Learning and the development of memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment are processes that cannot be separated from psychology and sociology. This article deals with the physiology of learning and memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment. Topics include understanding the relationship between experience and the storage of acquired knowledge, how the brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification deals with “useless” knowledge, and how infants start to understand their surroundings.
Last updated: Apr 28, 2023
Contents
Learning is the process of acquiring new knowledge or skills by study, instruction, or experience. Learning is the precondition for the brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification to store experiences and use those experiences in our actions to gain benefits and prevent damage.
Humans adapt to their environment by learning. When an individual learns to expect and prepare for a significant event such as the arrival of food or pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways, it is called learning by classical conditioning. When a person learns to repeat a behavior that brings a reward and understands how to avoid doing something that brings unwanted results, the process is termed learning by operant conditioning Operant conditioning Learning situations in which the sequence responses of the subject are instrumental in producing reinforcement. When the correct response occurs, which involves the selection from among a repertoire of responses, the subject is immediately reinforced. Psychotherapy. When an individual learns about things they have neither experienced nor observed merely based on observation and through language, the process is termed cognitive learning. This chapter will discuss how a person learns.
Learning processes during the first 6 months of an infant’s life hold great significance in the development of the nervous system Nervous system The nervous system is a small and complex system that consists of an intricate network of neural cells (or neurons) and even more glial cells (for support and insulation). It is divided according to its anatomical components as well as its functional characteristics. The brain and spinal cord are referred to as the central nervous system, and the branches of nerves from these structures are referred to as the peripheral nervous system. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification. Environmental stimuli and experiences also play a role as they lead to the formation of new synapses and the improvement of already existing synaptic connections. The ability of the brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification to form and improve these connections are referred to as neuroplasticity, which is based on physiological or neuroanatomical conditions.
Most brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification cells are already formed in utero. The 1st neurons Neurons The basic cellular units of nervous tissue. Each neuron consists of a body, an axon, and dendrites. Their purpose is to receive, conduct, and transmit impulses in the nervous system. Nervous System: Histology and synapses begin to develop in the spinal cord Spinal cord The spinal cord is the major conduction pathway connecting the brain to the body; it is part of the CNS. In cross section, the spinal cord is divided into an H-shaped area of gray matter (consisting of synapsing neuronal cell bodies) and a surrounding area of white matter (consisting of ascending and descending tracts of myelinated axons). Spinal Cord: Anatomy approximately 7 weeks after conception. However, most nerve cells of infants are incapable of communication Communication The exchange or transmission of ideas, attitudes, or beliefs between individuals or groups. Decision-making Capacity and Legal Competence at the time of birth as they are not yet connected. These connections develop during the first 3 years of life by the formation of dendrites Dendrites Extensions of the nerve cell body. They are short and branched and receive stimuli from other neurons. Nervous System: Histology, which enable cells to absorb information. Moreover, synaptic connections are formed, which are responsible for relaying information. The extent of these connections is far greater than what is required, making it easy to adjust later if needed.
Babies react strongly to stimuli, which is an important indication that the learning process is being carried out. Besides, these stimuli are necessary for the brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification to develop. Thus, an environment with few stimuli hinders the development of infants.
Infants can recognize faces and vocal sounds during their developmental stage, enabling them to differentiate between familiar faces and strangers. After imprinting Imprinting The variable phenotypic expression of a gene depending on whether it is of paternal or maternal origin, which is a function of the DNA methylation pattern. Imprinted regions are observed to be more methylated and less transcriptionally active. Epigenetic Regulation their personal surroundings, infants lose a certain amount of flexibility related to their mental abilities. However, learning processes become more specific. This development occurs during the first 6 months of life.
The brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification uses neurons Neurons The basic cellular units of nervous tissue. Each neuron consists of a body, an axon, and dendrites. Their purpose is to receive, conduct, and transmit impulses in the nervous system. Nervous System: Histology to communicate and, to a large extent, manage itself. However, the development of neurons Neurons The basic cellular units of nervous tissue. Each neuron consists of a body, an axon, and dendrites. Their purpose is to receive, conduct, and transmit impulses in the nervous system. Nervous System: Histology and the resulting brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification capacities depend on environmental and sensory Sensory Neurons which conduct nerve impulses to the central nervous system. Nervous System: Histology stimuli. The brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification works in conjunction with the spinal cord Spinal cord The spinal cord is the major conduction pathway connecting the brain to the body; it is part of the CNS. In cross section, the spinal cord is divided into an H-shaped area of gray matter (consisting of synapsing neuronal cell bodies) and a surrounding area of white matter (consisting of ascending and descending tracts of myelinated axons). Spinal Cord: Anatomy to send and receive information via neurons Neurons The basic cellular units of nervous tissue. Each neuron consists of a body, an axon, and dendrites. Their purpose is to receive, conduct, and transmit impulses in the nervous system. Nervous System: Histology. The brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification processes perceptions, which are also connected; accordingly, it uses experiences that are already stored. However, most perceptions are suppressed. The brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification differentiates perceptions that must be processed during the learning process based on the following aspects:
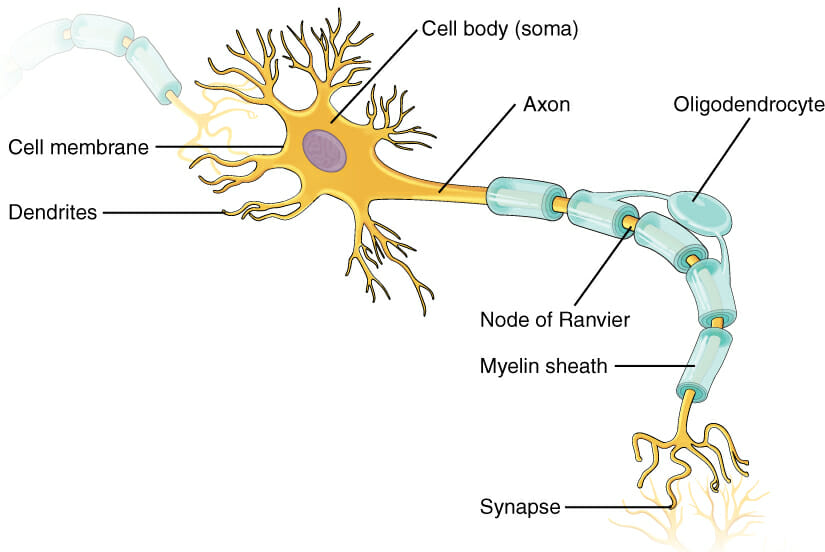
Parts of a neuron
Image: “The major parts of the neuron” by OpenStax College. License: CC BY 4.0Cognition and emotions play a major role in the learning process. Sensations are used as somatic markers, which influence processing, storage, and memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment. Learning also includes the strengthening of the most used neuronal pathways such that they can be used longer and, above all, faster.
The learning process starts with the processing of external influences. Learning leads to changes in the brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification, which can be classified under 4 categories, namely, expanding, tuning, reconstructing, and pruning.
Expanding refers to improving the number and strength of neuronal connections by developing a network of already existing information. Tuning describes the process of creating new connections. Relearning occurs during the process of reconstructing. In this time-consuming and exhaustive process, pre-existing learning achievements ( motor Motor Neurons which send impulses peripherally to activate muscles or secretory cells. Nervous System: Histology patterns and routine processes) are replaced by new ones that are better suited for the respective tasks. Pruning refers to regression Regression Corneal Abrasions, Erosion, and Ulcers of the neuronal pathways that are seldom or never used. During this process, connections can be changed such that they can no longer be activated.
Learning can be categorized as follows:
Humans need social interactions, and this also applies to the brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification. Mirror neurons Neurons The basic cellular units of nervous tissue. Each neuron consists of a body, an axon, and dendrites. Their purpose is to receive, conduct, and transmit impulses in the nervous system. Nervous System: Histology in the brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification are responsible for development of the required cognitive orientation Orientation Awareness of oneself in relation to time, place and person. Psychiatric Assessment patterns. A mirror neuron is a type of sensory-motor cell located in the brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification that is activated when an individual performs an action or observes another individual performing the same action. Thus, the neuron “mirrors” others’ actions. Physical activity is also important for brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification performance, and this particularly applies in the 1st few years of life.
Neurons Neurons The basic cellular units of nervous tissue. Each neuron consists of a body, an axon, and dendrites. Their purpose is to receive, conduct, and transmit impulses in the nervous system. Nervous System: Histology of the cerebellum Cerebellum The cerebellum, Latin for “little brain,” is located in the posterior cranial fossa, dorsal to the pons and midbrain, and its principal role is in the coordination of movements. The cerebellum consists of 3 lobes on either side of its 2 hemispheres and is connected in the middle by the vermis. Cerebellum: Anatomy and basal ganglia Basal Ganglia Basal ganglia are a group of subcortical nuclear agglomerations involved in movement, and are located deep to the cerebral hemispheres. Basal ganglia include the striatum (caudate nucleus and putamen), globus pallidus, substantia nigra, and subthalamic nucleus. Basal Ganglia: Anatomy are responsible for motor Motor Neurons which send impulses peripherally to activate muscles or secretory cells. Nervous System: Histology learning. Declarative memory Declarative Memory Geriatric Changes is located in the medial temporal lobe Temporal lobe Lower lateral part of the cerebral hemisphere responsible for auditory, olfactory, and semantic processing. It is located inferior to the lateral fissure and anterior to the occipital lobe. Cerebral Cortex: Anatomy. Hippocampal lesions lead to anterograde amnesia Anterograde amnesia Loss of the ability to form new memories beyond a certain point in time. This condition may be organic or psychogenic in origin. Organically induced anterograde amnesia may follow craniocerebral trauma; seizures; anoxia; and other conditions which adversely affect neural structures associated with memory formation (e.g., the hippocampus; fornix (brain); mammillary bodies; and anterior thalamic nuclei). Wernicke Encephalopathy and Korsakoff Syndrome, a condition in which new information cannot be stored.
