Orotic aciduria is an extremely rare genetic disorder that can result in crystalluria, megaloblastic anemia Megaloblastic anemia Megaloblastic anemia is a subset of macrocytic anemias that arises because of impaired nucleic acid synthesis in erythroid precursors. This impairment leads to ineffective RBC production and intramedullary hemolysis that is characterized by large cells with arrested nuclear maturation. The most common causes are vitamin B12 and folic acid deficiencies. Megaloblastic Anemia, developmental delay, and failure to thrive Failure to Thrive Failure to thrive (FTT), or faltering growth, describes suboptimal weight gain and growth in children. The majority of cases are due to inadequate caloric intake; however, genetic, infectious, and oncological etiologies are also common. Failure to Thrive. The disorder is caused by an enzyme deficiency in the pyrimidine synthesis Synthesis Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) pathway resulting in the accumulation of orotic acid. Depletion of nucleotides Nucleotides The monomeric units from which DNA or RNA polymers are constructed. They consist of a purine or pyrimidine base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. Nucleic Acids leads to the symptoms of the disease. Diagnosis is made with genetic sequencing as well as urine studies. Options for treatment include uridine monophosphate Uridine monophosphate 5'-uridylic acid. A uracil nucleotide containing one phosphate group esterified to the sugar moiety in the 2. Purine and Pyrimidine Metabolism and uridine triacetate.
Last updated: Apr 23, 2025
Type I:
Type II:
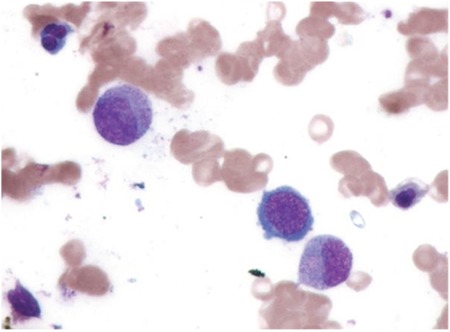
Blood smear of megaloblastic anemia:
Megaloblastic anemia is seen on blood smear in patients with orotic aciduria because of decreased pyrimidine synthesis, which reduces the amount of nucleotide-lipid cofactors necessary for RBC membrane synthesis.
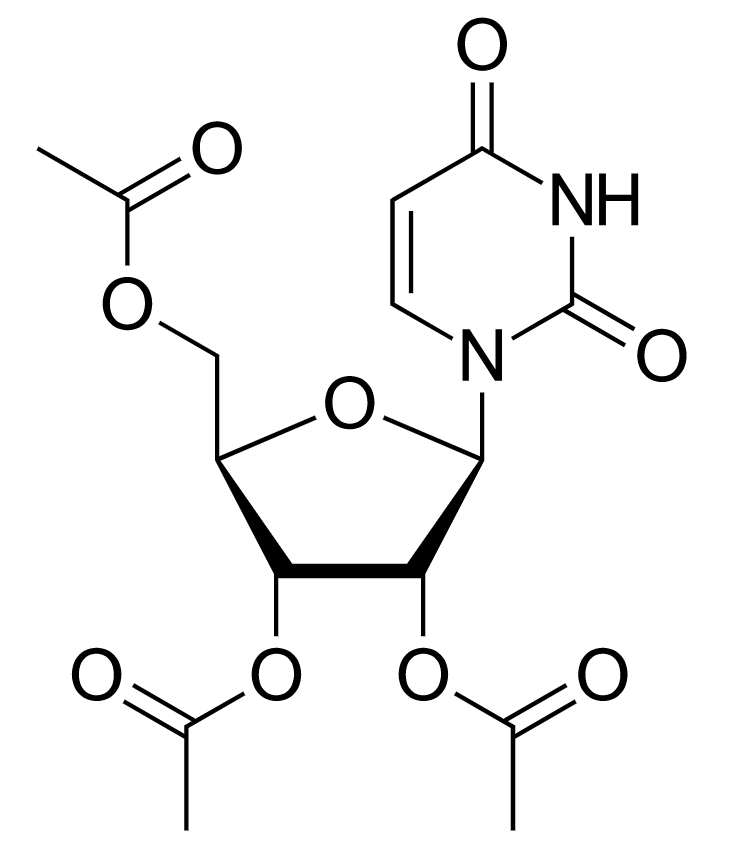
Structure of uridine triacetate, an orally active prodrug of uridine that is used in the treatment of orotic aciduria
Image: “Uridine triacetate structure” by Vaccinationist. License: Public Domain