En la población pediátrica, la imagenología a menudo juegan un papel crítico en el diagnóstico, especialmente en el diagnóstico de anomalías congénitas. En los niños, las TC se evitan en la medida de lo posible debido al alto riesgo de exposición a la radiación. Además, tanto la TC como (especialmente) la RM requieren que los niños permanezcan quietos durante períodos de tiempo significativos y, a menudo, requieren sedación para completar el estudio. Por estas razones, la radiografía simple (a menudo con contraste), la fluoroscopia y el ultrasonido son las modalidades de imagenología de elección para la mayoría de los casos sospechosos de patología gastrointestinal. Algunas afecciones que se pueden diagnosticar mediante imagenología incluyen estenosis pilórica hipertrófica, enterocolitis necrosante, malrotación del intestino medio con o sin vólvulo, atresia intestinal, intususcepción, apendicitis, enfermedad de Hirschsprung, linfadenitis mesentérica y obstrucciones del árbol biliar.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Se deben considerar varias cuestiones adicionales durante la obtención de imagenología pediátrica, que incluyen:
Antes de la interpretación de cualquier imagen, el médico debe tomar ciertos pasos preparatorios. Siempre se debe seguir el mismo abordaje sistemático:
Las imágenes siempre deben interpretarse utilizando un abordaje sistemático.
Esofagograma, contraste gastrointestinal superior (i.e., “estudio de deglución”) y estudios del tránsito del intestino delgado:
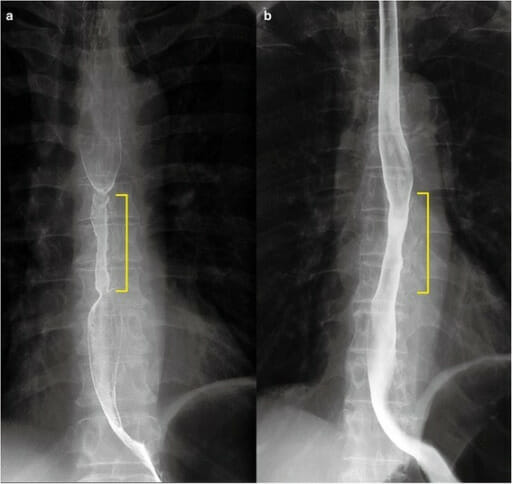
Esofagograma con bario que muestra un estrechamiento sutil en esófago medio (marcador amarillo)
Imagen: “Barium esophagram 1 month after endoscopic submucosal dissection.” por Department of Gastroenterology, Keiyukai Daini Hospital. Licencia: CC BY 4.0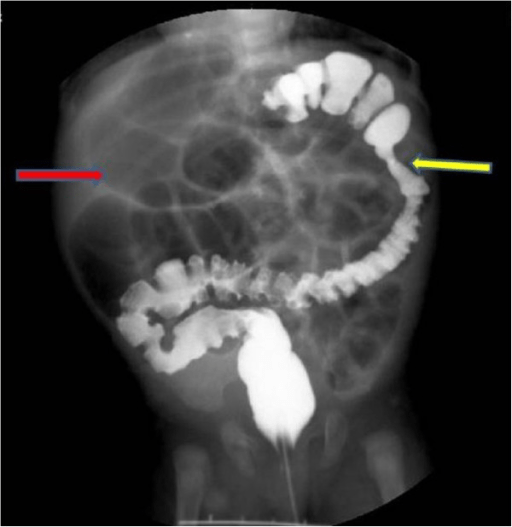
Un estudio de enema de bario que demuestra atresia colónica: una niña de 2 meses de edad muestra retraso en la evacuación de meconio, distensión abdominal y vómitos que comienzan 10 días después del nacimiento. El enema de bario revela atresia en el lado esplénico del colon (flecha amarilla) y distensión del íleon (flecha roja).
Imagen: “Case 3” por Pediatric Surgery Department of the First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China. Licencia: CC BY 2.0La estenosis hipertrófica de píloro se refiere al AL Amyloidosis engrosamiento congénito de la musculatura del píloro que produce estenosis severa y casi obstrucción de la salida gástrica. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes se presentan con vómitos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum proyectil no biliosos y una masa del tamaño de una aceituna en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la parte superior del abdomen. La estenosis hipertrófica del píloro se puede tratar quirúrgicamente.
