El cáncer de pulmón es la principal causa de muerte relacionada con el cáncer y se define como la transformación maligna del tejido pulmonar. La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos están relacionados con el consumo de tabaco a largo plazo. La enfermedad suele clasificarse histológicamente como cáncer de pulmón de células pequeñas o cáncer de pulmón de células no pequeñas. El perfil molecular del cáncer ofrece una mejor distinción del comportamiento biológico del tumor Tumor Inflammation, el pronóstico y las opciones de tratamiento. Los LOS Neisseria síntomas incluyen tos TOS Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a broad term used for a spectrum of syndromes related to the general region of the thoracic outlet, which involves the compression or irritation of elements of the brachial plexus, subclavian artery, or subclavian vein. Thoracic Outlet Syndrome, disnea, pérdida de peso y molestias torácicas. La propagación regional y las metástasis provocan síntomas y complicaciones adicionales en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum función de la localización y él ( los LOS Neisseria) órgano(s) afectado(s). Los LOS Neisseria síndromes paraneoplásicos relacionados incluyen la hipercalcemia, la hiponatremia, el síndrome de Lambert-Eaton, el síndrome de Cushing, la polidermatomiositis y la dermatomiositis. El diagnóstico definitivo y la estadificación se realizan mediante una biopsia, el estudio con pruebas de biomarcadores para determinar la presencia de mutaciones genéticas y la imagenología. El tratamiento depende del estadio del cáncer y el perfil molecular asociado. El cáncer de pulmón posee en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum líneas generales un mal pronóstico.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Subtipos:
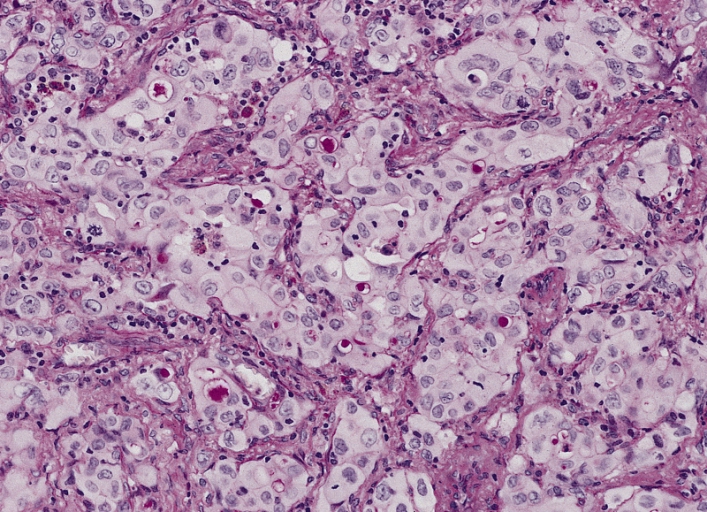
Adenocarcinoma de pulmón:
Un adenocarcinoma poco diferenciado (sólido) que muestra muchas células con vacuolas de mucina
Subtipos:
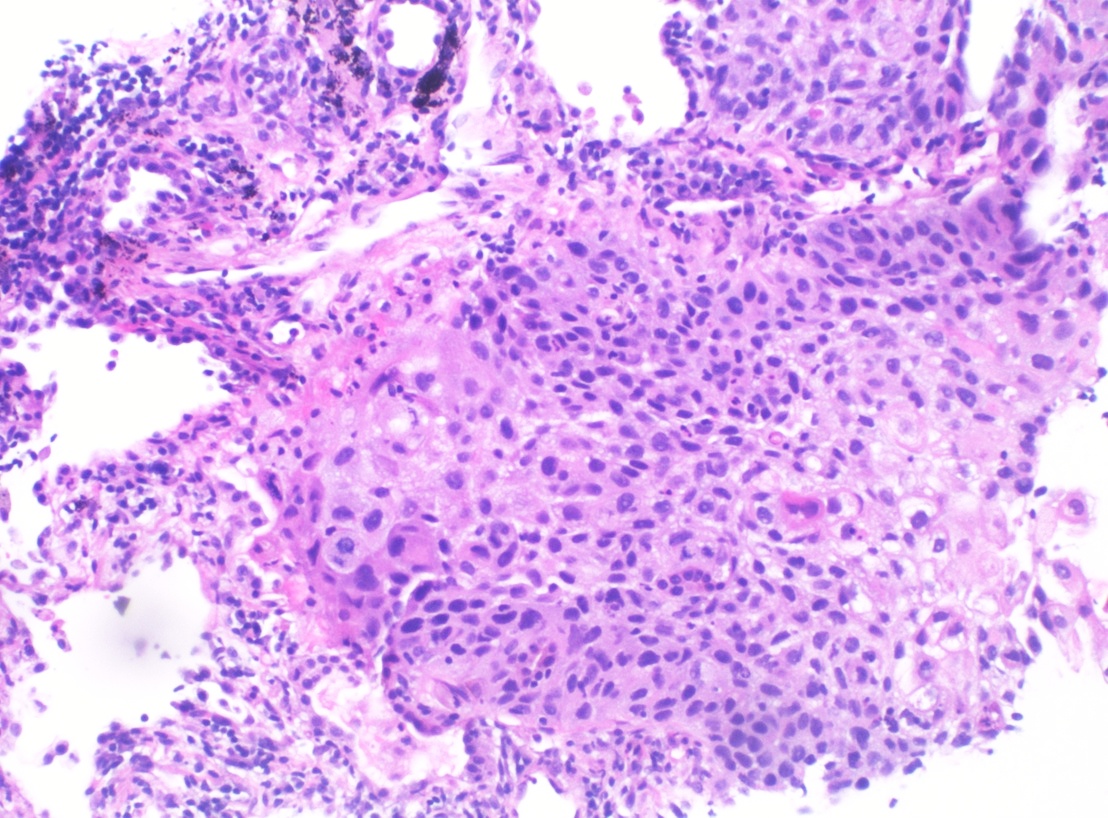
Carcinoma de células escamosas en la biopsia de pulmón:
Histopatología del carcinoma de células escamosas poco diferenciado de pulmón (tinción HyE)
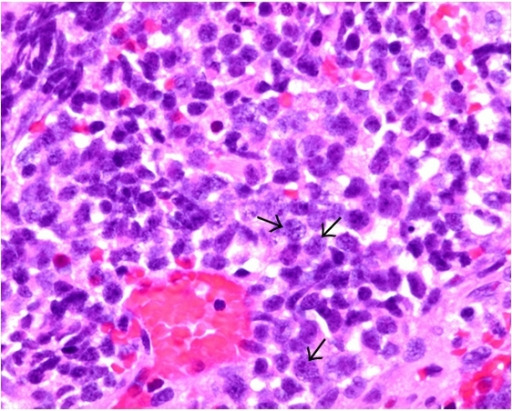
Carcinoma de células pequeñas:
Las células tumorales (véanse las flechas) presentan características de carcinoma de células pequeñas, entre las que se incluyen el moldeado nuclear, una elevada relación núcleo:citoplasma y núcleos con un patrón de cromatina fino o de sal y pimienta en la tinción de H&E.
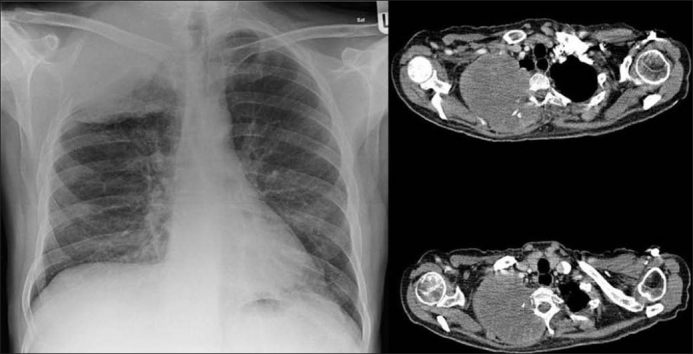
El tumor de Pancoast:
La radiografía de tórax de la izquierda muestra una neoplasia pulmonar derecha que invade la costilla y la pared torácica. La tomografía computarizada de la derecha muestra el tumor invadiendo las costillas, la pared torácica y las vértebras torácicas.
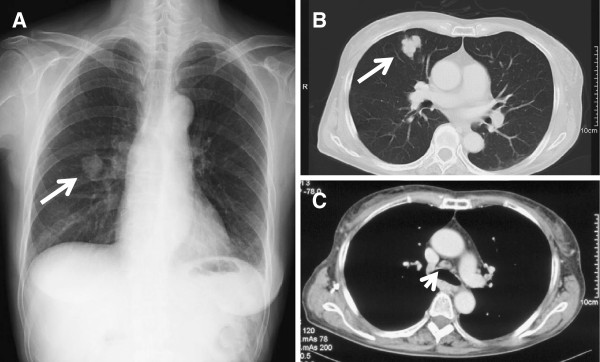
Radiografía de tórax y TC en el momento del diagnóstico:
(A): Radiografía de tórax que muestra la sombra de una masa en la zona media derecha (flecha).
(B, C): TC de tórax convencional que muestra una masa solitaria de 30 mm en S5 del pulmón derecho (flecha) y linfadenopatía mediastínica (cabeza de flecha).
Además de la TC, se utilizan las siguientes modalidades para determinar la extensión de la enfermedad con fines de estadificación:
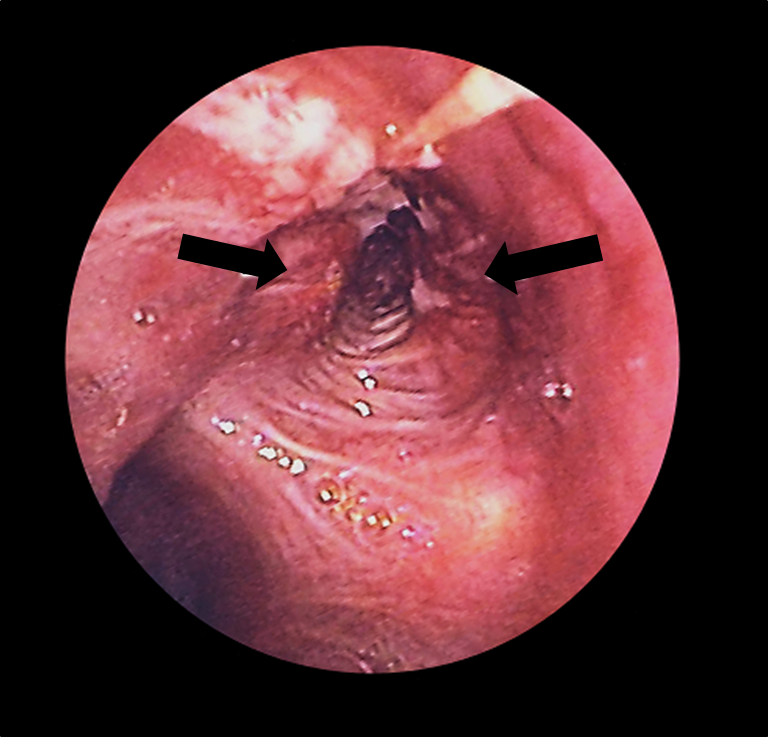
Broncoscopia:
Cáncer de pulmón (flechas) en el bronquio izquierdo visto con un broncoscopio
Las siguientes pruebas son posibles hallazgos para el cáncer de pulmón:
A continuación se presentan las directrices de estadificación de la 8va edición de la International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer Lung cancer Lung cancer is the malignant transformation of lung tissue and the leading cause of cancer-related deaths. The majority of cases are associated with long-term smoking. The disease is generally classified histologically as either small cell lung cancer or non-small cell lung cancer. Symptoms include cough, dyspnea, weight loss, and chest discomfort. Lung Cancer:
| Estadio | Descripción |
|---|---|
| Tx | El tumor Tumor Inflammation primario no puede ser evaluado. |
| T0 | No hay evidencia de un tumor Tumor Inflammation primario |
| Tis | Carcinoma in situ |
| T1 |
Tumor
Tumor
Inflammation ≤ 3 cm, rodeado de pulmón o
pleura
Pleura
The pleura is a serous membrane that lines the walls of the thoracic cavity and the surface of the lungs. This structure of mesodermal origin covers both lungs, the mediastinum, the thoracic surface of the diaphragm, and the inner part of the thoracic cage. The pleura is divided into a visceral pleura and parietal pleura.
