Puberty is a complex series of physical, psychosocial, and cognitive transitions usually experienced by adolescents (11–19 years of age). Puberty is marked by a growth in stature and the development of secondary sexual characteristics Secondary Sexual Characteristics Precocious Puberty, achievement of fertility, and changes in most body systems. Being familiar with normal puberty is important to be able to recognize and manage abnormalities such as precocious puberty Precocious puberty Precocious puberty (PP) is the appearance of secondary sexual characteristics due to elevated sex hormones before the age of 6-8 in girls and 9 in boys. Excess hormone secretion may occur only at the level of the sex hormone or may involve the whole hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis. Precocious Puberty or delayed puberty Delayed Puberty Delayed puberty (DP) is defined as the lack of testicular growth in boys past the age of 14 and the lack of thelarche in girls past the age of 13. Delayed puberty affects up to 5% of healthy boys and girls, and half of all cases are due to constitutional growth delay. Delayed Puberty.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Puberty is the time period from the 1st appearance of secondary sexual characteristics Secondary Sexual Characteristics Precocious Puberty until achieving complete sexual development. Puberty involves a complex series of physical, psychosocial, and cognitive changes.
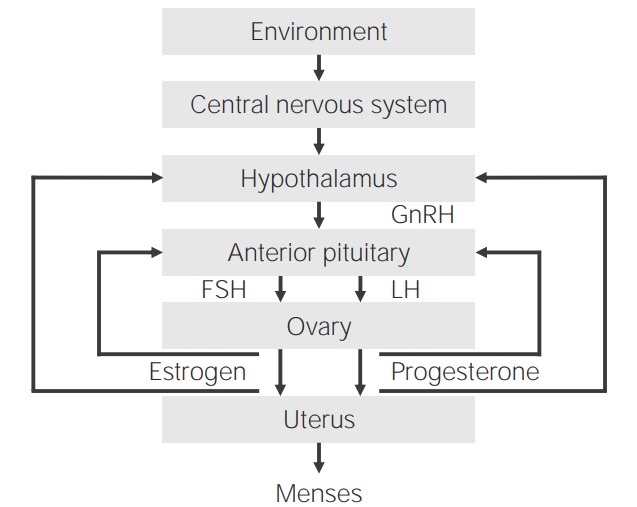
Normal hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal (HPG) axis in females
GnRH: gonadotropin-releasing hormonePuberty can be divided into 4 different consecutive stages, namely, thelarche, pubarche, growth spurt, and menarche Menarche The first menstrual cycle marked by the initiation of menstruation. Menstrual Cycle.
“ Tanner staging Tanner Staging Delayed Puberty” is a scale Scale Dermatologic Examination that measures the physical/sexual development in children and adolescents. This staging Staging Methods which attempt to express in replicable terms the extent of the neoplasm in the patient. Grading, Staging, and Metastasis technique involves the evaluation of genitalia in males, breast in females, and pubic hair in both.
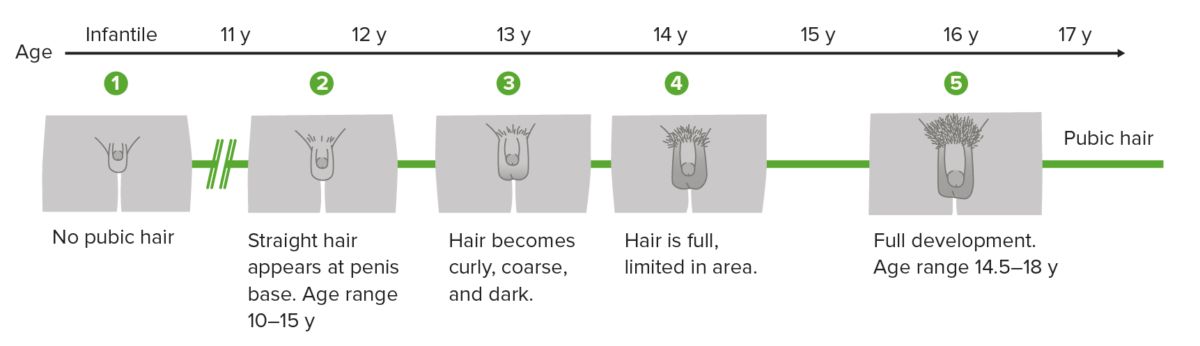
Tanner scale, also called sexual maturity rating (SMR), showing the different stages of penis, scrotum, and pubic hair development in boys
Image by Lecturio.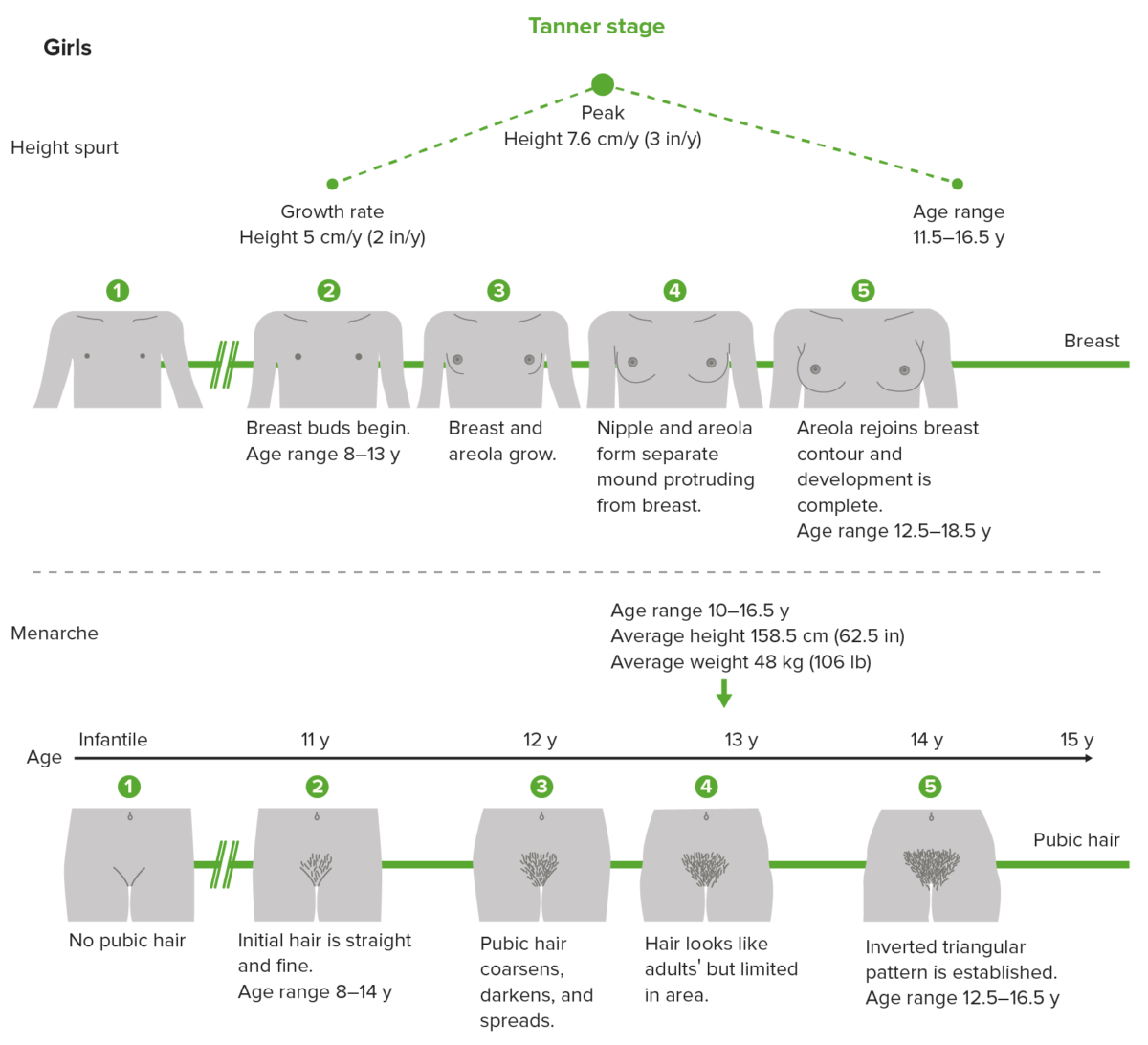
Tanner scale, also called sexual maturity rating (SMR), showing the different stages of breast and pubic hair development in girls
Image by Lecturio.| Tanner 1 | Tanner 2 | Tanner 3 | Tanner 4 | Tanner 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Prepubertal | 8–11.5 years | 11.5–13 years | 12–15 years | > 15 years |
| Pubic hair | Villus hair only | Sparse hair along the labia | Coarse and curly hair covers the pubis. | Adult hair that does not spread to the thigh Thigh The thigh is the region of the lower limb found between the hip and the knee joint. There is a single bone in the thigh called the femur, which is surrounded by large muscles grouped into 3 fascial compartments. Thigh: Anatomy | Adult hair reaching the thigh Thigh The thigh is the region of the lower limb found between the hip and the knee joint. There is a single bone in the thigh called the femur, which is surrounded by large muscles grouped into 3 fascial compartments. Thigh: Anatomy |
| Breasts Breasts The breasts are found on the anterior thoracic wall and consist of mammary glands surrounded by connective tissue. The mammary glands are modified apocrine sweat glands that produce milk, which serves as nutrition for infants. Breasts are rudimentary and usually nonfunctioning in men. Breasts: Anatomy | Elevation of papilla only | Breast buds are palpable (1st sign of puberty in females) and areolae are enlarged. | Breast tissue grows with no contour or separation. | Breasts Breasts The breasts are found on the anterior thoracic wall and consist of mammary glands surrounded by connective tissue. The mammary glands are modified apocrine sweat glands that produce milk, which serves as nutrition for infants. Breasts are rudimentary and usually nonfunctioning in men. Breasts: Anatomy enlarge and areolae form secondary mound on the breast. | Adult breast contours are present. Only the papilla is raised. |
| Other observations | Adrenarche and ovarian growth | Clitoral enlargement, labial pigmentation, growth of uterus Uterus The uterus, cervix, and fallopian tubes are part of the internal female reproductive system. The uterus has a thick wall made of smooth muscle (the myometrium) and an inner mucosal layer (the endometrium). The most inferior portion of the uterus is the cervix, which connects the uterine cavity to the vagina. Uterus, Cervix, and Fallopian Tubes: Anatomy | Axillary hair, acne | Menarche Menarche The first menstrual cycle marked by the initiation of menstruation. Menstrual Cycle and development of menses Menses The periodic shedding of the endometrium and associated menstrual bleeding in the menstrual cycle of humans and primates. Menstruation is due to the decline in circulating progesterone, and occurs at the late luteal phase when luteolysis of the corpus luteum takes place. Menstrual Cycle | Adult genitalia |
| Tanner 1 | Tanner 2 | Tanner 3 | Tanner 4 | Tanner 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Prepubertal | 8–11.5 years | 11.5–13 years | 12–15 years | > 15 years |
| Pubic hair | Villus hair only | Sparse hair at base of the penis Penis The penis is the male organ of copulation and micturition. The organ is composed of a root, body, and glans. The root is attached to the pubic bone by the crura penis. The body consists of the 2 parallel corpora cavernosa and the corpus spongiosum. The glans is ensheathed by the prepuce or foreskin. Penis: Anatomy | Coarse and curly hair appears over the pubis. | Adult-quality hair in the pubic area, sparing the thigh Thigh The thigh is the region of the lower limb found between the hip and the knee joint. There is a single bone in the thigh called the femur, which is surrounded by large muscles grouped into 3 fascial compartments. Thigh: Anatomy | Adult-quality hair in the pubic area, reaching the thigh Thigh The thigh is the region of the lower limb found between the hip and the knee joint. There is a single bone in the thigh called the femur, which is surrounded by large muscles grouped into 3 fascial compartments. Thigh: Anatomy |
| Genitalia |
|
|
|
|
|
| Other observations | Adrenarche | Decrease in body fat | Gynecomastia Gynecomastia Gynecomastia is a benign proliferation of male breast glandular ductal tissue, usually bilateral, caused by increased estrogen activity, decreased testosterone activity, or medications. The condition is common and physiological in neonates, adolescent boys, and elderly men. Gynecomastia, breaking of voice, increased muscle mass Mass Three-dimensional lesion that occupies a space within the breast Imaging of the Breast | Axillary hair, voice change, acne | Facial hair, increase in muscle mass Mass Three-dimensional lesion that occupies a space within the breast Imaging of the Breast |