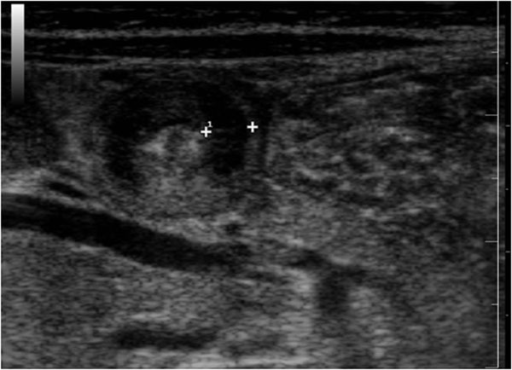
Características ultrasonográficas de la estenosis pilórica hipertrófica: la imagen muestra una sección transversal del píloro que muestra el “signo de la diana” (también denominado “signo de la rosquilla”). Los calibradores marcan la musculatura engrosada, con un anillo ecogénico interior que representa la mucosa.
Imagen: “Ultrasound features of hypertrophic pyloric stenosis” por Second University of Naples, Department of Clinical and Experimental Internistic. Licencia: CC BY 2.0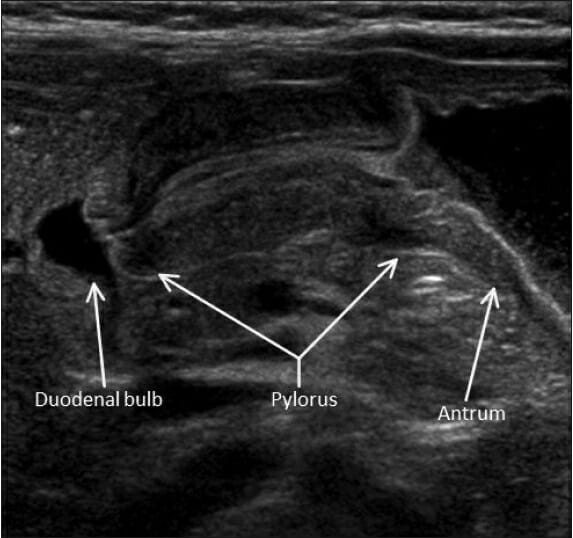
Imagen de ultrasonido que muestra una vista longitudinal del píloro en un caso de estenosis hipertrófica del píloro: se observa engrosamiento de la musculatura del píloro y elongación del canal.
Imagen: “Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis” por Herliczek TW. Licencia: CC BY 4.0La enterocolitis Enterocolitis Inflammation of the mucosa of both the small intestine and the large intestine. Etiology includes ischemia, infections, allergic, and immune responses. Yersinia spp./Yersiniosis necrosante es una emergencia gastrointestinal neonatal relativamente común debido a la infección por organismos formadores de gas, lo que resulta en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum necrosis Necrosis The death of cells in an organ or tissue due to disease, injury or failure of the blood supply. Ischemic Cell Damage isquémica de la mucosa intestinal. Los LOS Neisseria lactantes suelen presentar un cambio repentino en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la tolerancia a la alimentación y distensión abdominal en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la 1ra o 2da semana de vida.
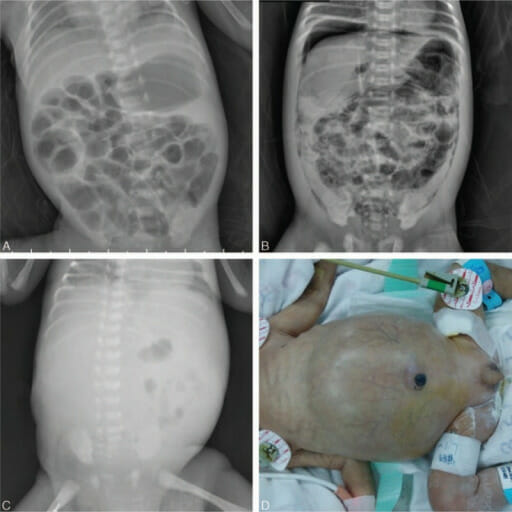
Enterocolitis necrosante en radiografía
(A) Gas venoso portal sutil con neumatosis intestinal
(B) Neumoperitoneo bajo el hemidiafragma derecho y neumatosis intestinal
(C) Escasez de gas en el abdomen
(D) Neonato con abdomen distendido
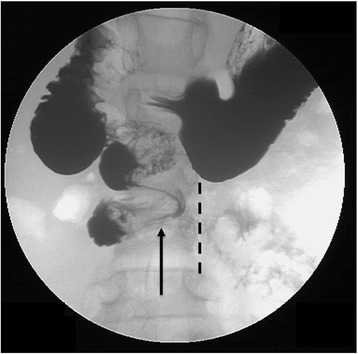
La imagen fluoroscópica anteroposterior después de la administración de contraste entérico positivo demuestra una apariencia de “sacacorchos” del duodeno, que no cruza al lado izquierdo de la columna (línea discontinua). Este hallazgo sugiere malrotación y vólvulo del intestino medio.
Imagen: “Upper gastrointestinal study (UGI) demonstrating intestinal malrotation and volvulus with abnormal position of the duodenal-jejunal junction to the right of the spine” por Pediatric Department, Shaare Zedek Medical Center, P.O. Box 3235, 9103102, Jerusalem, Israel. Licencia: CC BY 4.0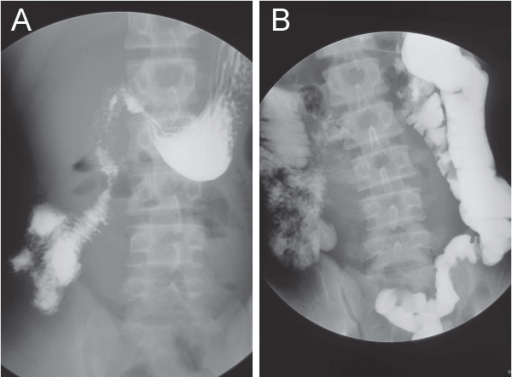
(A) La serie gastrointestinal superior con contraste de bario muestra que el duodeno permanece completamente en el hemiabdomen derecho sin cruzar la línea media, lo que es compatible con una malrotación.
(B) El tránsito a través del intestino delgado muestra que el ciego está ubicado en el cuadrante inferior izquierdo.
La atresia Atresia Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS) intestinal es una afección en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la que una parte del intestino no se canaliza durante el desarrollo, lo que provoca una obstrucción intestinal en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria recién nacidos. Aproximadamente ½ de todos los LOS Neisseria casos constituyen atresia Atresia Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS) duodenal. Los LOS Neisseria lactantes se presentan con vómitos y distensión abdominal. La cirugía es el tratamiento definitivo.
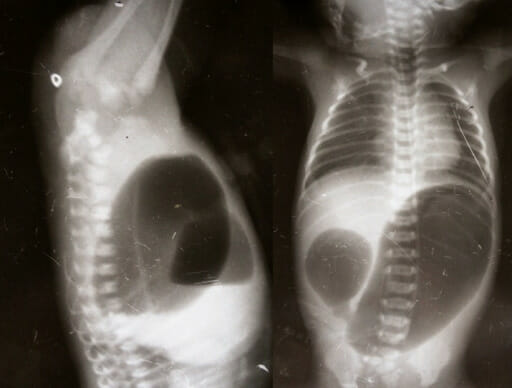
Radiografía que muestra el signo de la doble burbuja en un lactante con atresia duodenal
Imagen: “Invertogram showing high ARM and AP view showing duodenal atresia” por Manoj Saha, Department of Pediatric Surgery, Gauhati Medical College. Licencia: CC BY 3.0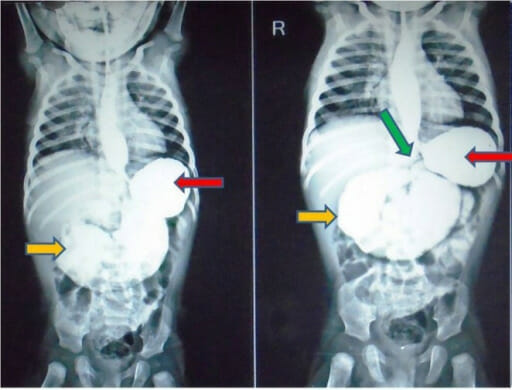
Imágenes, de una serie gastrointestinal con contraste, tomadas a los 5 y 15 minutos, que muestra estómago dilatado (flechas rojas) y distensión marcada del duodeno (flechas amarillas) hasta la unión duodenoyeyunal (flecha verde). Los hallazgos sugieren atresia yeyunal. También se observa reflujo gastroesofágico en el esófago, pero el resto del intestino distal parece normal.
Imagen: “Upper gastrointestinal contrast study” por Rahul Gupta, Praveen Mathur, Sharanabasappa Gubbi, Pradeep Kumar Gupta, Ramendra Shukla, and Anu Bhandari. Licencia: CC BY 3.0Intususcepción: invaginación de un segmento proximal del intestino en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un segmento adyacente más distal, con mayor frecuencia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la región ileocólica. La intususcepción es la emergencia abdominal más común en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum niños < 2 años de edad, que se presenta con la “tríada clásica” de dolor Dolor Inflammation abdominal tipo cólico de inicio súbito, una masa palpable en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum forma de salchicha y heces en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum gelatina de grosella.
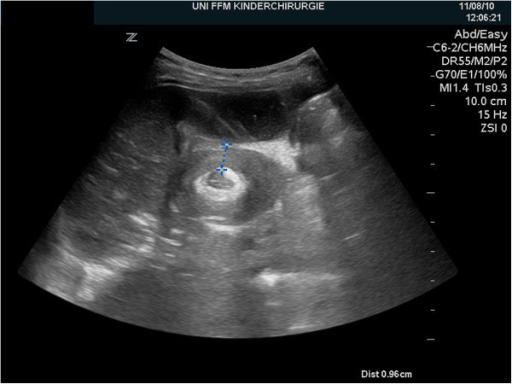
El ultrasonido del abdomen derecho muestra el típico signo ultrasonográfico de la “diana” de intususcepción ileocólica.
Imagen: “Ultrasonography of the right upper abdominal quadrant” por Department of Pediatric Surgery and Pediatric Urology, Johann Wolfgang Goethe University of Frankfurt. Licencia: CC BY 4.0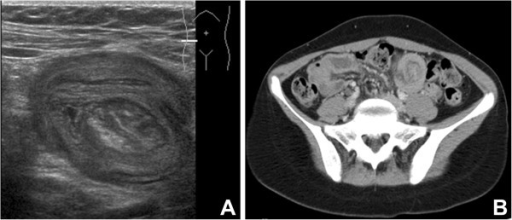
Ultrasonido (A) y TC (B) con evidencia de intususcepción
(A) Ultrasonido que muestra la apariencia de intestino dentro de un intestino, compatible con intususcepción intestinal
(B) TC, corte axial, con contraste intravenoso que muestra intususcepción en el cuadrante inferior izquierdo

La radiografía abdominal después de un enema de aire muestra un signo de “media luna” (menisco) que evidencia una intususcepción intestinal.
Imagen: “Abdominal radiograph after subsequent air enema” por Jaclyn Otero, Molly R. Posa, and Maria N. Kelly. Licencia: CC BY 4.0Obstrucción del íleon terminal por meconio anormalmente espeso y pegajoso. El íleo meconial a menudo se observa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum neonatos con fibrosis Fibrosis Any pathological condition where fibrous connective tissue invades any organ, usually as a consequence of inflammation or other injury. Bronchiolitis Obliterans quística y enfermedad de Hirschsprung. Los LOS Neisseria neonatos afectados generalmente se presentan con vómitos, incapacidad de evacuar el meconio dentro de las 12‒24 horas y distensión abdominal.
También conocida como megacolon Megacolon Megacolon is a severe, abnormal dilatation of the colon, and is classified as acute or chronic. There are many etiologies of megacolon, including neuropathic and dysmotility conditions, severe infections, ischemia, and inflammatory bowel disease. Megacolon agangliónico congénito, la enfermedad de Hirschsprung se caracteriza por la ausencia de células nerviosas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el colon Colon The large intestines constitute the last portion of the digestive system. The large intestine consists of the cecum, appendix, colon (with ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid segments), rectum, and anal canal. The primary function of the colon is to remove water and compact the stool prior to expulsion from the body via the rectum and anal canal. Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy distal, lo que provoca que el segmento afectado no se relaje, lo que lleva a una obstrucción funcional. Los LOS Neisseria neonatos afectados se presentan con emesis biliosa, distensión abdominal y incapacidad de evacuar el meconio. Es común su asociación con la enterocolitis Enterocolitis Inflammation of the mucosa of both the small intestine and the large intestine. Etiology includes ischemia, infections, allergic, and immune responses. Yersinia spp./Yersiniosis.
