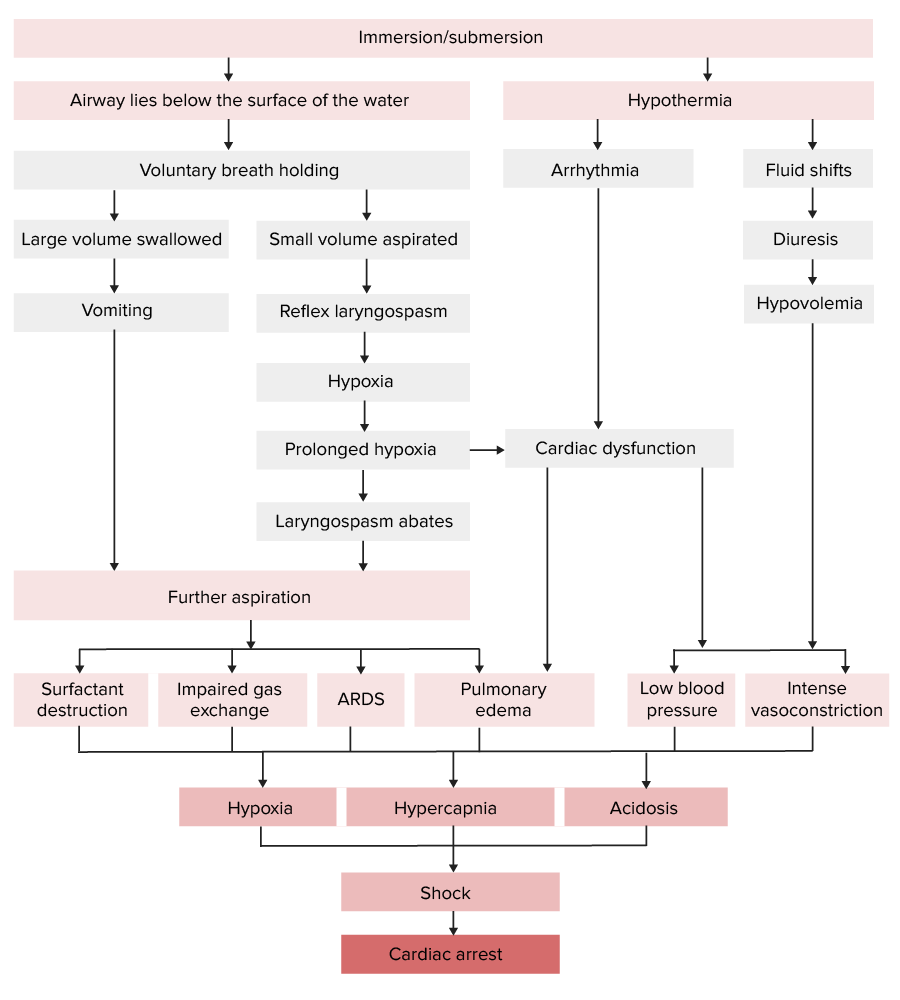
Pathophysiology of drowning:
Note that the respiratory and cardiovascular systems are both affected, leading to respiratory failure and shock.
ARDS: acute respiratory distress syndrome
Clinical manifestations of drowning are due to the effects of hypoxemia Hypoxemia Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome.
Vital signs:
Respiratory changes:
Cardiovascular changes:
Neurologic changes:
Neuronal damage from hypoxia Hypoxia Sub-optimal oxygen levels in the ambient air of living organisms. Ischemic Cell Damage and ischemia Ischemia A hypoperfusion of the blood through an organ or tissue caused by a pathologic constriction or obstruction of its blood vessels, or an absence of blood circulation. Ischemic Cell Damage causes:
Imaging is done via X-ray X-ray Penetrating electromagnetic radiation emitted when the inner orbital electrons of an atom are excited and release radiant energy. X-ray wavelengths range from 1 pm to 10 nm. Hard x-rays are the higher energy, shorter wavelength x-rays. Soft x-rays or grenz rays are less energetic and longer in wavelength. The short wavelength end of the x-ray spectrum overlaps the gamma rays wavelength range. The distinction between gamma rays and x-rays is based on their radiation source. Pulmonary Function Tests.
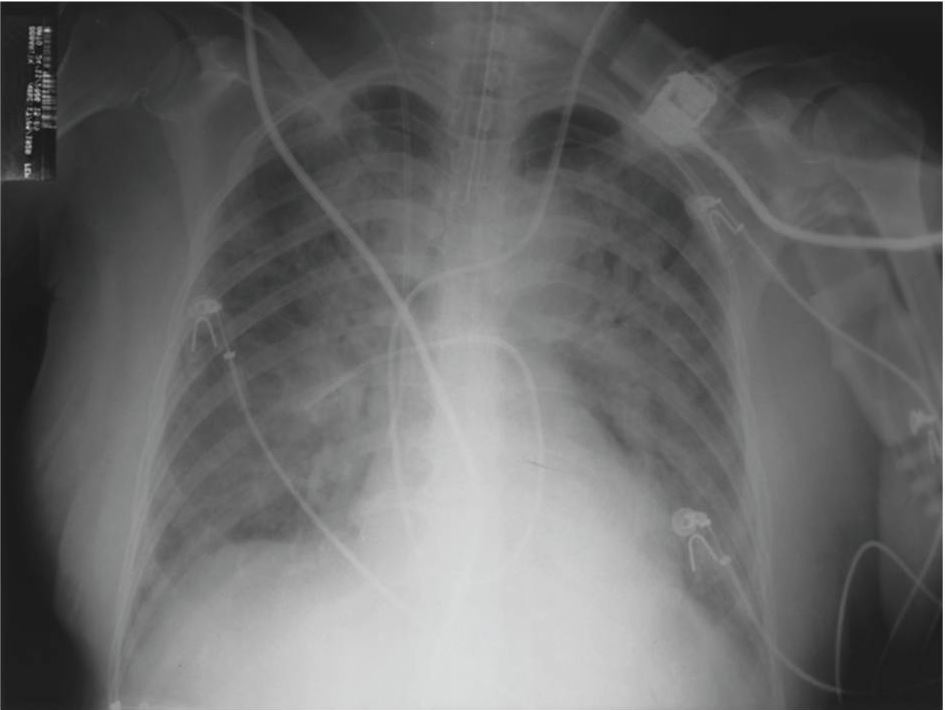
Chest radiograph showing bilateral pulmonary parenchymal infiltrate compatible with ARDS
Image: “Fulminant nonocclusive mesenteric ischemia just after hip arthroplasty” by Auxiliadora-Martins M, Alkmin-Teixeira GC, Feres O, Martins-Filho OA, Basile-Filho A. License: CC BY 3.0While prevention is the most effective intervention, rapid resuscitation Resuscitation The restoration to life or consciousness of one apparently dead. . Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome on-site is essential to improving patient prognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual’s condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas.
1. Safely remove patient from the water and begin primary survey Primary Survey Thoracic Trauma in Children and resuscitation Resuscitation The restoration to life or consciousness of one apparently dead. . Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome:
2. Once patient has been resuscitated and stabilized, initiate secondary survey Secondary Survey ABCDE Assessment or transport to the nearest medical facility:
3. Once the patient has arrived at a medical facility, perform the following:
The following are associated with poor prognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual’s condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas:
The best prevention is education on water safety: