Las infecciones de transmisión sexual (ITS) o enfermedades de transmisión sexual (ETS) son infecciones que se propagan durante el coito vaginal, el sexo anal o el sexo oral. Los LOS Neisseria síntomas y signos pueden incluir secreción vaginal, secreción del pene, disuria, lesiones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la piel (e.g., verrugas, úlceras) en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum o alrededor de los LOS Neisseria genitales y dolor Dolor Inflammation pélvico. Algunas infecciones pueden provocar infertilidad y enfermedades crónicas debilitantes. Y algunas ITS pueden afectar a los LOS Neisseria lactantes por transmisión vertical. El diagnóstico de las ITS incluye una combinación de los LOS Neisseria antecedentes clínicos y sexuales completos, la evaluación de los LOS Neisseria factores de riesgo, un examen físico genitourinario específico y pruebas de laboratorio/cultivos específicos de la enfermedad. El tratamiento y la prevención incluyen una combinación de agentes antibióticos/antivirales y la educación del paciente sobre prácticas sexuales seguras.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Las infecciones se transmiten principalmente por vía sexual, lo que puede incluir sexo sin protección vaginal, anal u oral.
| Tipo de ITS | Organismo | Signos y síntomas |
|---|---|---|
| Chancroide | Haemophilus ducreyi Haemophilus ducreyi A species of Haemophilus that appears to be the pathogen or causative agent of the sexually transmitted disease, chancroid. Haemophilus |
|
| Clamidia | Chlamydia trachomatis Chlamydia trachomatis Type species of Chlamydia causing a variety of ocular and urogenital diseases. Chlamydia |
|
| Gonorrea | Neisseria gonorrhoeae Neisseria gonorrhoeae A species of gram-negative, aerobic bacteria primarily found in purulent venereal discharges. It is the causative agent of gonorrhea. Neisseria |
|
| Granuloma inguinal o donovanosis Donovanosis Donovanosis (also known as granuloma inguinale) is an STD caused by Klebsiella granulomatis and is mainly seen in tropical regions. The condition is characterized by chronic, progressive, ulcerating disease mostly affecting the genital region. Donovanosis | Klebsiella Klebsiella Klebsiella are encapsulated gram-negative, lactose-fermenting bacilli. They form pink colonies on MacConkey agar due to lactose fermentation. The main virulence factor is a polysaccharide capsule. Klebsiella pneumoniae is the most important pathogenic species. Klebsiella granulomatis |
|
| Linfogranuloma venéreo ( LGV LGV Subacute inflammation of the inguinal lymph glands caused by certain immunotypes of Chlamydia trachomatis. It is a sexually transmitted disease in the U.S. But is more widespread in developing countries. It is distinguished from granuloma venereum, which is caused by calymmatobacterium granulomatis. Chlamydial Infections) | Serovares L1, L2 y L3 de Chlamydia trachomatis Chlamydia trachomatis Type species of Chlamydia causing a variety of ocular and urogenital diseases. Chlamydia |
|
| Infección por Mycoplasma genitalium Mycoplasma genitalium A species of gram-negative bacteria originally isolated from urethral specimens of patients with non-gonococcal urethritis. In primates it exists in parasitic association with ciliated epithelial cells in the genital and respiratory tracts. Mycoplasma | Mycoplasma genitalium Mycoplasma genitalium A species of gram-negative bacteria originally isolated from urethral specimens of patients with non-gonococcal urethritis. In primates it exists in parasitic association with ciliated epithelial cells in the genital and respiratory tracts. Mycoplasma |
|
| Sífilis | Treponema pallidum Treponema pallidum The causative agent of venereal and non-venereal syphilis as well as yaws. Treponema |
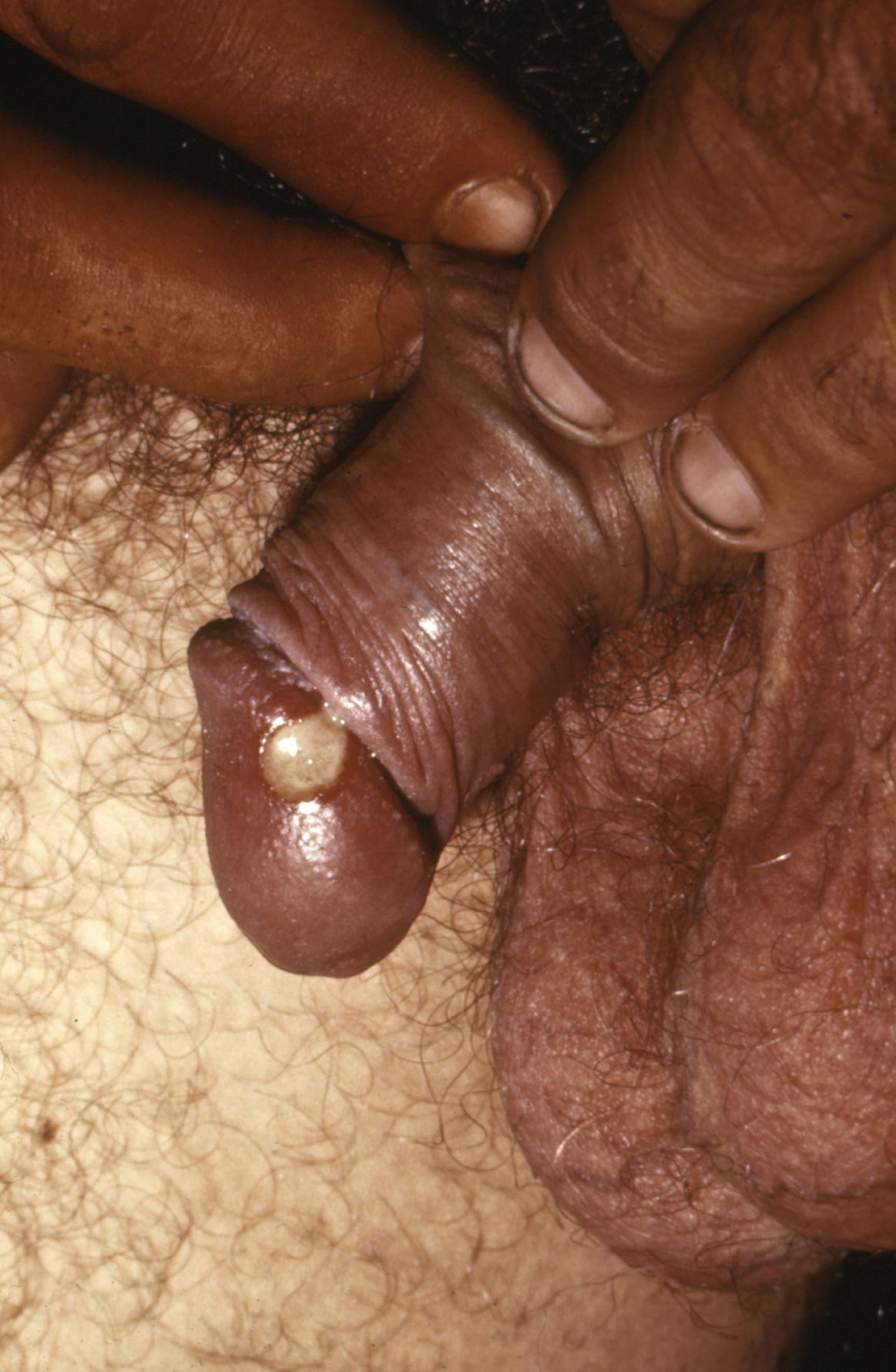
Chancroide: lesión de 1 cm en el glande del pene por Haemophilus ducreyi
Imagen: “Chancroid lesion haemophilus ducreyi PHIL 3728 lores” por Joe Miller. Licencia: Dominio Público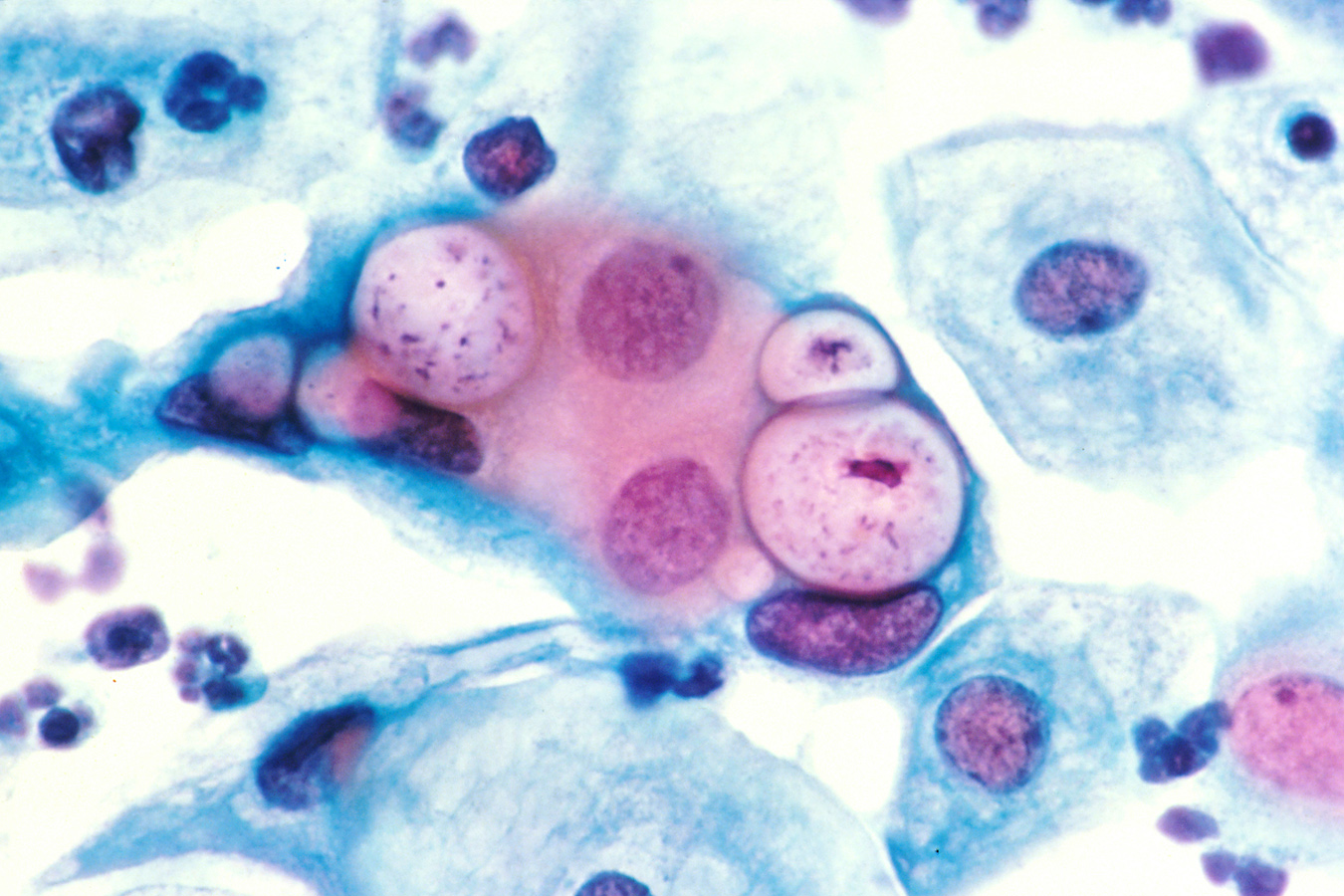
Tinción de Papanicolaou de una preparación citológica cervicovaginal que muestra 3 inclusiones intranucleares clamidales dentro de células epiteliales escamosas que están junto a varias células epiteliales normales
Imagen: “Pap smear showing Chlamydia in the vacuoles 500x H&E” por Dr. Lance Liotta Laboratory. Licencia: Dominio Público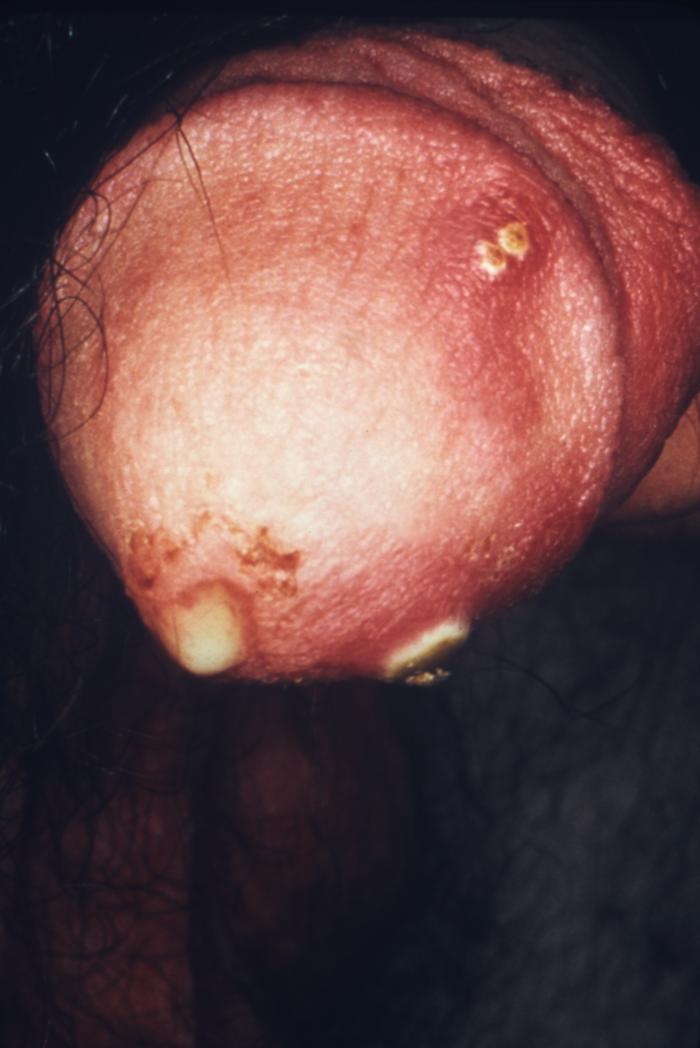
Secreción penil purulenta por infección de gonorrea urogenital
Imagen: “4065” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio público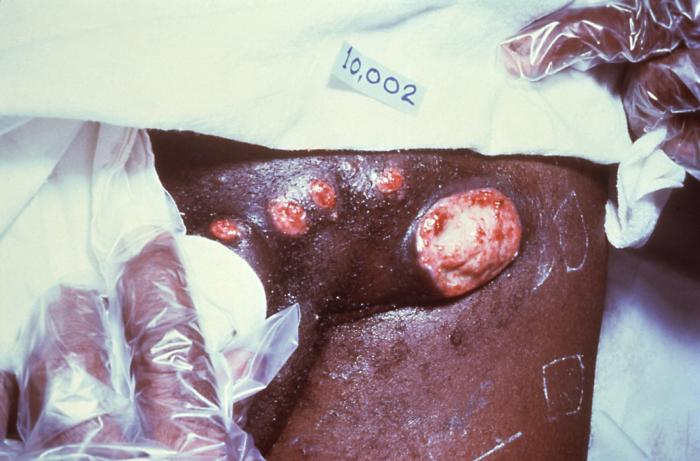
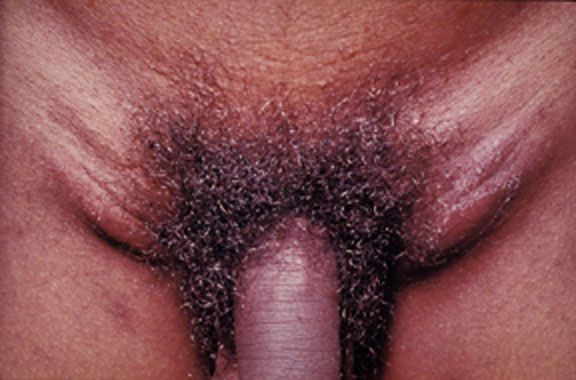
Lesiones ulcerosas de la donovanosis:
Región inguinal izquierda de un paciente, que revela la presencia de varias lesiones eritematosas ulcerosas, debidas a un caso de donovanosis
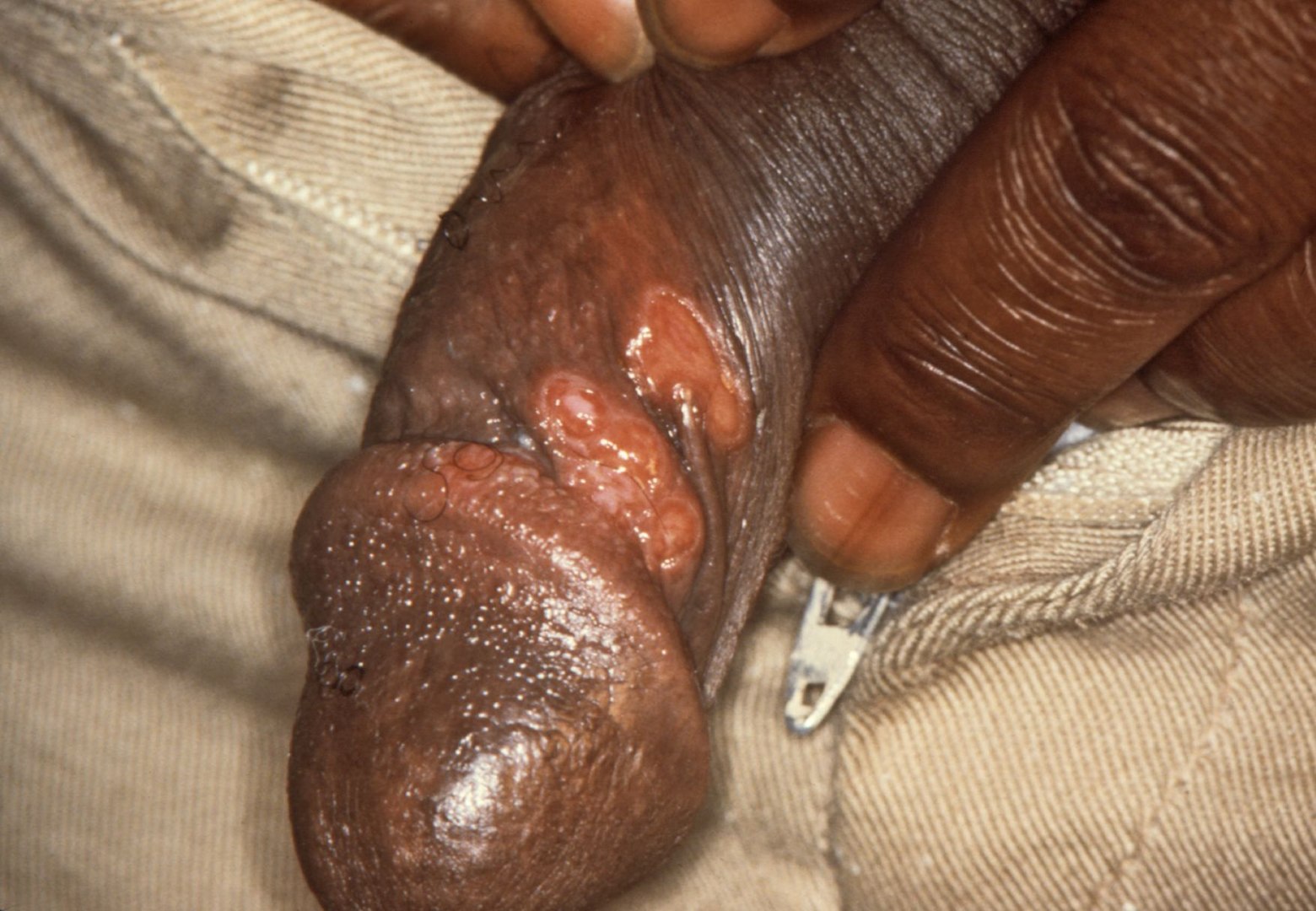
Linfogranuloma venéreo causado por los serovares invasivos L1, L2 o L3 de Chlamydia trachomatis:
Este joven adulto experimentó una aparición aguda de ganglios linfáticos sensibles y agrandados en ambas ingles.
Imagen: “Lymphogranuloma venerum: lymph nodes” por Herbert L. Fred, Hendrik A. van Dijk. Licencia: CC BY 2.0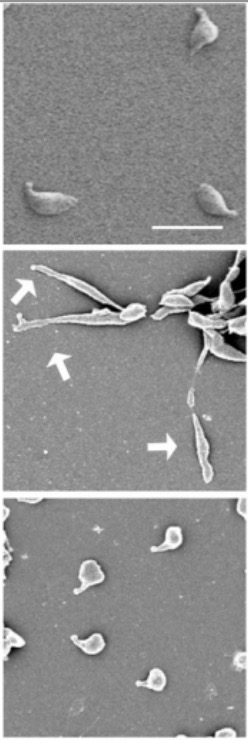
Micrografía electrónica de Mycloplasma genitalium:
Las imágenes superior e inferior muestran la típica morfología en forma de frasco. La imagen central muestra la morfología filamentosa (flechas).
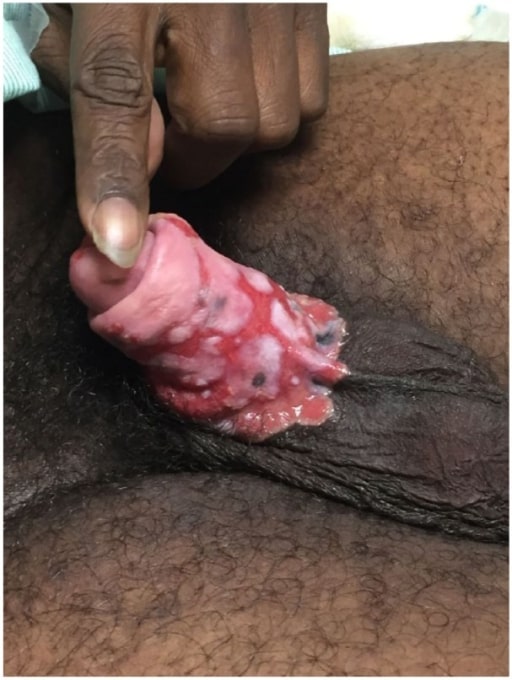
Chancro primario e indoloro de la sífilis (infección por Treponema pallidum)
Imagen: “Chancres on the penile shaft due to a primary syphilitic infection caused by Treponema pallidum 6803 lores” por M. Rein. Licencia: Dominio Público| Tipo de ITS | Organismo | Signos y síntomas |
|---|---|---|
| Herpes | VHS-1 o 2 | Si son sintomáticos,
los
LOS
Neisseria pacientes manifiestan:
|
| Hepatitis B Hepatitis B Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, which belongs to the Orthohepadnavirus genus and the Hepadnaviridae family. Most individuals with acute HBV infection are asymptomatic or have mild, self-limiting symptoms. Chronic infection can be asymptomatic or create hepatic inflammation, leading to liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis B Virus | Virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la hepatitis B Hepatitis B Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, which belongs to the Orthohepadnavirus genus and the Hepadnaviridae family. Most individuals with acute HBV infection are asymptomatic or have mild, self-limiting symptoms. Chronic infection can be asymptomatic or create hepatic inflammation, leading to liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis B Virus ( HBV HBV Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, which belongs to the Orthohepadnavirus genus and the Hepadnaviridae family. Hepatitis B virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Examples of types of exposure include sexual intercourse, IV drug use, and childbirth. Hepatitis B Virus) | Aguda:
|
| VIH | Dos especies de Lentivirus Lentivirus A genus of the family retroviridae consisting of non-oncogenic retroviruses that produce multi-organ diseases characterized by long incubation periods and persistent infection. Lentiviruses are unique in that they contain open reading frames (orfs) between the pol and env genes and in the 3′ env region. Five serogroups are recognized, reflecting the mammalian hosts with which they are associated. HIV-1 is the type species. Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) | Las diferentes etapas de la enfermedad incluyen:
|
| VPH | Diferentes tipos (6, 11, 16 y 18) de VPH |
|
Úlceras en el pene por herpes genital crónico refractario en un paciente con SIDA
Imagen: “Penile ulcers” por University of Texas Medical Branch School of Medicine, Galveston, TX, USA. Licencia: CC BY 3.0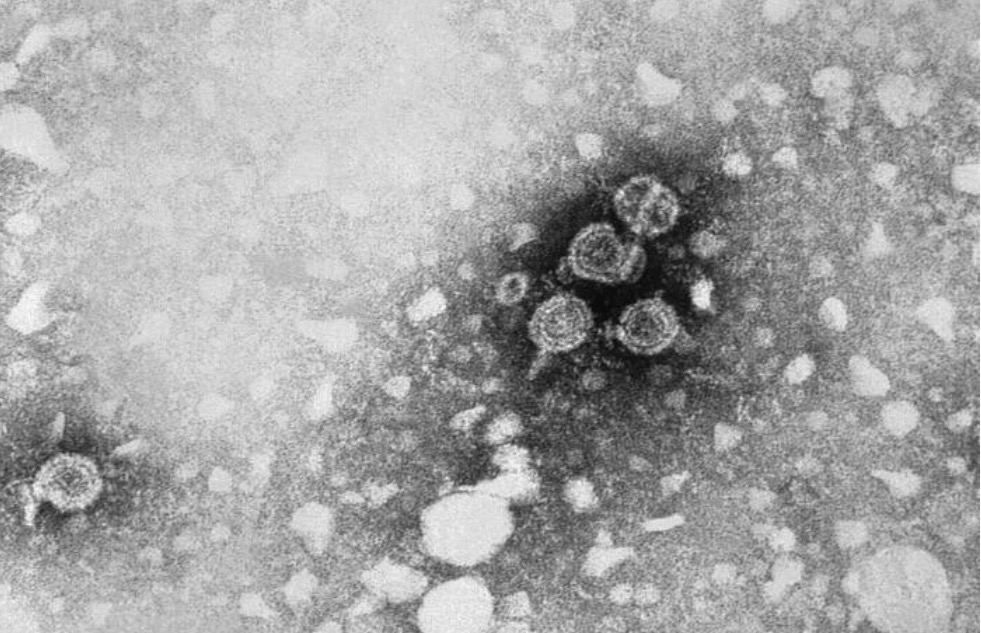
Hepatitis B:
Esta imagen de microscopía electrónica de transmisión (TEM, por sus siglas en inglés) revela la presencia de partículas del virus de la hepatitis B (HBV). Los viriones redondos, que miden 42 nm de diámetro, se conocen como partículas Dane.
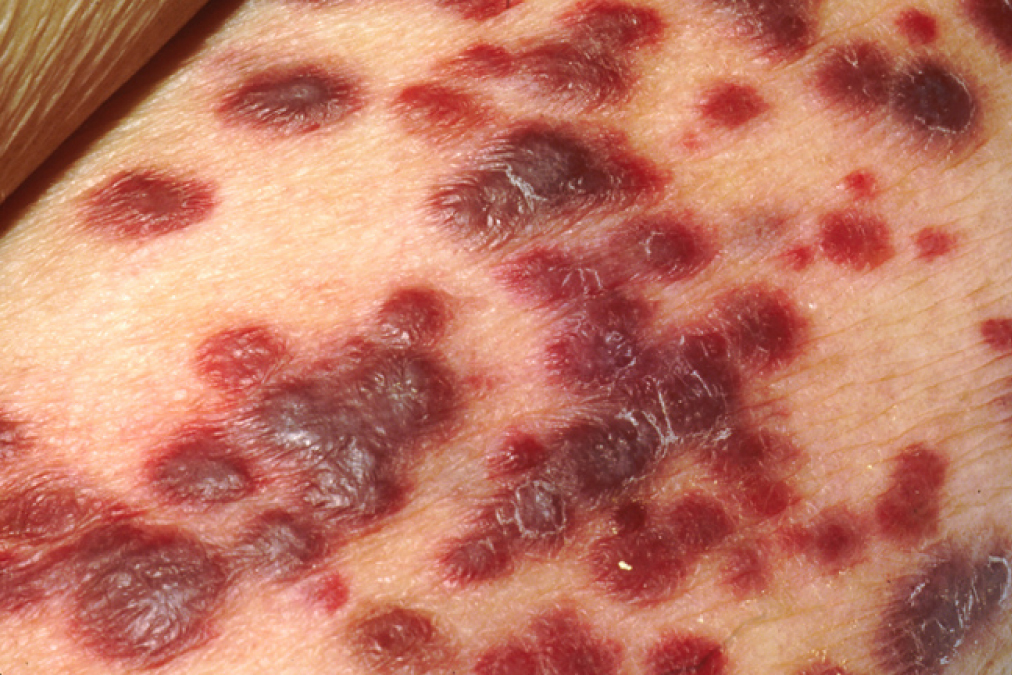
Lesiones cutáneas del sarcoma de Kaposi
Imagen: “Kaposi‘s sarcoma” por OpenStax College. Licencia: CC BY 3.0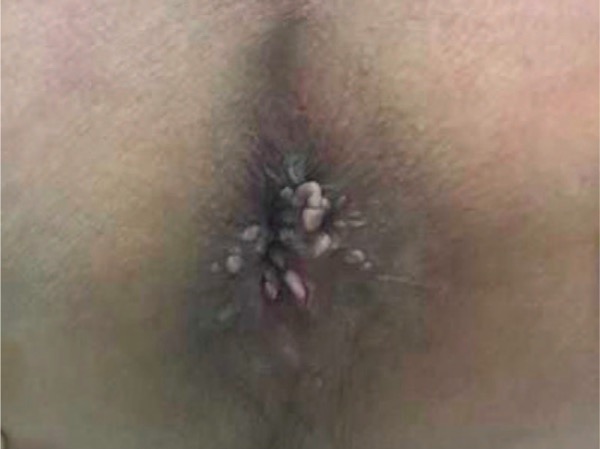
Verrugas anogenitales
Imagen: “Twenty molluscoid lesions” por Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. Licencia: CC BY 4.0| Tipo de ITS | Organismo | Signos y síntomas |
|---|---|---|
| Tricomoniasis | Trichomonas Trichomonas A genus of parasitic flagellate eukaryotes distinguished by the presence of four anterior flagella, an undulating membrane, and a trailing flagellum. Nitroimidazoles vaginalis |
|
| Piojos púbicos o ladillas | Pthirus pubis | Prurito en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la zona genital y perianal |
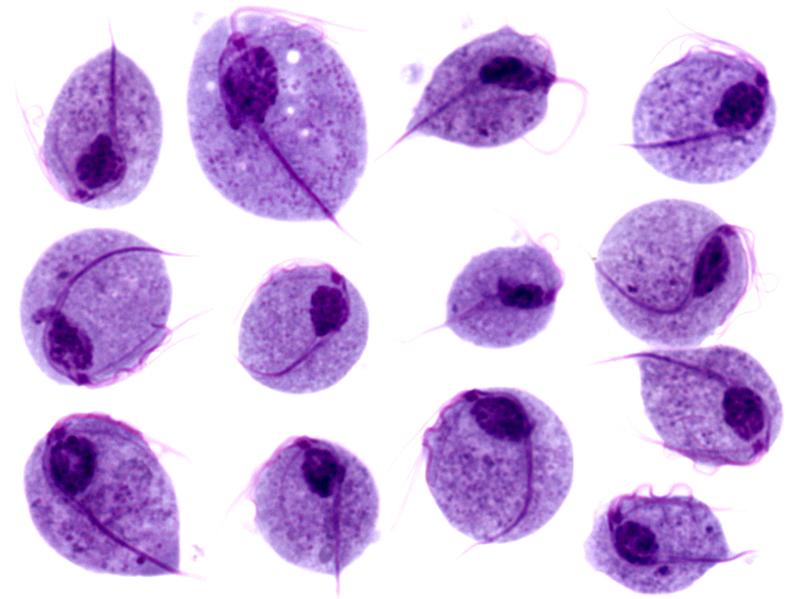
Imágenes microscópicas de trofozoitos de Trichomonas vaginalis
Imagen: “Trichomonas protozoa” por isis325. Licencia: CC BY 2.0.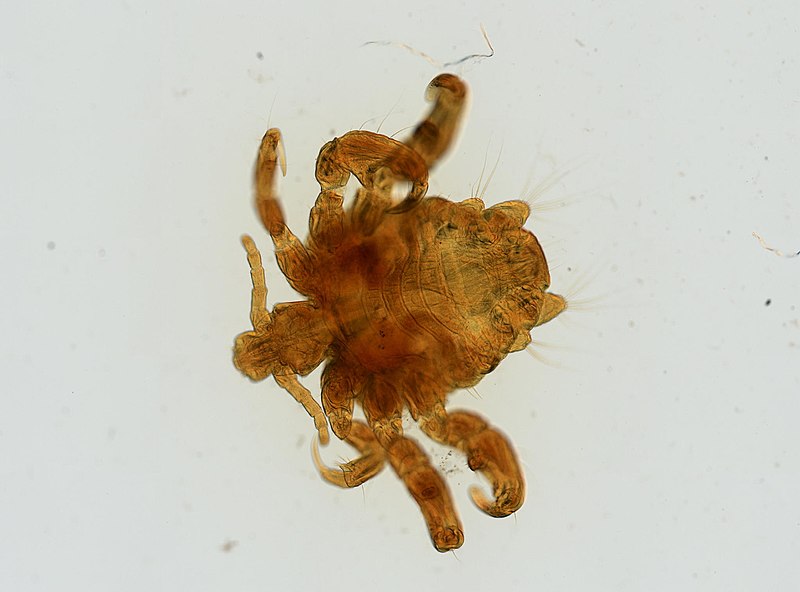
Pthirus pubis: piojo púbico o ladilla, un ectoparásito cuyo único huésped es el ser humano
Imagen: “Pthirus pubis” por Daniel J. Drew. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoAntecedentes sexuales completos:
Examen físico focalizado:
Las muestras para las pruebas se obtienen del lugar o los LOS Neisseria lugares de la infección/lesión, que pueden incluir zonas anogenitales, ganglios linfáticos y zonas orales.
Enfermedad bacteriana:
Enfermedad viral:
Enfermedad parasitaria:
| Tipo de ITS | Tratamiento |
|---|---|
| Chancroide | Azitromicina 1 g oral × 1 o Ceftriaxona 250 mg IM × 1 |
| Clamidia | Doxiciclina 100 mg por vía oral dos veces al AL Amyloidosis día x 7 días (primera línea); azitromicina 1 g por vía oral x 1 (alternativa, p. ej., embarazo) |
| Gonorrea | Ceftriaxona 500 mg IM × 1 (+ doxiciclina 7 días si no se ha HA Hemolytic anemia (HA) is the term given to a large group of anemias that are caused by the premature destruction/hemolysis of circulating red blood cells (RBCs). Hemolysis can occur within (intravascular hemolysis) or outside the blood vessels (extravascular hemolysis). Hemolytic Anemia descartado clamidia) |
| Granuloma inguinal o donovanosis Donovanosis Donovanosis (also known as granuloma inguinale) is an STD caused by Klebsiella granulomatis and is mainly seen in tropical regions. The condition is characterized by chronic, progressive, ulcerating disease mostly affecting the genital region. Donovanosis |
|
| Linfogranuloma venéreo ( LGV LGV Subacute inflammation of the inguinal lymph glands caused by certain immunotypes of Chlamydia trachomatis. It is a sexually transmitted disease in the U.S. But is more widespread in developing countries. It is distinguished from granuloma venereum, which is caused by calymmatobacterium granulomatis. Chlamydial Infections) | Doxiciclina 100 mg oral dos veces al AL Amyloidosis día × 21 días |
| Infección por Mycoplasma genitalium Mycoplasma genitalium A species of gram-negative bacteria originally isolated from urethral specimens of patients with non-gonococcal urethritis. In primates it exists in parasitic association with ciliated epithelial cells in the genital and respiratory tracts. Mycoplasma | Si es sensible a macrólidos:
|
| Sífilis | Penicilina G (parenteral) |
| Tipo de ITS | Tratamiento |
|---|---|
| Herpes | Antivirales:
|
| VPH | Terapia citodestructiva:
|
| VIH | Terapia antirretroviral combinada con lo siguiente:
|
| Hepatitis B Hepatitis B Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, which belongs to the Orthohepadnavirus genus and the Hepadnaviridae family. Most individuals with acute HBV infection are asymptomatic or have mild, self-limiting symptoms. Chronic infection can be asymptomatic or create hepatic inflammation, leading to liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis B Virus |
|
| Tipo de ITS | Tratamiento |
|---|---|
| Tricomoniasis |
|
| Piojo púbico | Permetrina tópica o piretrinas tópicas con butóxido de piperonilo |