Fibroadenomas are the most common benign tumor Tumor Inflammation of the female breast and the most common breast tumor Tumor Inflammation in adolescent and young women. The tumors are well-circumscribed, mobile, and often encapsulated Encapsulated Klebsiella, with a rubbery or firm consistency Consistency Dermatologic Examination. Fibroadenomas are hormonally responsive, so they may increase in size during pregnancy Pregnancy The status during which female mammals carry their developing young (embryos or fetuses) in utero before birth, beginning from fertilization to birth. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care and usually regress after menopause Menopause Menopause is a physiologic process in women characterized by the permanent cessation of menstruation that occurs after the loss of ovarian activity. Menopause can only be diagnosed retrospectively, after 12 months without menstrual bleeding. Menopause. Histologically, fibroadenomas are composed of a biphasic proliferation of both glandular and stromal elements. Fibroadenomas are associated with a slightly increased risk of carcinoma, with a somewhat higher risk if so-called “complex” features are present. Diagnosis is based on physical findings and ultrasonography. Management is based on regular Regular Insulin checkups to monitor growth.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
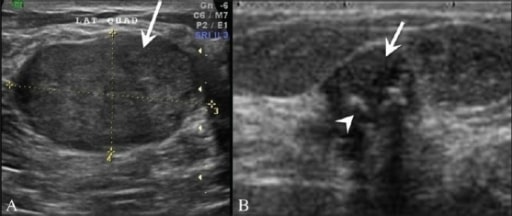
A: Breast ultrasonography in a 25-year-old patient shows a homogenous, hypoechoic, gently lobulated lesion (arrow), suggestive of a fibroadenoma.
B: Ultrasonography shows a degenerating fibroadenoma (arrow) with coarse calcifications (arrowhead) and posterior shadowing from the calcific foci.
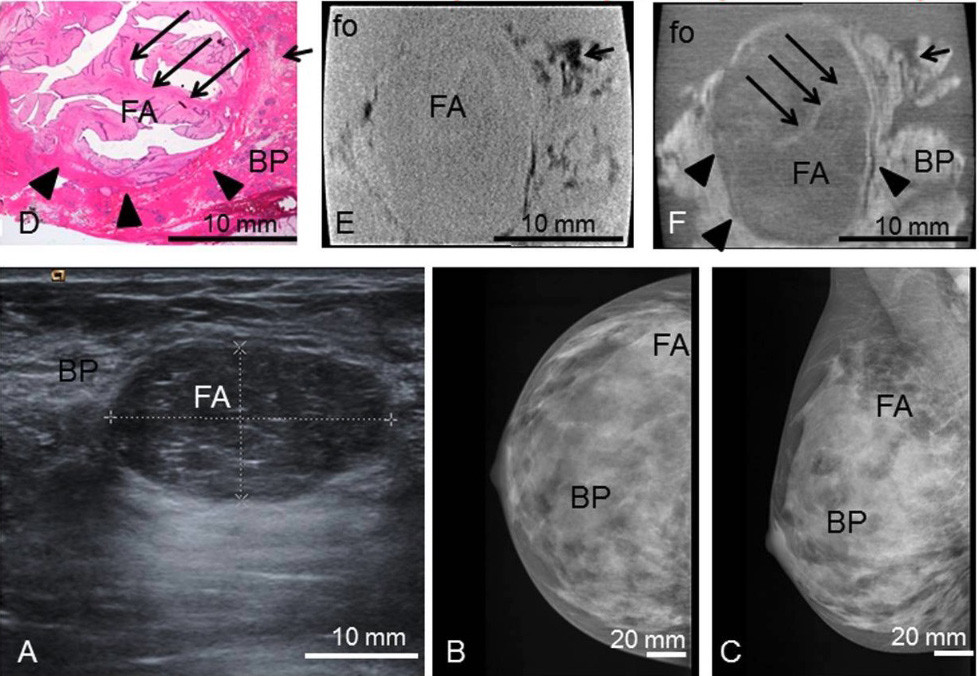
Preoperative imaging, histology, absoption- and phase-contrast CT:
Preoperative ultrasonography (A) with typical benign imaging characteristics of the fibroadenoma (FA) (oval form, smooth margins, posterior enhancement);
preoperative craniocaudal (B) and mediolateral oblique (C) mammography projections show the fibroadenoma (FA) partially hidden within the dense breast parenchyma (BP) (ACR IV).
Representative histological slice (D) and corresponding absorption- (E) and phase-contrast CT (F) image. The black sharp lines in the corners of (E) and (F) correspond to the walls of the plastic container. The ducts are artificially torn open in (D) due to cutting and staining procedures.