Pleura: Anatomy visceral, sin invasión del bronquio principal:
|
| T2 |
Tumor
Tumor
Inflammation > 3 cm pero ≤ 5 cm, o:
|
| T3 T3 A T3 thyroid hormone normally synthesized and secreted by the thyroid gland in much smaller quantities than thyroxine (T4). Most T3 is derived from peripheral monodeiodination of T4 at the 5′ position of the outer ring of the iodothyronine nucleus. The hormone finally delivered and used by the tissues is mainly t3. Thyroid Hormones | Tumor Tumor Inflammation > 5 cm pero ≤ 7 cm, o nódulos tumorales asociados en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el mismo lóbulo que el tumor Tumor Inflammation primario o invasión directa de la pared torácica, del nervio frénico o del pericardio parietal Parietal One of a pair of irregularly shaped quadrilateral bones situated between the frontal bone and occipital bone, which together form the sides of the cranium. Skull: Anatomy |
| T4 T4 The major hormone derived from the thyroid gland. Thyroxine is synthesized via the iodination of tyrosines (monoiodotyrosine) and the coupling of iodotyrosines (diiodotyrosine) in the thyroglobulin. Thyroxine is released from thyroglobulin by proteolysis and secreted into the blood. Thyroxine is peripherally deiodinated to form triiodothyronine which exerts a broad spectrum of stimulatory effects on cell metabolism. Thyroid Hormones | Tumor Tumor Inflammation > 7 cm, o nódulos tumorales asociados en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un lóbulo ipsilateral diferente al AL Amyloidosis tumor Tumor Inflammation primario, o invasión de diafragma, mediastino, corazón, grandes vasos, tráquea, esófago, nervio laríngeo recurrente, cuerpo vertebral o carina |
| Estadio | Descripción |
|---|---|
| Nx | No es posible evaluar los LOS Neisseria ganglios linfáticos regionales |
| N0 | No hay metástasis en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria ganglios linfáticos regionales |
| N1 | Ganglios linfáticos peribronquiales y/o hiliares ipsilaterales y afectación de los LOS Neisseria ganglios intrapulmonares |
| N2 | Afectación de los LOS Neisseria ganglios linfáticos mediastínicos y/o subcarinales ipsilaterales |
| N3 | Afectación de ganglio linfático mediastínico contralateral, hiliar contralateral, escaleno ipsilateral o contralateral, o del supraclavicular |
| Estadio | Descripción |
|---|---|
| M0 | No hay metástasis a distancia |
| M1 | Metástasis a distancia:
|
| Agrupación de estadios | Estadio TNM |
|---|---|
| Oculto |
|
| 0 |
|
| I |
|
| II |
|
| III |
|
| IV |
|
| Estadio (SCLC) | Descripción |
|---|---|
| Enfermedad limitada | |
| Enfermedad extensa |
|
Cirugía:
Quimioterapia:
Radioterapia:
Terapias dirigidas:
Inmunoterapia:
| Estadio (NSCLC) | Abordaje terapéutico |
|---|---|
| Estadio I-II |
|
| Estadio III |
|
| Estadio IV* |
|
| Estadio (SCLC) | Descripción |
|---|---|
| Enfermedad limitada |
|
| Enfermedad extensa* |
|
La modificación de los LOS Neisseria factores de riesgo es más eficaz que el tamizaje para reducir la mortalidad por cáncer de pulmón.