Pica is an eating disorder characterized by a desire or recurrent compulsion to eat substances that are nonnutritive and not food. These compulsions Compulsions Repetitive behaviors or mental acts that the individual is driven to perform in relation to an obsession. Obsessive-compulsive Disorder (OCD) and ingested substances are inappropriate for age or culture. Pica manifests most commonly during childhood and pregnancy Pregnancy The status during which female mammals carry their developing young (embryos or fetuses) in utero before birth, beginning from fertilization to birth. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care and, therefore, carry a high risk for malnutrition Malnutrition Malnutrition is a clinical state caused by an imbalance or deficiency of calories and/or micronutrients and macronutrients. The 2 main manifestations of acute severe malnutrition are marasmus (total caloric insufficiency) and kwashiorkor (protein malnutrition with characteristic edema). Malnutrition in children in resource-limited countries and anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship usually present with nutritional deficiencies or complications from ingesting nonfood substances. Management aims are to stabilize patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship medically and then provide appropriate behavioral therapy as a 1st-line option.
Last updated: Apr 4, 2025
Pica is an eating disorder of unclear etiology characterized by a desire or compulsion to eat substances that are not food in a context that is not developmentally, socially, or culturally appropriate.
The specific substances that are craved vary:
Diagnosis of pica is clinical, based on observed patterns of behavior:
Further testing should be directed by etiology, symptomatology Symptomatology Scarlet Fever, and ingested substances:
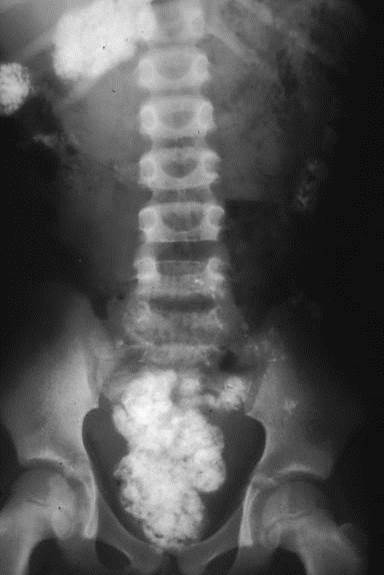
Abdominal X-ray of a patient with pica:
Patients with pica have a compulsion to ingest nonnutritive material. Some patients fixate on eating earth, which can cause bowel blockage. Abdominal X-rays can help identify the ingested foreign substance (bright material seen in the pelvis of the patient).
Pica is classified as an eating disorder and can have features in common with other such disorders.