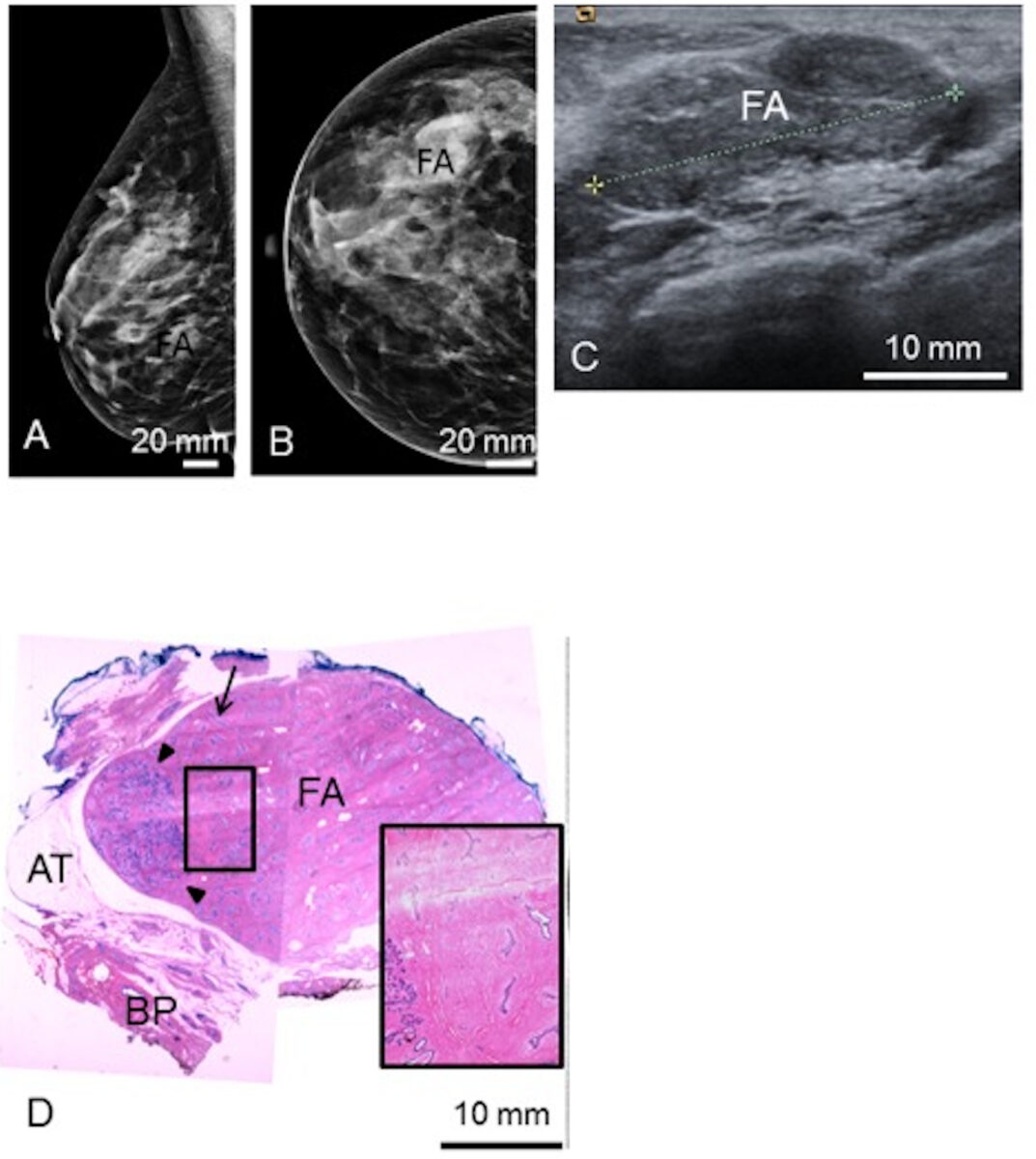
Preoperative mediolateral-oblique (A) and craniocaudal (B) mammogram and ultrasonography (C) show the fibroadenoma (FA).
A representative histological slice (D) shows the FA, surrounded by adipose tissue (AT) and breast parenchyma (BP).
(D) The black rectangle shows a zoomed view of a polygonal sclerotic frame filled with basophilic branched ducts; 1 linear duct is indicated by the arrow.
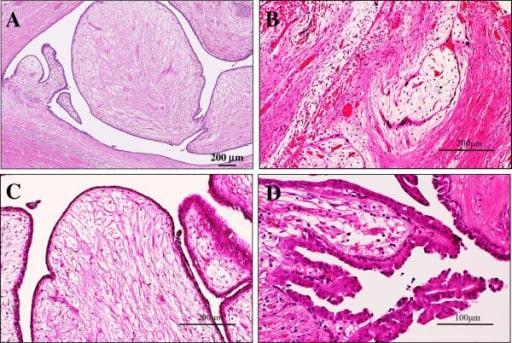
Microscopic examination of the intraductal fibroadenoma or intraductal phyllodes tumor of the breast
A: Low-power view shows that its polypoid parts are composed of leaf-like processes with a hypocellular and prominent myxoid stroma protruding into cystic spaces, reminiscent of intracanalicular type fibroadenoma or benign phyllodes tumor features (H&E stains). Bar = 200 μm.
B: In some areas, there are foci of a typical intracanalicular variant of fibroadenoma, in which duct lumens are compressed by the proliferating myxoid stroma (H&E stains). Bar = 200 μm.
C: On high-power view, those stromal cells show no significant atypia, but the covering hyperplastic epithelial components are also bland looking in 2 cell layers. Mitotic figures are very rarely seen (H&E stains). Bar = 200 μm.
D: In others, tiny foci of benign intraductal papilloma with characteristic delicate fibrovascular stalks are rarely seen (H&E stains). Bar = 100 μm.
The following conditions are differential diagnoses of fibroadenomas: