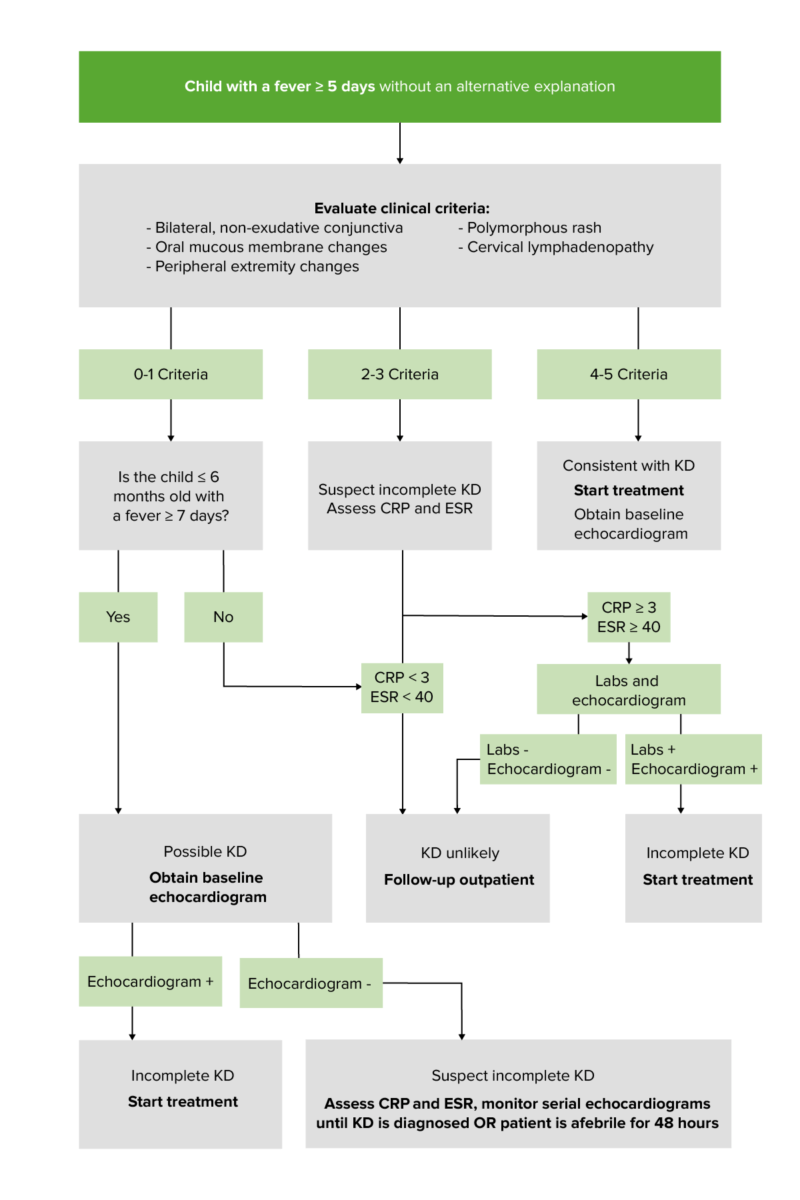
La enfermedad de Kawasaki, también conocida como síndrome ganglionar mucocutáneo o poliarteritis infantil, es una vasculitis Vasculitis Inflammation of any one of the blood vessels, including the arteries; veins; and rest of the vasculature system in the body. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus necrotizante de vasos de mediano calibre que afecta predominantemente a los LOS Neisseria niños < 5 años de edad. La etiología es desconocida actualmente, pero se postula que involucra a una combinación de factores ambientales y genéticos. Los LOS Neisseria sistemas implicados son múltiples, pero la enfermedad muestra una predilección por las arterias coronarias, lo que puede llevar a serias complicaciones. El diagnóstico puede realizarse basándose en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum criterios clínicos. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria casos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria que se puede sospechar una enfermedad de Kawasaki incompleta, el diagnóstico puede apoyarse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum estudios de laboratorio y ecocardiografía. El tratamiento incluye inmunoglobulina intravenosa y dosis altas de aspirina. El seguimiento requiere ecocardiogramas seriados para controlar la presencia de aneurismas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las arterias coronarias.
Last updated: May 14, 2025
La etiología de la enfermedad de Kawasaki es desconocida. Hay varias teorías:
Teoría de la respuesta inmunológica
Teoría de la predisposición genética
Teoría de los LOS Neisseria factores ambientales
Teoría de la infección
COVID-19 COVID-19 Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is an infectious disease caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) that mainly affects the respiratory system but can also cause damage to other body systems (cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, renal, and central nervous systems). y Síndrome inflamatorio multisistémico infantil
Durante la pandemia de COVID-19 COVID-19 Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is an infectious disease caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) that mainly affects the respiratory system but can also cause damage to other body systems (cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, renal, and central nervous systems). , se identificó una nueva afección hiperinflamatoria denominada Síndrome Inflamatorio Multisistémico Infantil (MIS-C, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) asociada a la infección por SARS-CoV-2.
La aparición del MIS-C ha HA Hemolytic anemia (HA) is the term given to a large group of anemias that are caused by the premature destruction/hemolysis of circulating red blood cells (RBCs). Hemolysis can occur within (intravascular hemolysis) or outside the blood vessels (extravascular hemolysis). Hemolytic Anemia reforzado las teorías de que la EK también puede ser desencadenada por agentes infecciosos.
La enfermedad de Kawasaki es una enfermedad sistémica e inflamatoria que afecta a las arterias de mediano calibre, especialmente a las coronarias.
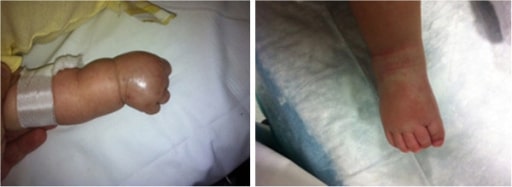
Edema y erupción polimorfa en las manos y los pies de un paciente de 3 meses de edad con enfermedad de Kawasaki
Imagen: “Patient’s limbs” por Unit of Broncho-Pneumology and Cystic Fibrosis, Department of Medical and Pediatric Science, University of Catania, Via Santa Sofia 78, Catania 95123, Italy. Licencia: CC BY 2.0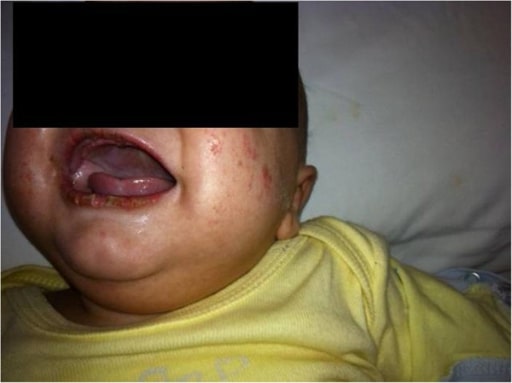
Fisura labial junto a una erupción polimorfa en la enfermedad de Kawasaki
Imagen: “Patient’s face” por Unit of Broncho-Pneumology and Cystic Fibrosis, Department of Medical and Pediatric Science, University of Catania, Via Santa Sofia 78, Catania 95123, Italy. Licencia: CC BY 2.0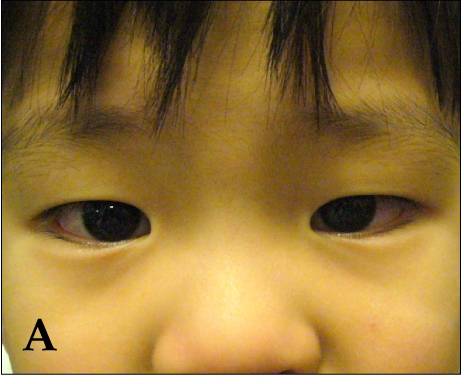
Conjuntivitis bilateral no exudativa observada en un paciente con enfermedad de Kawasaki
Imagen: “Kawasaki symptoms A” por Dong Soo Kim. Licencia: CC BY 2.0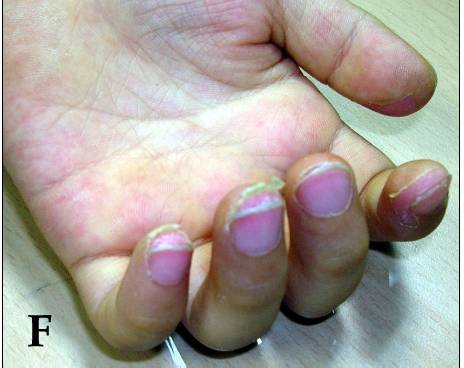
Descamación de las yemas de los dedos observada en enfermedad de Kawasaki a los 10–14 días
Imagen: “Desquamation of the fingers” por Dong Soo Kim. Licencia: CC BY 2.0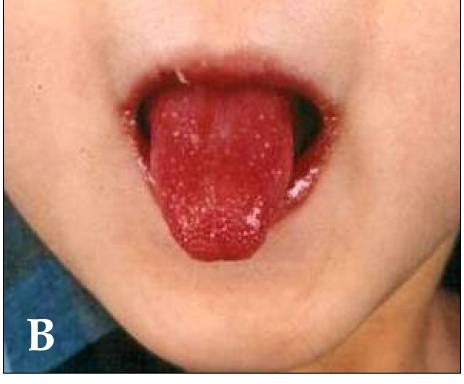
Lengua de fresa y labios rojos e hinchados con grietas verticales y hemorragias en un paciente con enfermedad de Kawasaki
Imagen: “Kawasaki disease” por Dong Soo Kim. Licencia: CC BY 2.0| Sistema | Manifestaciones |
|---|---|
| Gastrointestinal | Diarrea, dolor Dolor Inflammation abdominal, vómitos, disfunción hepática, pancreatitis Pancreatitis Inflammation of the pancreas. Pancreatitis is classified as acute unless there are computed tomographic or endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatographic findings of chronic pancreatitis. The two most common forms of acute pancreatitis are alcoholic pancreatitis and gallstone pancreatitis. Acute Pancreatitis, hidrops biliar, ascitis, infarto esplénico |
| Musculoesquelético | Poliartritis, artralgia |
| Sistema cardiovascular | Miocarditis, pericarditis Pericarditis Pericarditis is an inflammation of the pericardium, often with fluid accumulation. It can be caused by infection (often viral), myocardial infarction, drugs, malignancies, metabolic disorders, autoimmune disorders, or trauma. Acute, subacute, and chronic forms exist. Pericarditis, taquicardia, valvulopatía |
| Genitourinario | Uretritis, prostatitis Prostatitis Prostatitis is inflammation or an irritative condition of the prostate that presents as different syndromes: acute bacterial, chronic bacterial, chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain, and asymptomatic. Bacterial prostatitis is easier to identify clinically and the management (antibiotics) is better established. Prostatitis, cistitis, nefritis intersticial, síndrome nefrótico |
| Sistema nervioso central | Letargo, aumento de la irritabilidad, meningitis Meningitis Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes of the brain, and spinal cord. The causes of meningitis are varied, with the most common being bacterial or viral infection. The classic presentation of meningitis is a triad of fever, altered mental status, and nuchal rigidity. Meningitis aséptica, sordera neurosensorial |
| Respiratorio | Falta de aire, síntomas gripales, derrame pleural, tos TOS Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a broad term used for a spectrum of syndromes related to the general region of the thoracic outlet, which involves the compression or irritation of elements of the brachial plexus, subclavian artery, or subclavian vein. Thoracic Outlet Syndrome, rinorrea |
| Piel | Eritema e induración en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el lugar de vacunación con BCG BCG An active immunizing agent and a viable avirulent attenuated strain of Mycobacterium bovis, which confers immunity to mycobacterial infections. It is used also in immunotherapy of neoplasms due to its stimulation of antibodies and non-specific immunity. Cancer Immunotherapy (bacilo de Calmette-Guérin), líneas de Beau, gangrena de dedos |
