La insuficiencia cardíaca es un síndrome clínico que se caracteriza por síntomas típicos (p. ej., disnea, hinchazón de tobillos y fatiga) que pueden ir acompañados de signos (p. ej., presión venosa yugular elevada, crepitaciones pulmonares y edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema periférico) causados por una anomalía cardíaca estructural o funcional, lo que resulta en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una reducción del gasto cardíaco o en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum presiones intracardíacas elevadas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum reposo o durante el esfuerzo. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la insuficiencia cardíaca, la alteración del llenado ventricular o de la eyección de sangre provoca fatiga, disnea y retención de líquidos o edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema. La ecocardiografía puede confirmar el diagnóstico y dar información sobre la fracción de eyección. El tratamiento está dirigido a la eliminación del exceso de líquido y a la disminución de la demanda de oxígeno del corazón. El pronóstico depende de la causa subyacente, del cumplimiento del tratamiento médico y de la presencia de comorbilidades.
Last updated: Sep 6, 2024
Los síntomas de insuficiencia cardíaca avanzada se pueden identificar con la frase I NEED HELP (“yo necesito ayuda” en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum Ingles):
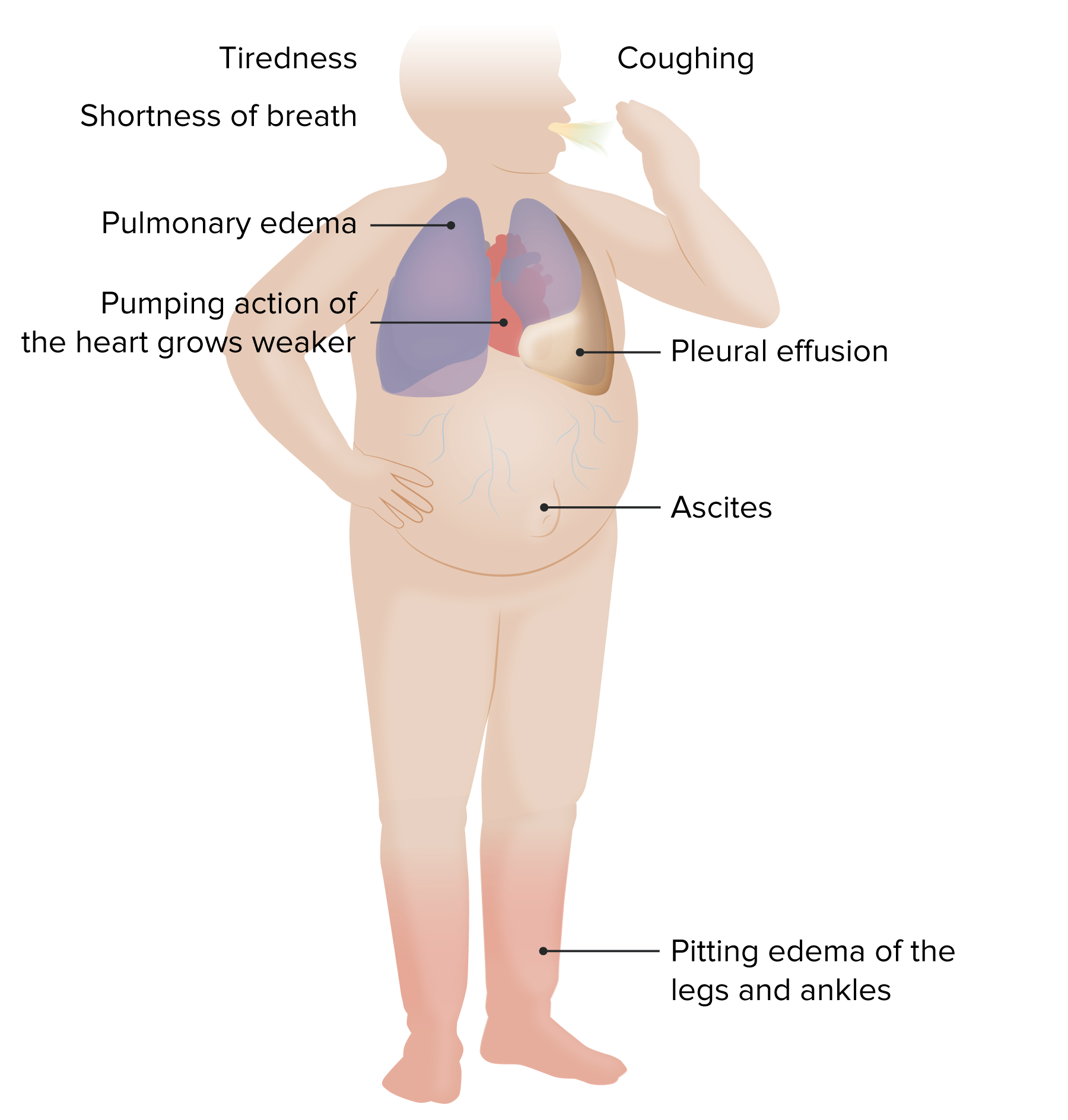
Síntomas/signos de insuficiencia cardíaca
Imagen por Lecturio.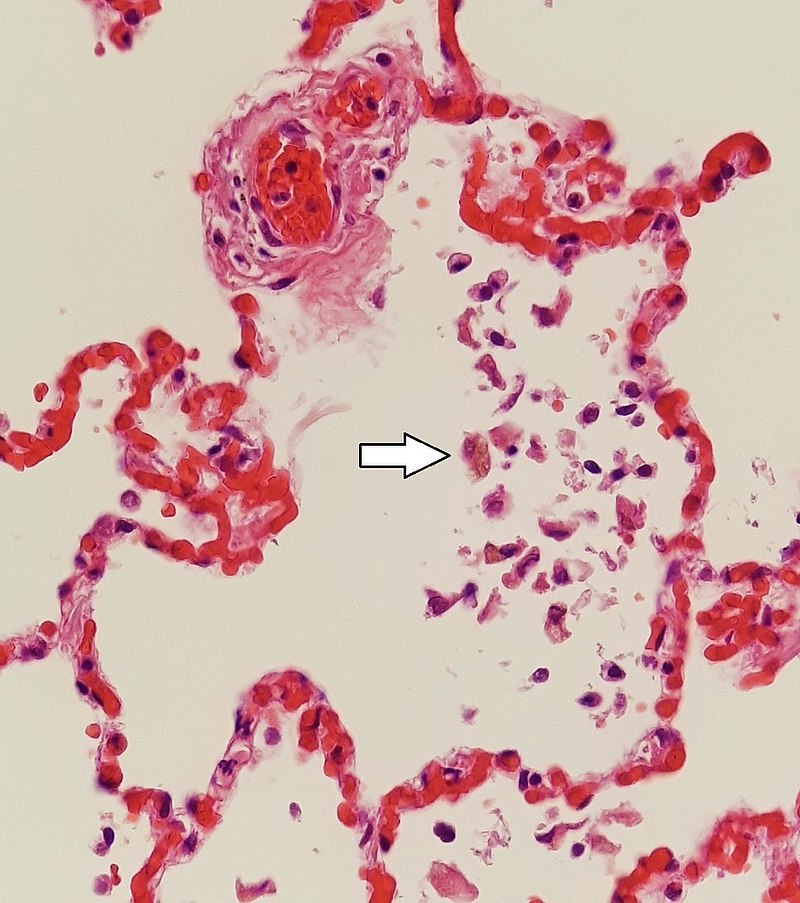
Los capilares pequeños y congestionados pueden reventar, dando lugar a una hemorragia intraalveolar marcada por macrófagos cargados de hemosiderina (flecha blanca). También conocidas como “células de insuficiencia cardíaca”, estas células indican insuficiencia cardíaca congestiva.
Imagen: “Siderophages (one indicated by white arrow) and pulmonary congestion, indicating left congestive heart failure” por Mikael Häggström, M.D. – Own work. Licencia: CC0 1.0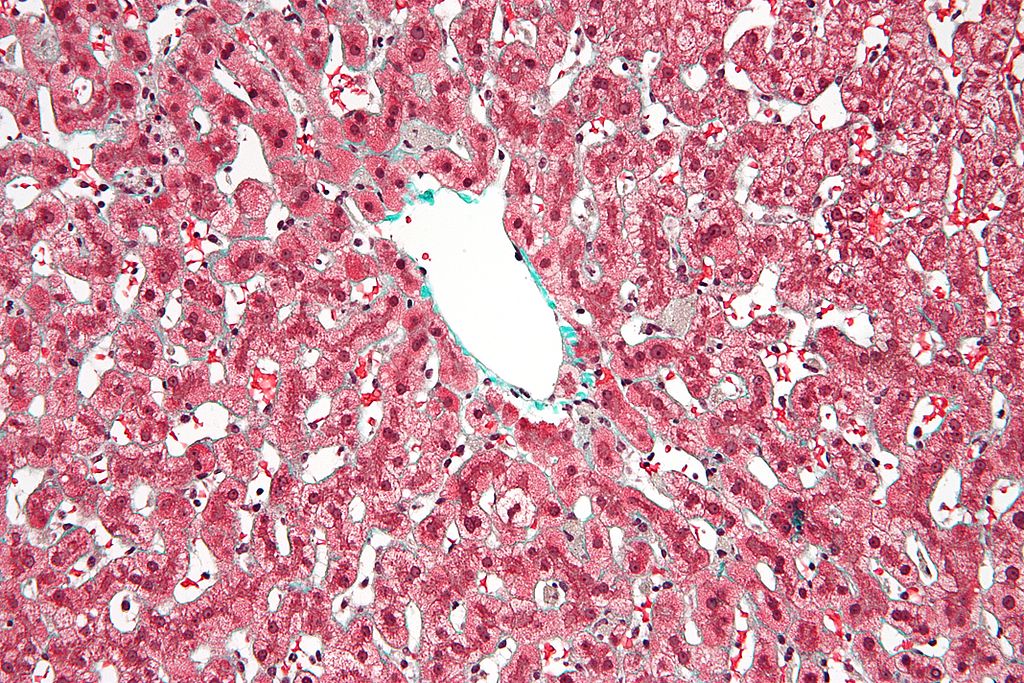
Micrografía de una hepatopatía congestiva o hígado en nuez moscada debido a una congestión venosa, generalmente debida a una insuficiencia cardíaca congestiva. Esto puede provocar una cirrosis cardíaca.
Imagen: “Congestive hepatopathy high mag” por Nephron – Own work. Licencia: CC BY-SA 3.0| Prueba | Hallazgos |
|---|---|
| BNP BNP A peptide that is secreted by the brain and the heart atria, stored mainly in cardiac ventricular myocardium. It can cause natriuresis; diuresis; vasodilation; and inhibits secretion of renin and aldosterone. It improves heart function. It contains 32 amino acids. Renal Sodium and Water Regulation/pro-BNP |
|
| Radiografía de tórax |
|
| ECG ECG An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphic representation of the electrical activity of the heart plotted against time. Adhesive electrodes are affixed to the skin surface allowing measurement of cardiac impulses from many angles. The ECG provides 3-dimensional information about the conduction system of the heart, the myocardium, and other cardiac structures. Electrocardiogram (ECG) |
|
| Ecocardiograma |
|
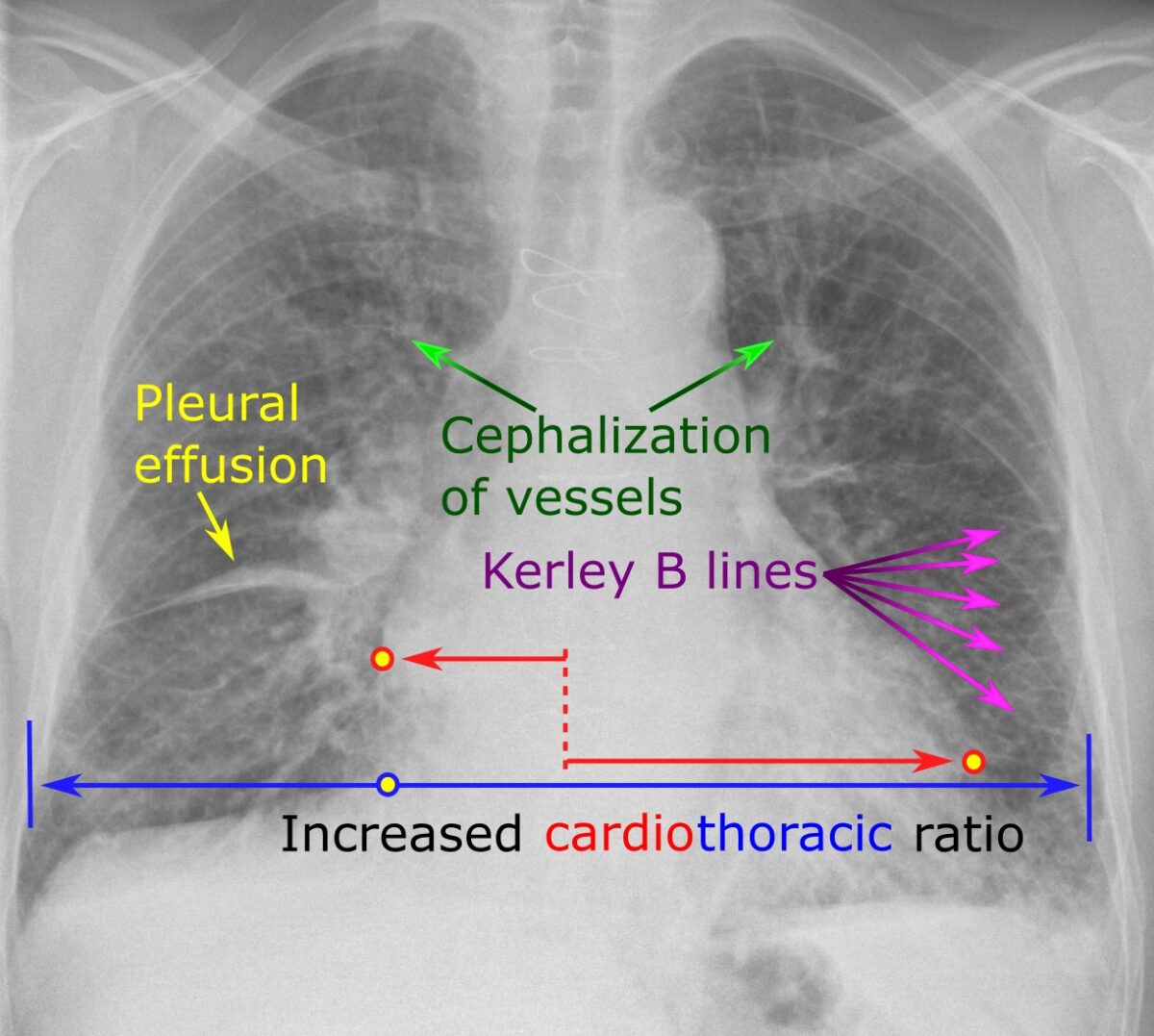
Radiografía de tórax que muestra los hallazgos característicos de la insuficiencia cardíaca
Imagen: “Chest radiograph with signs of congestive heart failure – annotated” por Mikael Häggström – Own work. Licencia: CC0 1.0Una buena mnemotecnia para recordar estos hallazgos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la radiografia de tórax es “ABCDE” ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés):
insuficiencia cardíaca, se realizan pruebas adicionales para determinar la etiología y la estratificación del riesgo mediante la clasificación del estadio de la insuficiencia cardíaca.
insuficiencia cardíaca inexplicada):
La descompensación aguda de la insuficiencia cardíaca provoca dificultad respiratoria, generalmente debido a la acumulación de líquido en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria pulmones ( edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema pulmonar).
Para recordar el tratamiento de la insuficiencia cardíaca aguda o la exacerbación de la insuficiencia cardíaca, recuerde la “LMNOP” ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés):
Las modificaciones del estilo de vida disminuyen la morbilidad y la mortalidad en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la insuficiencia cardíaca.
Resumen:
Clases de medicamentos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum detalle:
| Estadio A | Estadio B | Estadio C | Estadio D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum riesgo de insuficiencia cardíaca | Enfermedad cardíaca estructura, sin síntomas | Enfermedad cardíaca estructura con síntomas | IC IC Inhaled Anesthetics avanzada | |
| N/A | NYHA clase I | NYHA clase I–IV | NYHA IV | |
| Medidas generales | ||||
| Terapia farmacológica inicial | Según indicado por otros factores de riesgo |
|
|
|
| Terapia farmacológica secundaria(adicionales) | N/A | N/A |
En
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum clase II-IV, añadir:
|
|
Aparte de las complicaciones cardiovasculares, como las arritmias y la disfunción valvular, las complicaciones a largo plazo pueden ser:
Las siguientes afecciones son factores de riesgo y/o causas de la insuficiencia cardíaca congestiva:
Referencias