Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation Resuscitation The restoration to life or consciousness of one apparently dead. . Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome ( CPR CPR The artificial substitution of heart and lung action as indicated for heart arrest resulting from electric shock, drowning, respiratory arrest, or other causes. The two major components of cardiopulmonary resuscitation are artificial ventilation and closed-chest cardiac massage. Cardiac Arrest) is an emergency procedure used in patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with cardiac arrest Cardiac arrest Cardiac arrest is the sudden, complete cessation of cardiac output with hemodynamic collapse. Patients present as pulseless, unresponsive, and apneic. Rhythms associated with cardiac arrest are ventricular fibrillation/tachycardia, asystole, or pulseless electrical activity. Cardiac Arrest. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation Resuscitation The restoration to life or consciousness of one apparently dead. . Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome combines the use of chest compressions, artificial ventilation Ventilation The total volume of gas inspired or expired per unit of time, usually measured in liters per minute. Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing, and, when available, an automatic external defibrillator Defibrillator Cardiac electrical stimulators that apply brief high-voltage electroshocks to the heart. These stimulators are used to restore normal rhythm and contractile function in hearts of patients who are experiencing ventricular fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia that is not accompanied by a palpable pulse. Some defibrillators may also be used to correct certain noncritical dysrhythmias (called synchronized defibrillation or cardioversion), using relatively low-level discharges synchronized to the patient's ECG waveform. Cardiac Arrest (AED) to maintain circulatory flow Flow Blood flows through the heart, arteries, capillaries, and veins in a closed, continuous circuit. Flow is the movement of volume per unit of time. Flow is affected by the pressure gradient and the resistance fluid encounters between 2 points. Vascular resistance is the opposition to flow, which is caused primarily by blood friction against vessel walls. Vascular Resistance, Flow, and Mean Arterial Pressure and oxygenation to vital structures. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation Resuscitation The restoration to life or consciousness of one apparently dead. . Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome is an integral part of basic life support Basic Life Support Airway Management ( BLS BLS Airway Management) and advanced cardiovascular life support (ACLS). High-quality CPR CPR The artificial substitution of heart and lung action as indicated for heart arrest resulting from electric shock, drowning, respiratory arrest, or other causes. The two major components of cardiopulmonary resuscitation are artificial ventilation and closed-chest cardiac massage. Cardiac Arrest improves the likelihood of survival. Some patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship in critical situations request a do not resuscitate (DNR) order, which instructs health care providers not to do CPR CPR The artificial substitution of heart and lung action as indicated for heart arrest resulting from electric shock, drowning, respiratory arrest, or other causes. The two major components of cardiopulmonary resuscitation are artificial ventilation and closed-chest cardiac massage. Cardiac Arrest if a patient suffers cardiac arrest Cardiac arrest Cardiac arrest is the sudden, complete cessation of cardiac output with hemodynamic collapse. Patients present as pulseless, unresponsive, and apneic. Rhythms associated with cardiac arrest are ventricular fibrillation/tachycardia, asystole, or pulseless electrical activity. Cardiac Arrest.
Last updated: Jan 17, 2023
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation Resuscitation The restoration to life or consciousness of one apparently dead. . Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome consists of chest compressions and rescue breaths carried out sequentially.
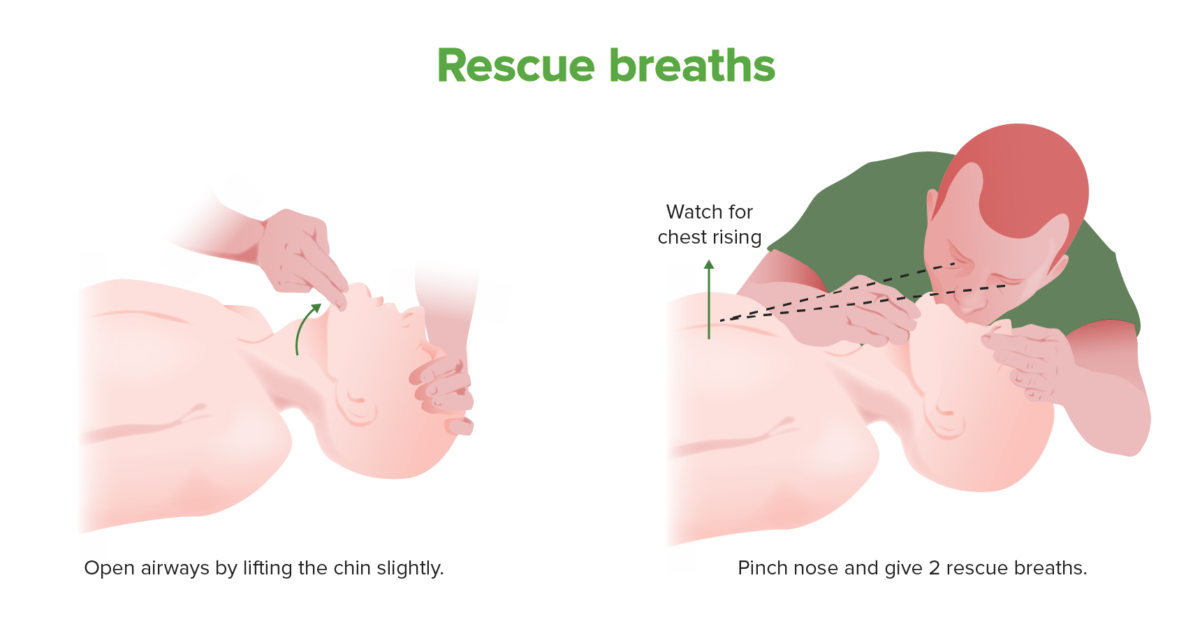
Rescue breath technique
Rescue breaths should be provided to apneic patients during CPR. Chest compressions should take precedence, especially in children, over rescue breaths.
If patient’s chest does not rise, foreign object may be obstructing airway Airway ABCDE Assessment:
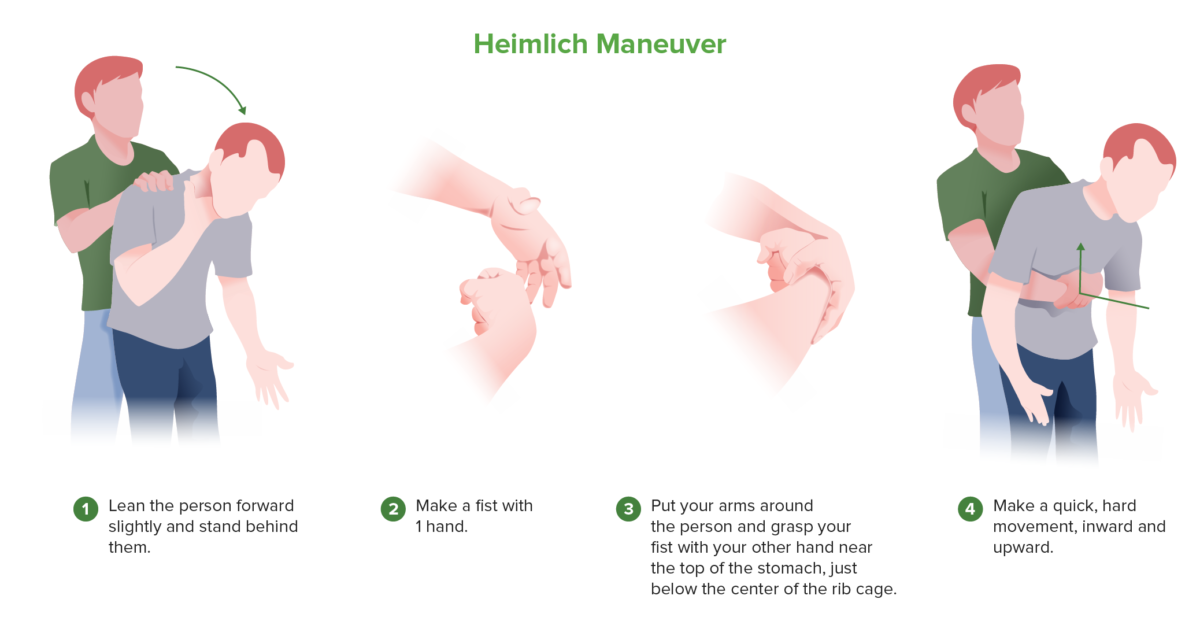
Heimlich maneuver
In a choking patient or an unconscious patient on whom rescue breaths are not providing adequate ventilation, airway obstruction with a foreign object should be considered. The Heimlich maneuver works by producing positive pressure in the lungs, forcefully expelling any foreign body in the upper airway.
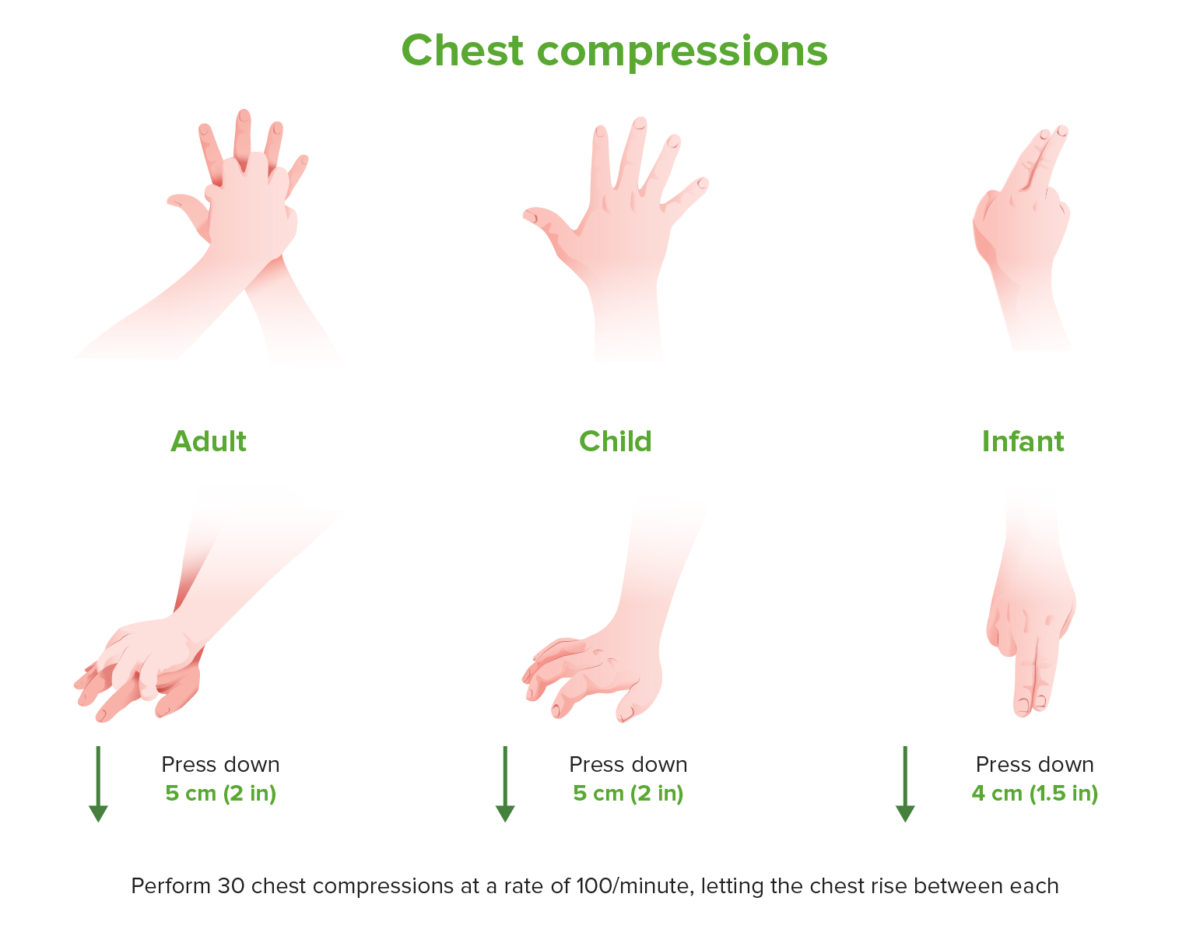
Hand placement in CPR for adults, children and infants
Hand positioning and depth of chest compression vary among adults, children and infants, while rate remains consistent.
Early defibrillation Defibrillation Ventricular Fibrillation (V-fib) has been shown to significantly improve morbidity Morbidity The proportion of patients with a particular disease during a given year per given unit of population. Measures of Health Status and mortality Mortality All deaths reported in a given population. Measures of Health Status in ventricular fibrillation Ventricular fibrillation Ventricular fibrillation (VF or V-fib) is a type of ventricular tachyarrhythmia (> 300/min) often preceded by ventricular tachycardia. In this arrhythmia, the ventricle beats rapidly and sporadically. The ventricular contraction is uncoordinated, leading to a decrease in cardiac output and immediate hemodynamic collapse. Ventricular Fibrillation (V-fib) ( VF VF Ventricular fibrillation (VF or V-fib) is a type of ventricular tachyarrhythmia (> 300/min) often preceded by ventricular tachycardia. In this arrhythmia, the ventricle beats rapidly and sporadically. The ventricular contraction is uncoordinated, leading to a decrease in cardiac output and immediate hemodynamic collapse. Ventricular Fibrillation (V-fib))/ventricular tachycardia Tachycardia Abnormally rapid heartbeat, usually with a heart rate above 100 beats per minute for adults. Tachycardia accompanied by disturbance in the cardiac depolarization (cardiac arrhythmia) is called tachyarrhythmia. Sepsis in Children ( VT VT Ventricular tachycardia is any heart rhythm faster than 100 beats/min, with 3 or more irregular beats in a row, arising distal to the bundle of his. Ventricular tachycardia is the most common form of wide-complex tachycardia, and it is associated with a high mortality rate. Ventricular Tachycardia) cardiac arrest Cardiac arrest Cardiac arrest is the sudden, complete cessation of cardiac output with hemodynamic collapse. Patients present as pulseless, unresponsive, and apneic. Rhythms associated with cardiac arrest are ventricular fibrillation/tachycardia, asystole, or pulseless electrical activity. Cardiac Arrest.
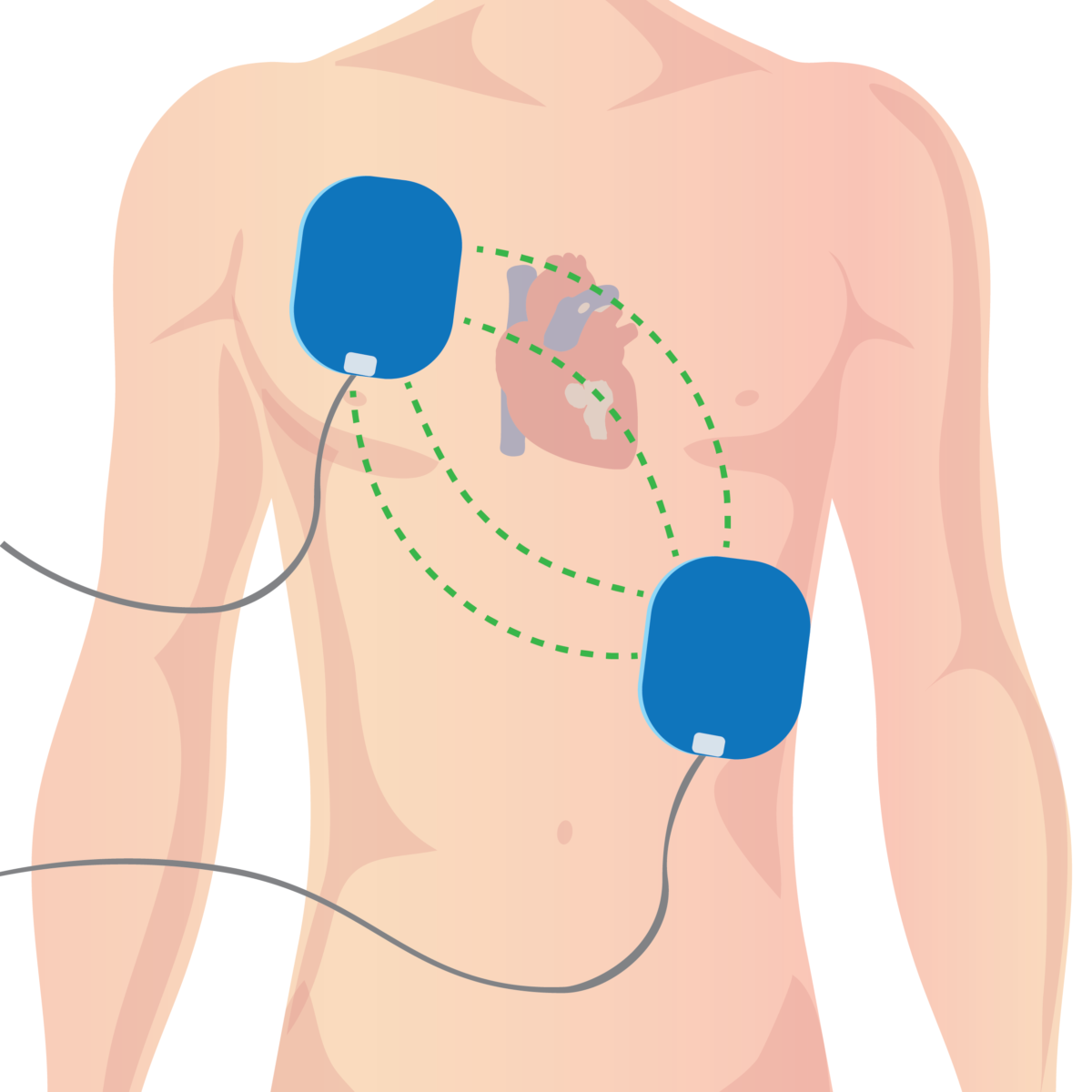
Automated external defibrillator pad placement in adults
In adults, AED pads should be placed per manufacturer recommendation, usually under the right collarbone and on the left side of the chest.
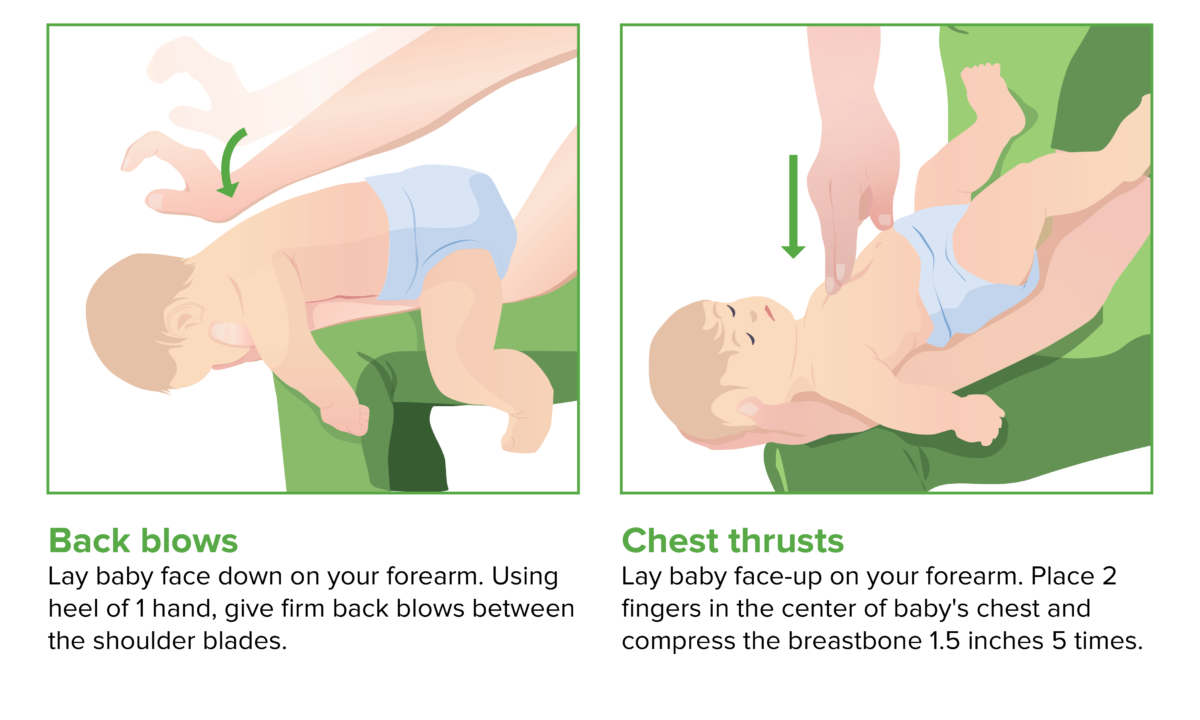
Back blows and chest thrusts (CPR in children)
Image by Lecturio.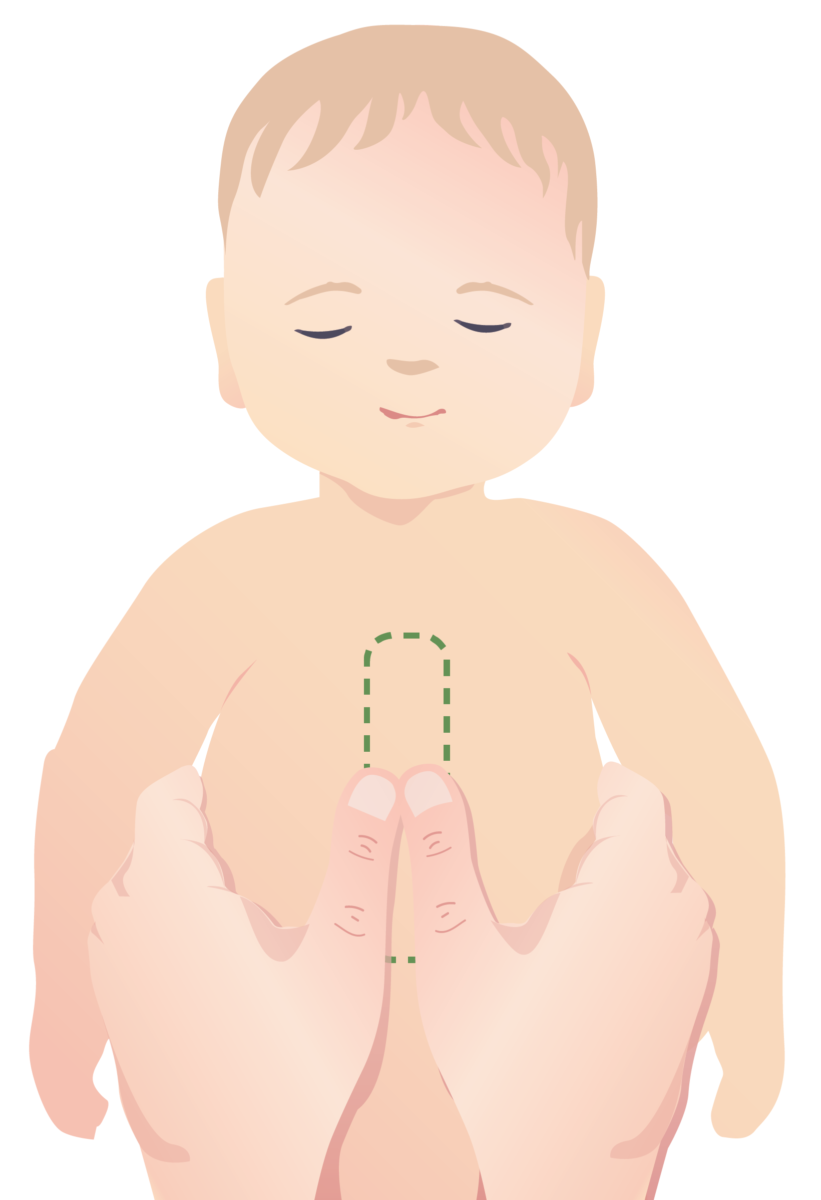
Two-hand technique for performing CPR on an infant
In smaller infants, effective chest compressions can be performed by wrapping both hands around the chest and placing the thumbs on the xiphoid process.
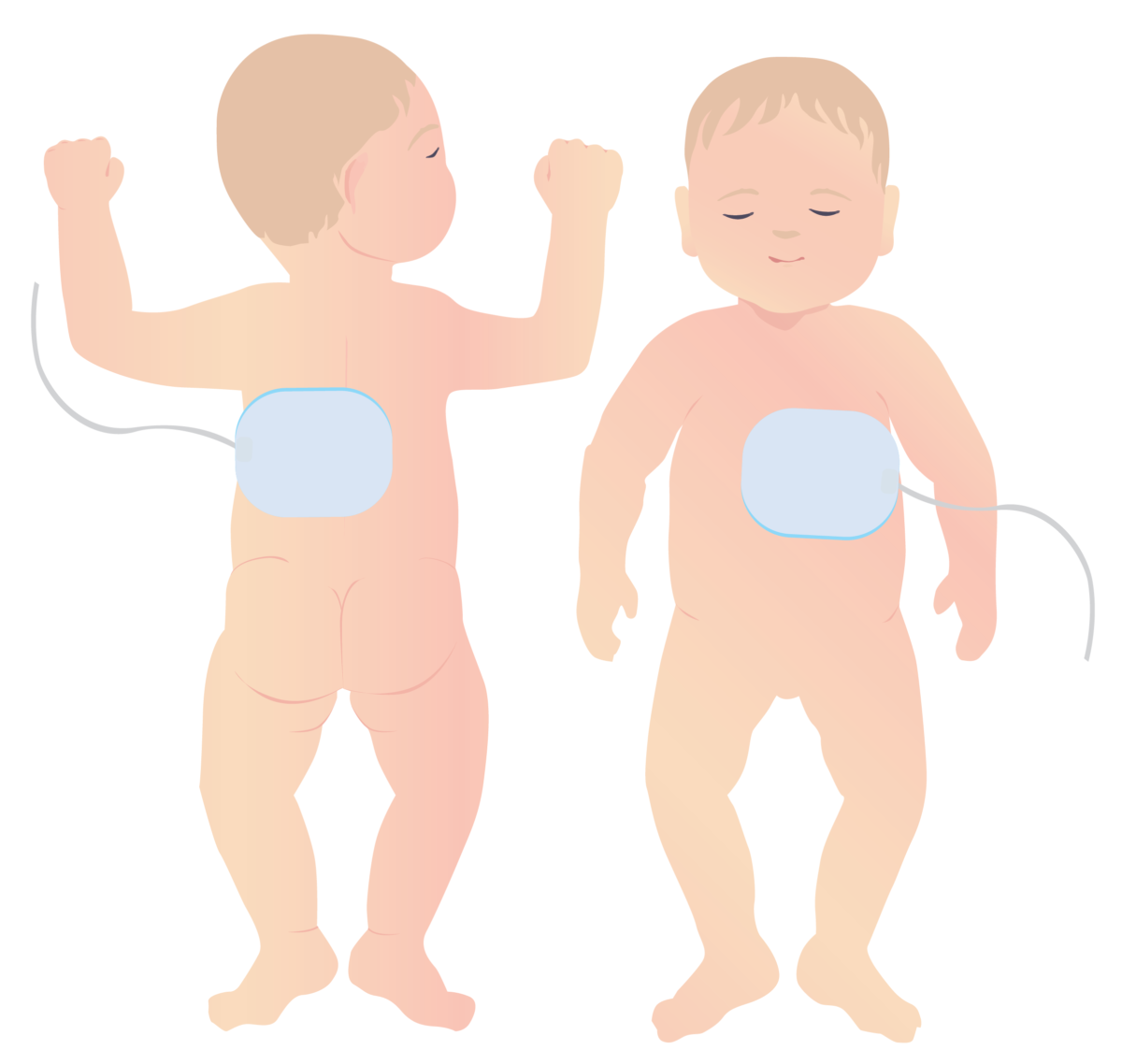
Appropriate placement of defibrillator pads on pediatric patient
Small children require pediatric-sized defibrillator pads. Unlike in adults, these should be placed on the front and the back, as shown.
A DNR order is a medical order, part of a patient’s advance directives Advance Directives The term advance directive (AD) refers to treatment preferences and/or the designation of a surrogate decision-maker in the event that a person becomes unable to make medical decisions on their own behalf. Advance directives represent the ethical principle of autonomy and may take the form of a living