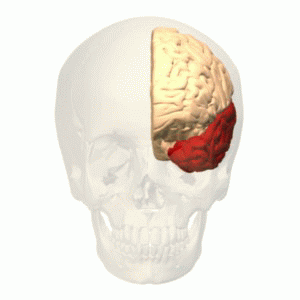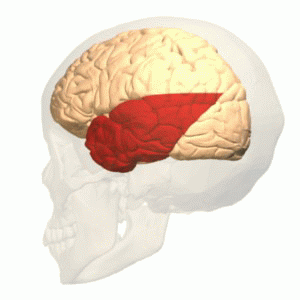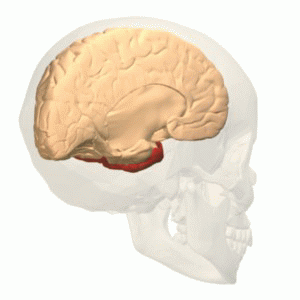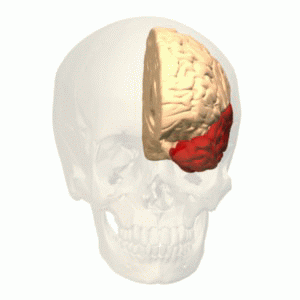
Temporal lobe
Image: “Temporal lobe animation” by Database Center for Life Science(DBCLS). License: CC BY-SA 2.1 JP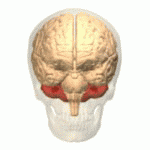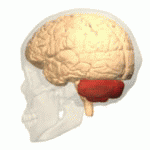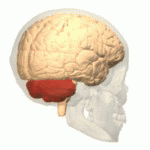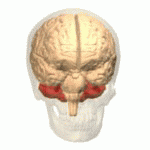
Cerebellum
Image: “Cerebellum animation small” by Database Center for Life Science(DBCLS). License: CC BY-SA 2.1 JPThe striatum Striatum Striped gray matter and white matter consisting of the neostriatum and paleostriatum (globus pallidus). It is located in front of and lateral to the thalamus in each cerebral hemisphere. The gray substance is made up of the caudate nucleus and the lentiform nucleus (the latter consisting of the globus pallidus and putamen). The white matter is the internal capsule. Basal Ganglia: Anatomy is associated with procedural memory Procedural memory Dissociative Amnesia and uses the pathway of the neocortex Neocortex The largest portion of the cerebral cortex in which the neurons are arranged in six layers in the mammalian brain: molecular, external granular, external pyramidal, internal granular, internal pyramidal and multiform layers. Cerebral Cortex: Anatomy. Associative learning for emotional and motor Motor Neurons which send impulses peripherally to activate muscles or secretory cells. Nervous System: Histology processes occurs in the amygdala Amygdala Almond-shaped group of basal nuclei anterior to the inferior horn of the lateral ventricle of the temporal lobe. The amygdala is part of the limbic system. Limbic System: Anatomy and cerebellum Cerebellum The cerebellum, Latin for “little brain,” is located in the posterior cranial fossa, dorsal to the pons and midbrain, and its principal role is in the coordination of movements. The cerebellum consists of 3 lobes on either side of its 2 hemispheres and is connected in the middle by the vermis. Cerebellum: Anatomy, respectively. Nonassociative learning occurs in the form of habituation and sensitization (both via reflex circuits).
The Hebbian theory explains how connections between certain neurons Neurons The basic cellular units of nervous tissue. Each neuron consists of a body, an axon, and dendrites. Their purpose is to receive, conduct, and transmit impulses in the nervous system. Nervous System: Histology can be strengthened. This theory asserts that “ neurons Neurons The basic cellular units of nervous tissue. Each neuron consists of a body, an axon, and dendrites. Their purpose is to receive, conduct, and transmit impulses in the nervous system. Nervous System: Histology that fire together, wire together,” which means that when activity in a cell repeatedly elicits action potentials in a 2nd cell, the synaptic strength is potentiated.
If an axon of neuron A is located close enough to neuron B such that neuron B can be stimulated by neuron A repeatedly or continuously, the efficiency of neuron A for the stimulation by neuron B is increased by growth processes or changes in metabolism in 1 or both neurons Neurons The basic cellular units of nervous tissue. Each neuron consists of a body, an axon, and dendrites. Their purpose is to receive, conduct, and transmit impulses in the nervous system. Nervous System: Histology. This suggests that experience-related changes in the nervous systems depend on certain conditions.
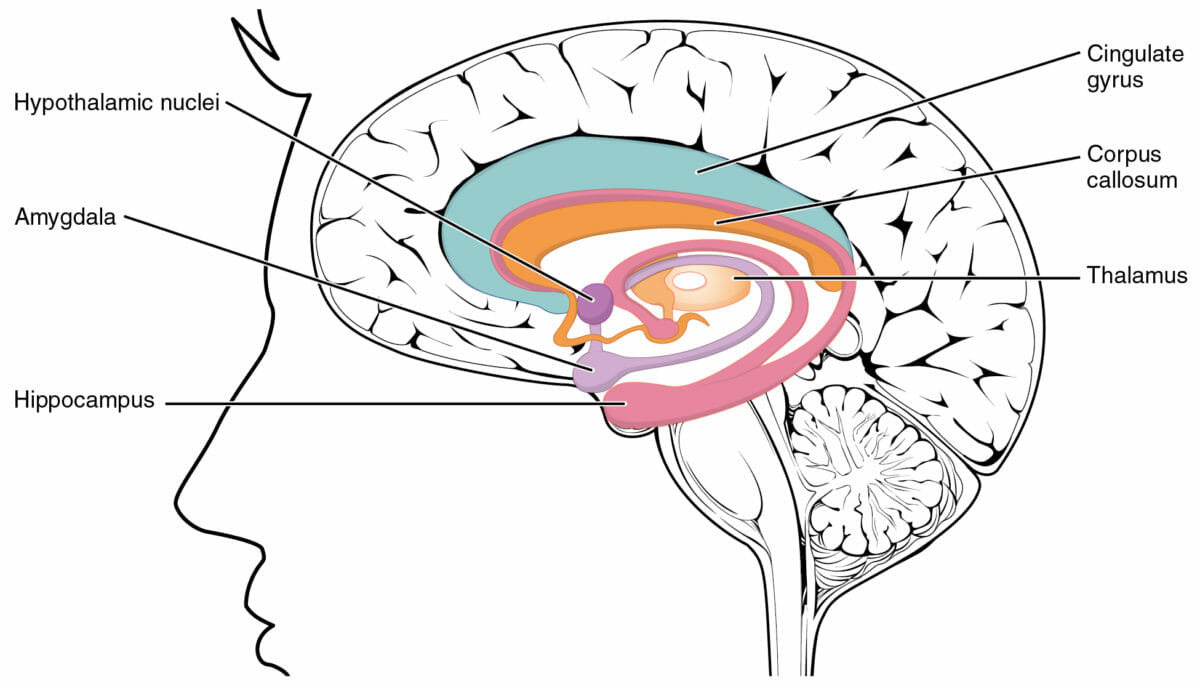
The Papez circuit Papez circuit Limbic System: Anatomy exists in all mammals and is important for memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment development. It is located in the center of the limbic system Limbic system The limbic system is a neuronal network that mediates emotion and motivation, while also playing a role in learning and memory. The extended neural network is vital to numerous basic psychological functions and plays an invaluable role in processing and responding to environmental stimuli. Limbic System: Anatomy, which is present above the brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification stem. The Papez circuit Papez circuit Limbic System: Anatomy plays a vital role in social behavior, solicitude, love, fear, and learning by imitation.
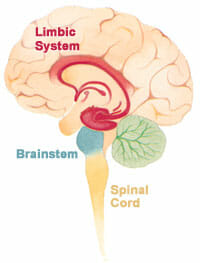
Limbic system
Image: “Brain limbic system” by Pixelsquid. License: Public Domain, edited by Lecturio.The Papez circuit Papez circuit Limbic System: Anatomy is a chain of neurons Neurons The basic cellular units of nervous tissue. Each neuron consists of a body, an axon, and dendrites. Their purpose is to receive, conduct, and transmit impulses in the nervous system. Nervous System: Histology named after its discoverer James Papez. Research Research Critical and exhaustive investigation or experimentation, having for its aim the discovery of new facts and their correct interpretation, the revision of accepted conclusions, theories, or laws in the light of newly discovered facts, or the practical application of such new or revised conclusions, theories, or laws. Conflict of Interest on the tasks of the Papez circuit Papez circuit Limbic System: Anatomy for memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment performance is ongoing. However, the assumption that the circuit controls anger and rage is already outdated, as it has been discovered that the circuit is even more complex than Papez had thought.
It is currently believed that the Papez circuit Papez circuit Limbic System: Anatomy plays a role in memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment storage by transferring information from the primary memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment (short-term memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment) to the secondary (long-term memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment) or tertiary memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment (an independent component of long-term memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment).
The Papez circuit Papez circuit Limbic System: Anatomy proceeds as follows: hippocampus → fornix Fornix Vagina, Vulva, and Pelvic Floor: Anatomy → mammillary body in the hypothalamus Hypothalamus The hypothalamus is a collection of various nuclei within the diencephalon in the center of the brain. The hypothalamus plays a vital role in endocrine regulation as the primary regulator of the pituitary gland, and it is the major point of integration between the central nervous and endocrine systems. Hypothalamus (corpora mammillaria) → cingulate cortex → hippocampus
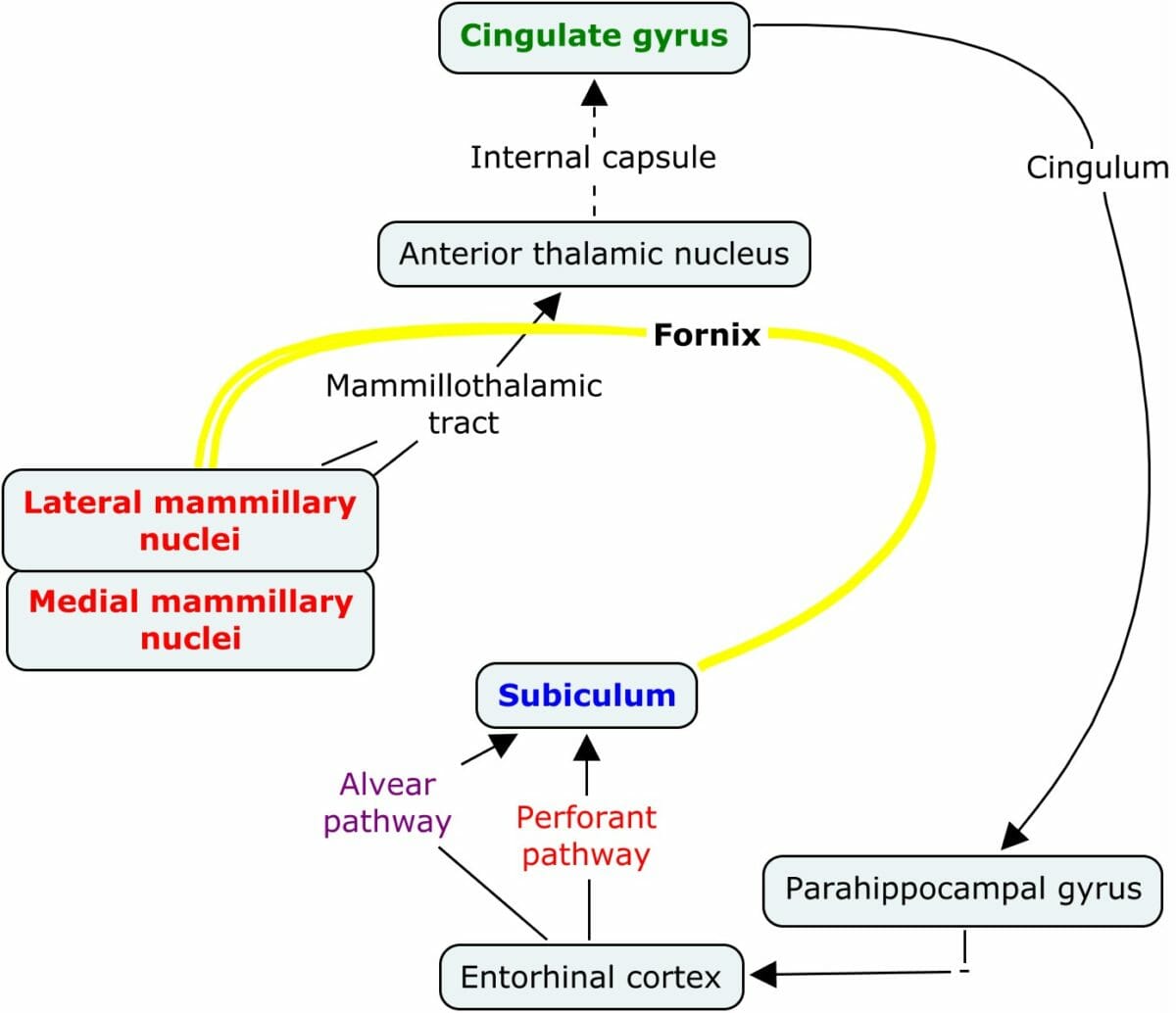
Papez circuit
Image: “Papez Circuit” by مستخدم:NotMySecondOpinion. License: Public DomainThe specialist term for mind and memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment is called the mnestic function. Some things are easier to remember than others. For example, important events are easier to remember than those that hold no meaning, and positive experiences are easier to remember than neutral experiences. Moreover, the process of remembering is easier in a prevailing positive mood, which also means that remembering things is more difficult in a state of fatigue Fatigue The state of weariness following a period of exertion, mental or physical, characterized by a decreased capacity for work and reduced efficiency to respond to stimuli. Fibromyalgia or grief.
Note: Encoding is the process of transferring sensory Sensory Neurons which conduct nerve impulses to the central nervous system. Nervous System: Histology information into a construct, which is then stored in our memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment system. Working memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment stores information for immediate use as part of mental activity (i.e., learning or problem solving).
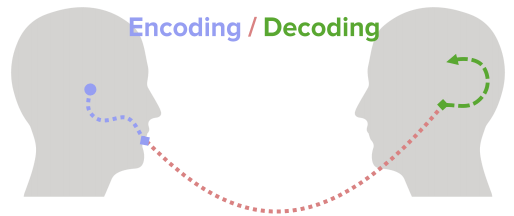
Schematic of the encoding/decoding model of communication in which the sender or “encoder” uses verbal and nonverbal symbols to deliver a message. The decoder or receiver then interprets the message.
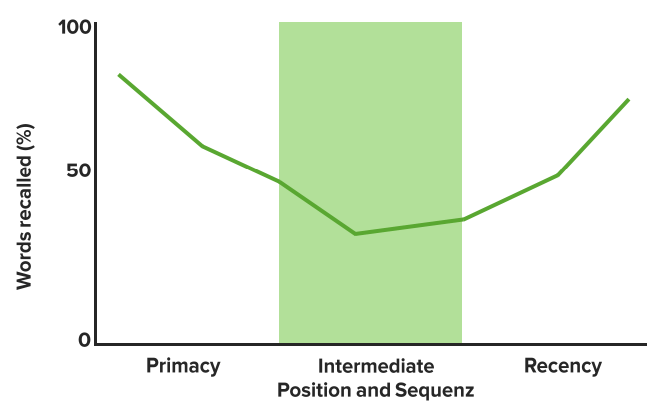
Image by Lecturio.The primary effect is a cognitive bias Bias Epidemiological studies are designed to evaluate a hypothesized relationship between an exposure and an outcome; however, the existence and/or magnitude of these relationships may be erroneously affected by the design and execution of the study itself or by conscious or unconscious errors perpetrated by the investigators or the subjects. These systematic errors are called biases. Types of Biases that results in a subject recalling the 1st items on a list.
The recency effect is a cognitive bias Bias Epidemiological studies are designed to evaluate a hypothesized relationship between an exposure and an outcome; however, the existence and/or magnitude of these relationships may be erroneously affected by the design and execution of the study itself or by conscious or unconscious errors perpetrated by the investigators or the subjects. These systematic errors are called biases. Types of Biases that results in a subject recalling the last items on a list.
Humans have declarative memory Declarative Memory Geriatric Changes (explicit memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment) and procedural memory Procedural memory Dissociative Amnesia (implicit memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment). Declarative memory Declarative Memory Geriatric Changes stores information that can be reproduced because humans are conscious of the experience. In contrast, procedural memory Procedural memory Dissociative Amnesia stores experiences for which one has no direct memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment of the learning process. Nevertheless, this type of memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment influences our behavior. A classic example of procedural memory Procedural memory Dissociative Amnesia is the learning of a new language.
The ultra-short-term memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment receives stimuli from sensory Sensory Neurons which conduct nerve impulses to the central nervous system. Nervous System: Histology organs in the form of neuronal excitation. This process has a duration of < 1 second, and perception Perception The process by which the nature and meaning of sensory stimuli are recognized and interpreted. Psychiatric Assessment is via the eyes or ears. Ultra-short-term memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment via the eye is referred to as iconic memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment, whereas that via the ears is known as echoic memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment (it perishes just as fast). Only the stimuli that reach the short-term memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment remain, as ultra-short-term memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment has no storage capabilities.
Memories in the primary (short-term/working) memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment are available for as long as we occupy ourselves with them. If that process is interrupted, the memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment is lost too. Memories that begin in the primary memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment can be available permanently, but only if they are transferred to the long-term memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment. Short-term memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment is the usual transitory path for experiences to pass into long-term memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment; however, this is occasionally short-circuited so that information can pass directly from the sensory Sensory Neurons which conduct nerve impulses to the central nervous system. Nervous System: Histology memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment to the long-term memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment.
The hippocampus, located in the cerebral cortex Cerebral cortex The cerebral cortex is the largest and most developed part of the human brain and CNS. Occupying the upper part of the cranial cavity, the cerebral cortex has 4 lobes and is divided into 2 hemispheres that are joined centrally by the corpus callosum. Cerebral Cortex: Anatomy, is involved in transmitting information from the primary memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment to the long-term memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment. The hippocampus is thought to be involved in this process because when lesions appear in the hippocampus, only the short-term memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment remains intact. Another term for primary memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment is labile memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment, as it is very unstable. A single distraction is enough to forget the information that has been perceived or heard. Calcium Calcium A basic element found in nearly all tissues. It is a member of the alkaline earth family of metals with the atomic symbol ca, atomic number 20, and atomic weight 40. Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the body and combines with phosphorus to form calcium phosphate in the bones and teeth. It is essential for the normal functioning of nerves and muscles and plays a role in blood coagulation (as factor IV) and in many enzymatic processes. Electrolytes plays a major role in these processes.
Repetition is particularly important for storing memories in long-term memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment. This concept is easily understandable when the high amount of repetition required to learn new movement patterns is considered, e.g., when learning a new sport.
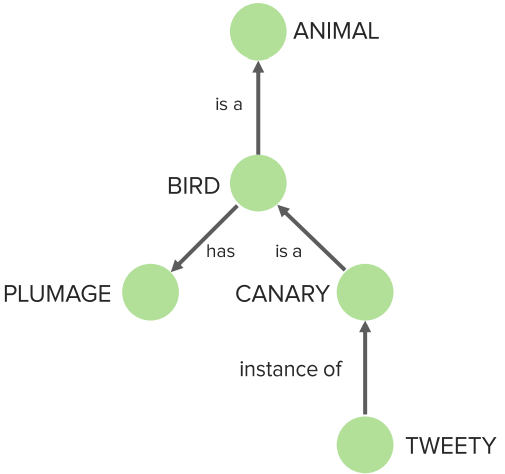
Example of a semantic network as an approach to storing information by representing the semantic relations between concepts
Image by Lecturio.The dual-coding hypothesis Hypothesis A hypothesis is a preliminary answer to a research question (i.e., a “guess” about what the results will be). There are 2 types of hypotheses: the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis. Statistical Tests and Data Representation indicates that it is easier to remember words with associated images.
The method of loci involves imagining moving through a familiar place and having stops or loci.