| General | Irritabilidad, disminución de la ingesta, letargo |
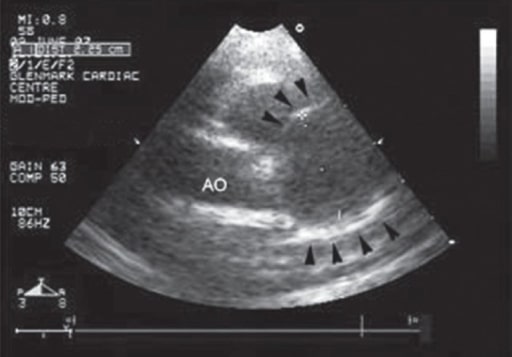
Vista ecocardiográfica a nivel de la válvula aórtica que muestra un aumento del tamaño de un aneurisma de la arteria coronaria (puntas de flecha) secundario a la enfermedad de Kawasaki
Imagen: “Follow-up echocardiography” por Department of Cardiology, Dr. Balabhai Nanavati Hospital, Mumbai, India. Licencia: CC BY 2.0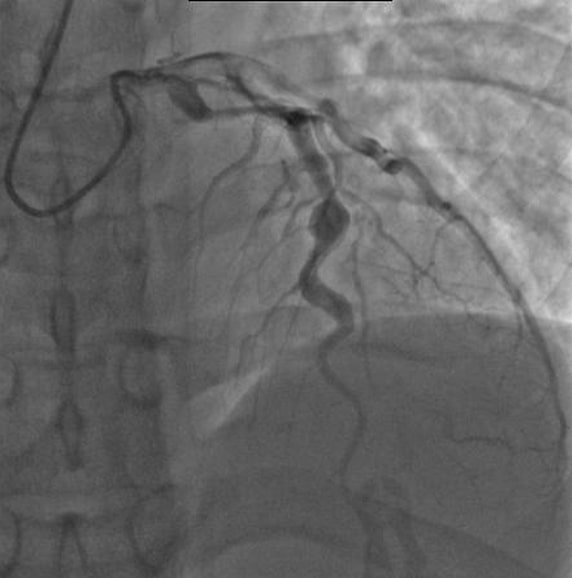
Angiografía de un paciente con enfermedad de Kawasaki que muestra la arteria coronaria descendente anterior ectásica, en la que el mayor aneurisma mide 6,5 mm de diámetro
Imagen: “Angiography showing ectatic LAD,” por mprice18. Licencia: CC BY 3.0CRASH y Burn ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés):
C –
Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis is a common inflammation of the bulbar and/or palpebral conjunctiva. It can be classified into infectious (mostly viral) and noninfectious conjunctivitis, which includes allergic causes. Patients commonly present with red eyes, increased tearing, burning, foreign body sensation, and photophobia.
Conjunctivitis (conjuntivitis)
R –
Rash
Rash
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (erupción)
A – Adenopathy (adenopatía)
S –
Strawberry tongue
Strawberry tongue
Kawasaki Disease (lengua de fresa)
H – Hands and feet (manos y pies)
Burn – (quemadura): fiebre
| Medicamento | Indicación |
|---|---|
| Clopidogrel Clopidogrel A ticlopidine analog and platelet purinergic p2y receptor antagonist that inhibits adenosine diphosphate-mediated platelet aggregation. It is used to prevent thromboembolism in patients with arterial occlusive diseases; myocardial infarction; stroke; or atrial fibrillation. Antiplatelet Drugs, dipiridamol y otros medicamentos antiplaquetarios | Para aneurismas de pequeño a mediano tamaño de las arterias coronarias y con un alto riesgo para la formación de trombos |
| Heparina de bajo peso molecular, warfarina y otros anticoagulantes | Para aneurismas grandes de las arterias coronarias y un alto riesgo de formación de trombos |
| Infliximab Infliximab A chimeric monoclonal antibody to tnf-alpha that is used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis; ankylosing spondylitis; psoriatic arthritis and Crohn’s disease. Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs), ciclofosfamida y ciclosporina | Casos refractarios con aneurisma coronario |
| Corticosteroides | Pacientes que no responden a los LOS Neisseria tratamientos y terapias estándar o que corren el riesgo de presentar resistencia a la inmunoglobulina intravenosa |
References: