Enzyme kinetics is the study of enzyme-catalyzed reaction rates and what factors affect enzymatic reaction speeds. These parameters often include temperature, pH, and substrate concentration. The relation of these parameters to reaction velocity can be mathematically modeled, providing insight into ideal conditions for a particular enzymatic reaction and potential physiologic control mechanisms.
Last updated: Apr 23, 2025
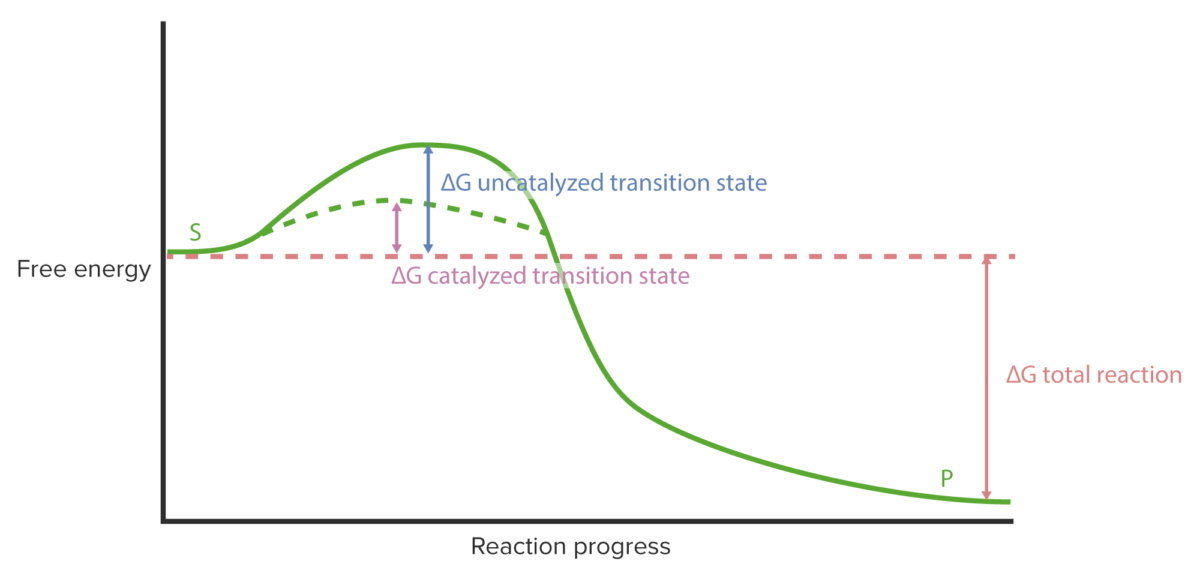
Enzyme kinetics: reaction progress curve
Image by Lecturio.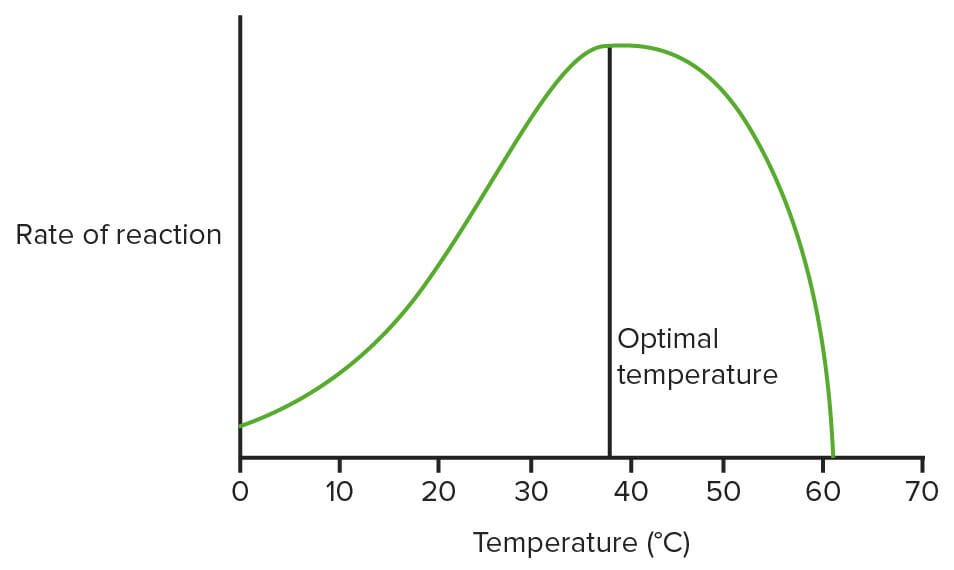
Graph showing the effect of temperature on enzymes:
This is not using real data, just a diagram to show what the general pattern is. (Optimal temperature = 37.5°C here)
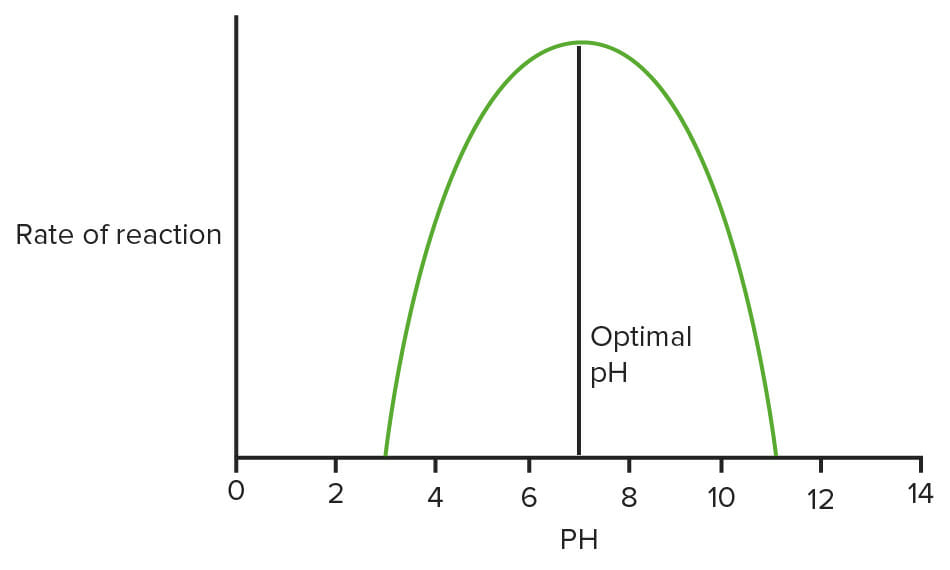
Optimum pH and temperature at which enzymes function
Image: “Effect of temperature on enzymes” by domdomegg. License: CC BY 4.0, edited by Lecturio.Steady state conditions
Early changes in concentrations of S, enzyme (E), enzyme-substrate complex Enzyme-substrate complex Temporary molecule formed by the non-covalent binding of the enzyme and substrate. Basics of Enzymes (ES), and P change dramatically and are difficult to measure. Steady state occurs when changes in E and ES are relatively small.
Initial reaction rate (Vo)
The initial rate of the reaction is used to avoid the measurement of the reverse reaction once enough product has been made.
Michaelis-Menten graph
Plotting the initial reaction rate (V0) on the y-axis against the substrate Substrate A substance upon which the enzyme acts. Basics of Enzymes concentration on the x-axis on a graph results in a hyperbolic curve, which approaches the maximum velocity Vmax at high substrate Substrate A substance upon which the enzyme acts. Basics of Enzymes concentrations due to saturation of the enzyme with substrate Substrate A substance upon which the enzyme acts. Basics of Enzymes.
Michaelis-Menten constant (KM)
KM is the substrate Substrate A substance upon which the enzyme acts. Basics of Enzymes concentration at which half-maximal velocity (½ Vmax) is reached (KM is measured on the x-axis while ½ Vmax is measured on the y-axis).
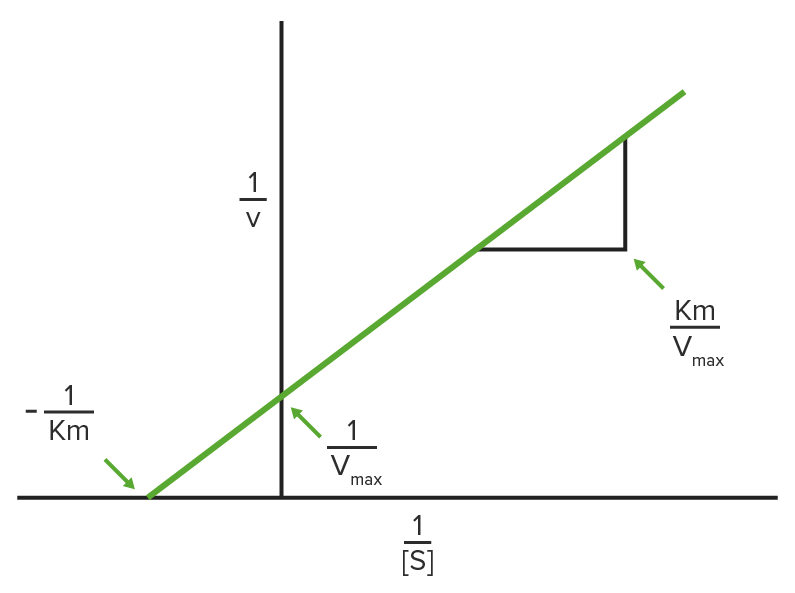
Lineweaver-Burke plot
1/V0 is plotted on the y-axis and 1 / [S] is plotted on the x-axis, resulting in a linear plot of the same data used in Michaelis-Menten kinetics.
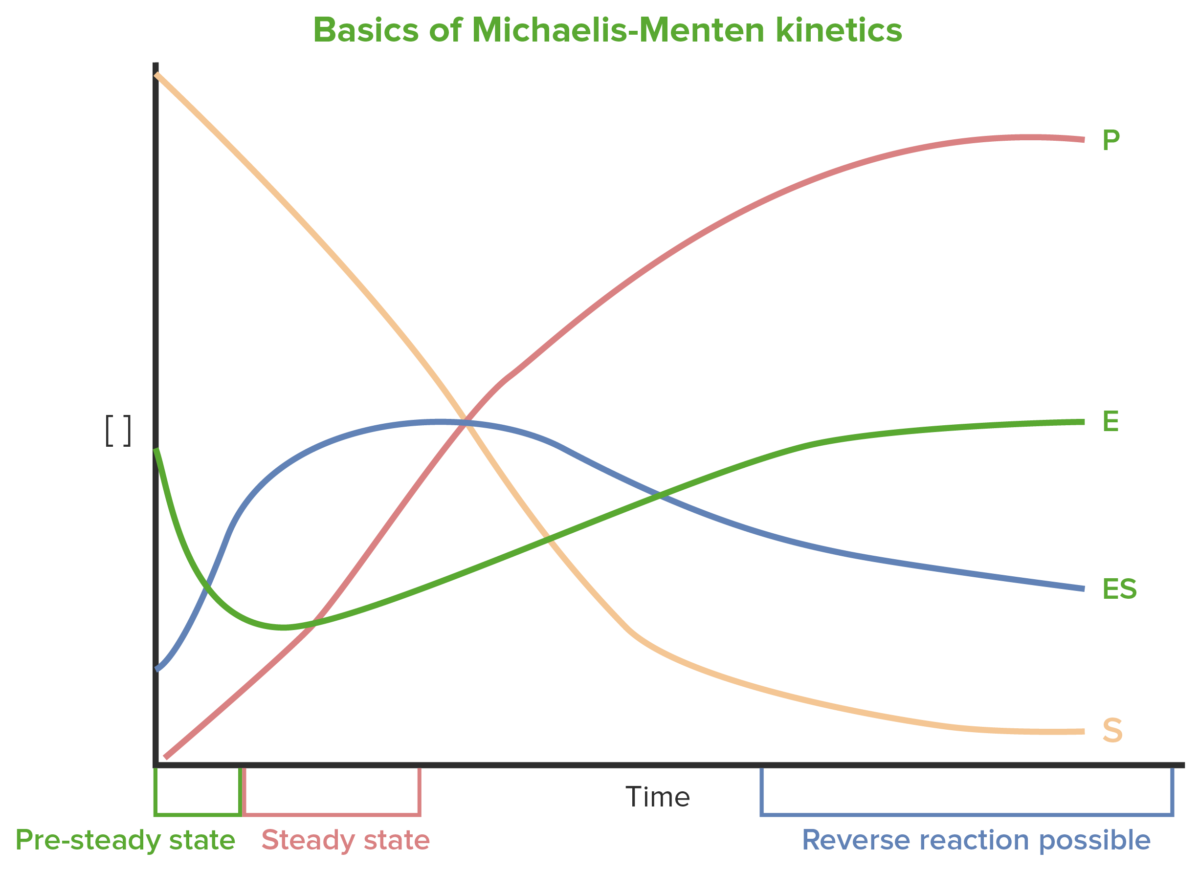
Basics of Michaelis-Menten kinetics
Image by Lecturio.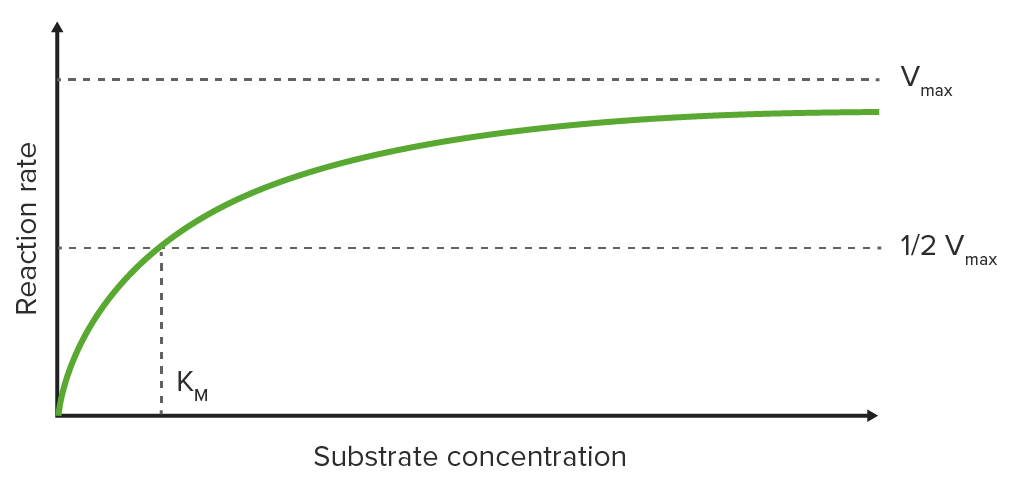
Michaelis-Menten graph:
Saturation curve for an enzyme reaction showing the relation between the substrate concentration and reaction rate
Basics of Michaelis-Menten kinetics
Image by Lecturio.