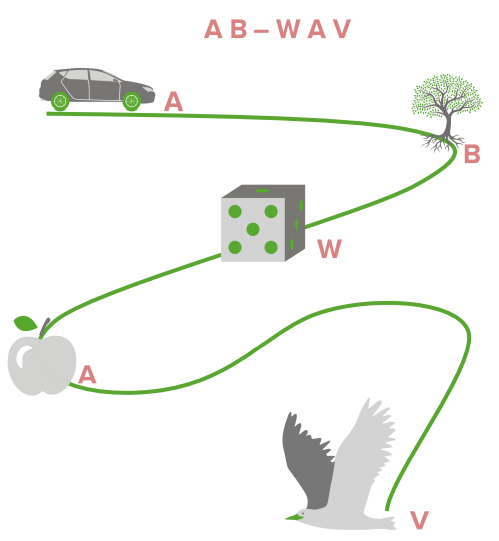
Schematic example of the method of loci, also called the journey method or the memory journey, which is a memory-enhancement strategy based on visual imagery that enhances information recall
Image by Lecturio.The self-reference effect involves making new information personally relevant, e.g., “I live on Beatrice Ave …”
The hippocampus plays an important role in learning. The physiologic substrate Substrate A substance upon which the enzyme acts. Basics of Enzymes of learning consists of continuous electrophysiologic, morphologic, and molecular changes in nerve cells. Long-term potentiation is necessary for the long-term availability of information. It facilitates the stimulation of afferent Afferent Neurons which conduct nerve impulses to the central nervous system. Nervous System: Histology axons Axons Nerve fibers that are capable of rapidly conducting impulses away from the neuron cell body. Nervous System: Histology over a period of weeks and also leads to greater calcium Calcium A basic element found in nearly all tissues. It is a member of the alkaline earth family of metals with the atomic symbol ca, atomic number 20, and atomic weight 40. Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the body and combines with phosphorus to form calcium phosphate in the bones and teeth. It is essential for the normal functioning of nerves and muscles and plays a role in blood coagulation (as factor IV) and in many enzymatic processes. Electrolytes influx.
Thoughts stored in the long-term memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment are available during the entire lifespan of that individual. The process of creating long-term memories is mediated by neurotransmitters such as glutamate Glutamate Derivatives of glutamic acid. Included under this heading are a broad variety of acid forms, salts, esters, and amides that contain the 2-aminopentanedioic acid structure. Synthesis of Nonessential Amino Acids ( glutamic acid Glutamic acid A non-essential amino acid naturally occurring in the l-form. Glutamic acid is the most common excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Urea Cycle).
The highly complex system of learning and memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment is susceptible to malfunctions. If anomalies occur, the differential diagnosis must be made with the greatest care, because even changes in the mineral balance of the body can lead to disorders that give the impression of a disease (e.g., calcium Calcium A basic element found in nearly all tissues. It is a member of the alkaline earth family of metals with the atomic symbol ca, atomic number 20, and atomic weight 40. Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the body and combines with phosphorus to form calcium phosphate in the bones and teeth. It is essential for the normal functioning of nerves and muscles and plays a role in blood coagulation (as factor IV) and in many enzymatic processes. Electrolytes deficiency). Furthermore, cases of dementia Dementia Major neurocognitive disorders (NCD), also known as dementia, are a group of diseases characterized by decline in a person’s memory and executive function. These disorders are progressive and persistent diseases that are the leading cause of disability among elderly people worldwide. Major Neurocognitive Disorders are increasing, which is partly due to the increase in life expectancy Life expectancy Based on known statistical data, the number of years which any person of a given age may reasonably expected to live. Population Pyramids.
Amnesia is a memory disorder in which an individual loses access to stored information. “Amnesia” is derived from the Greek words a (without) and mnémē ( memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment). Amnesia is not an independent disease, but the symptom of a disease or the consequence of an influence on the brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification. The influence can be internal or external.
Individuals with amnesia cannot recall prior experiences or knowledge; this can affect either all or only certain parts and types of information. For example, patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship can lose access to memories from certain stages of their lives. In most cases, they can remember events that occurred long ago rather than events that occurred recently. Several forms of amnesia cannot be differentiated from each other; however, the following variants are of importance:
Alzheimer disease Alzheimer disease As the most common cause of dementia, Alzheimer disease affects not only many individuals but also their families. Alzheimer disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that causes brain atrophy and presents with a decline in memory, cognition, and social skills. Alzheimer Disease is characterized by variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables degrees of cortical atrophy Atrophy Decrease in the size of a cell, tissue, organ, or multiple organs, associated with a variety of pathological conditions such as abnormal cellular changes, ischemia, malnutrition, or hormonal changes. Cellular Adaptation, seen as gyral narrowing and sulcal widening, mostly in the frontal Frontal The bone that forms the frontal aspect of the skull. Its flat part forms the forehead, articulating inferiorly with the nasal bone and the cheek bone on each side of the face. Skull: Anatomy, temporal, and parietal Parietal One of a pair of irregularly shaped quadrilateral bones situated between the frontal bone and occipital bone, which together form the sides of the cranium. Skull: Anatomy lobes. If there is marked atrophy Atrophy Decrease in the size of a cell, tissue, organ, or multiple organs, associated with a variety of pathological conditions such as abnormal cellular changes, ischemia, malnutrition, or hormonal changes. Cellular Adaptation, there will be compensatory ventricular enlargement ( hydrocephalus Hydrocephalus Excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid within the cranium which may be associated with dilation of cerebral ventricles, intracranial. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage ex vacuo) secondary to the reduced brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification volume. The outcome is the impaired relay of information. Furthermore, AD AD The term advance directive (AD) refers to treatment preferences and/or the designation of a surrogate decision-maker in the event that a person becomes unable to make medical decisions on their own behalf. Advance directives represent the ethical principle of autonomy and may take the form of a living will, health care proxy, durable power of attorney for health care, and/or a physician’s order for life-sustaining treatment. Advance Directives may make information processing or learning nearly impossible. The basic abnormality in AD AD The term advance directive (AD) refers to treatment preferences and/or the designation of a surrogate decision-maker in the event that a person becomes unable to make medical decisions on their own behalf. Advance directives represent the ethical principle of autonomy and may take the form of a living will, health care proxy, durable power of attorney for health care, and/or a physician’s order for life-sustaining treatment. Advance Directives is the accumulation of Aβ and tau proteins Proteins Linear polypeptides that are synthesized on ribosomes and may be further modified, crosslinked, cleaved, or assembled into complex proteins with several subunits. The specific sequence of amino acids determines the shape the polypeptide will take, during protein folding, and the function of the protein. Energy Homeostasis in specific regions of the brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification due to excessive production and defective removal. Amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles Neurofibrillary Tangles Abnormal structures located in various parts of the brain and composed of dense arrays of paired helical filaments (neurofilaments and microtubules). These double helical stacks of transverse subunits are twisted into left-handed ribbon-like filaments that likely incorporate the following proteins: (1) the intermediate filaments: medium- and high-molecular-weight neurofilaments; (2) the microtubule-associated proteins map-2 and tau; (3) actin; and (4) ubiquitins. As one of the hallmarks of alzheimer disease, the neurofibrillary tangles eventually occupy the whole of the cytoplasm in certain classes of cell in the neocortex, hippocampus, brain stem, and diencephalon. The number of these tangles, as seen in post mortem histology, correlates with the degree of dementia during life. Some studies suggest that tangle antigens leak into the systemic circulation both in the course of normal aging and in cases of alzheimer disease. Alzheimer Disease are the 2 pathologic hallmarks of AD AD The term advance directive (AD) refers to treatment preferences and/or the designation of a surrogate decision-maker in the event that a person becomes unable to make medical decisions on their own behalf. Advance directives represent the ethical principle of autonomy and may take the form of a living will, health care proxy, durable power of attorney for health care, and/or a physician’s order for life-sustaining treatment. Advance Directives.
The regions of the brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification involved in processing information and memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment performance are particularly affected by AD AD The term advance directive (AD) refers to treatment preferences and/or the designation of a surrogate decision-maker in the event that a person becomes unable to make medical decisions on their own behalf. Advance directives represent the ethical principle of autonomy and may take the form of a living will, health care proxy, durable power of attorney for health care, and/or a physician’s order for life-sustaining treatment. Advance Directives.
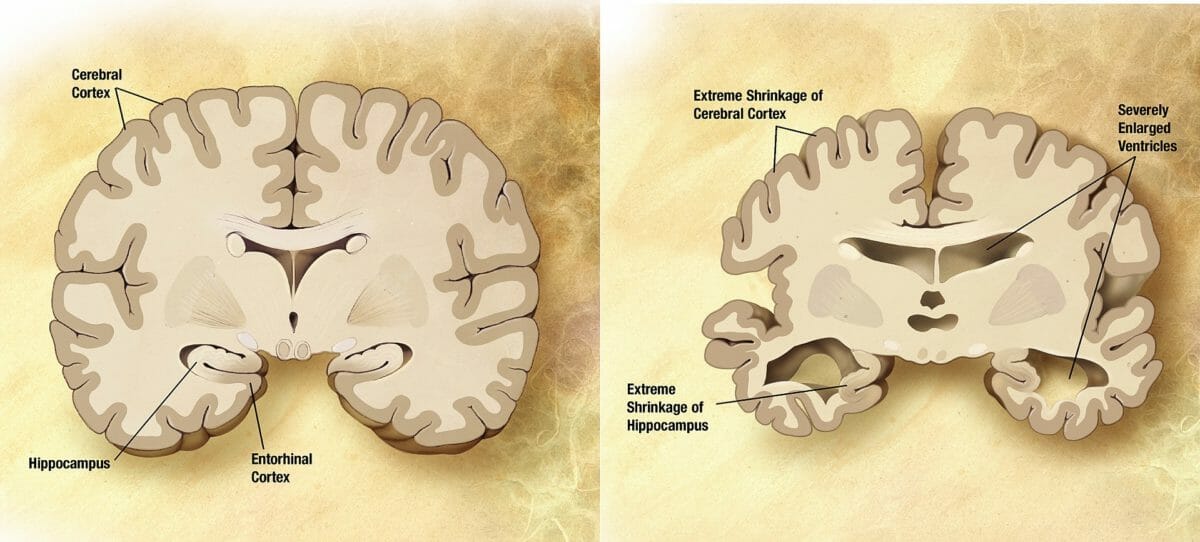
Left: healthy brain
Right: brain affected by Alzheimer disease