will, health care proxy, durable power of attorney for health care (DPAHC), and/or a physician’s order for life-sustaining treatment (POLST). Advance Directives.
Do not resuscitate orders prevent healthcare providers from performing the following procedures in case a patient’s breathing stops or heart rate Heart rate The number of times the heart ventricles contract per unit of time, usually per minute. Cardiac Physiology stops:
Advance directives Advance Directives The term advance directive (AD) refers to treatment preferences and/or the designation of a surrogate decision-maker in the event that a person becomes unable to make medical decisions on their own behalf. Advance directives represent the ethical principle of autonomy and may take the form of a living will, health care proxy, durable power of attorney for health care (DPAHC), and/or a physician’s order for life-sustaining treatment (POLST). Advance Directives:
Being under a DNR order does not prohibit patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship from receiving appropriate medical care Medical care Conflict of Interest (surgeries, biopsies, dialysis Dialysis Renal replacement therapy refers to dialysis and/or kidney transplantation. Dialysis is a procedure by which toxins and excess water are removed from the circulation. Hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis (PD) are the two types of dialysis, and their primary difference is the location of the filtration process (external to the body in hemodialysis versus inside the body for PD). Peritoneal Dialysis and Hemodialysis, blood samples, move to intensive care unit ( ICU ICU Hospital units providing continuous surveillance and care to acutely ill patients. West Nile Virus), etc ETC The electron transport chain (ETC) sends electrons through a series of proteins, which generate an electrochemical proton gradient that produces energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Electron Transport Chain (ETC).).