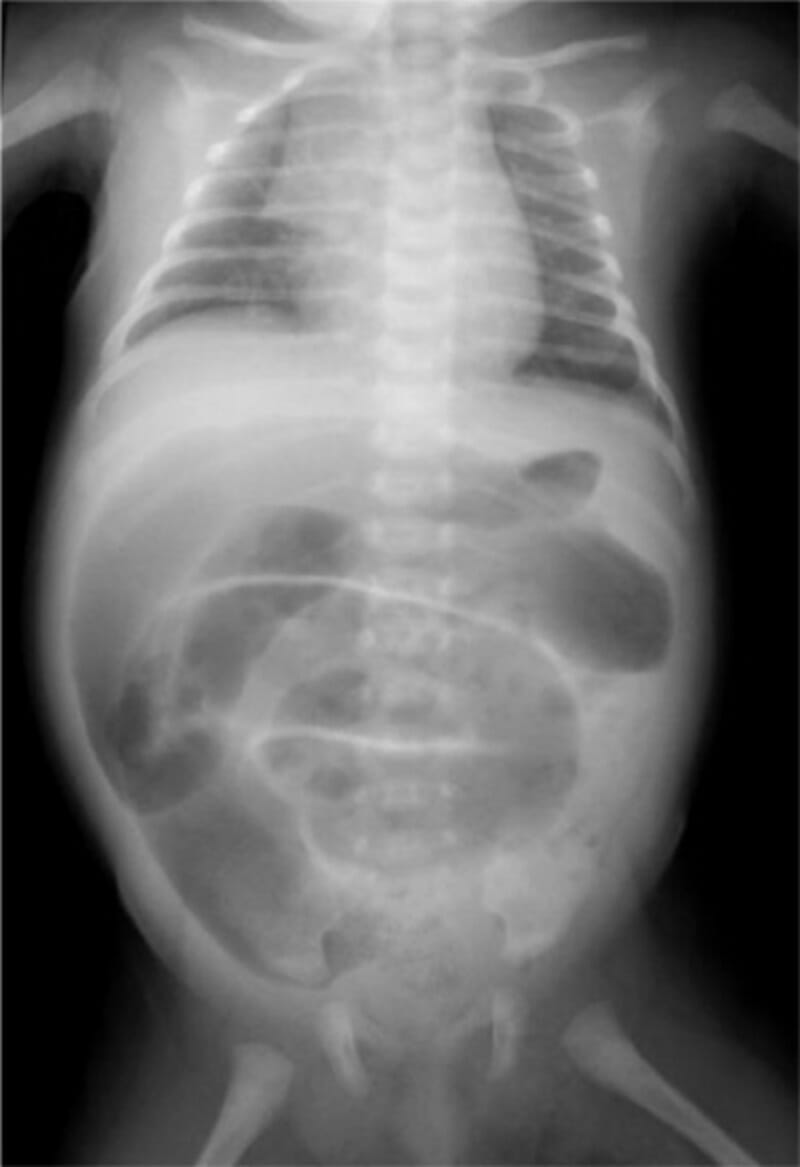
Radiografía abdominal anteroposterior de un neonato con enfermedad de Hirschsprung que muestra asas del intestino grueso distendidas llenas de aire: no se puede identificar ninguna parte del colon descendente o sigmoide.
Imagen: “Abdominal plain X-ray shows a generalized distention of the loops of the large intestine” por Nusrat et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0La apendicitis es la inflamación del apéndice, que característicamente se presenta con dolor Dolor Inflammation periumbilical que migra al AL Amyloidosis cuadrante inferior derecho con defensa, náuseas/vómitos y fiebre. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum niños, el diagnóstico es generalmente clínico con/sin el uso de ultrasonido. Generalmente, el tratamiento es quirúrgico.
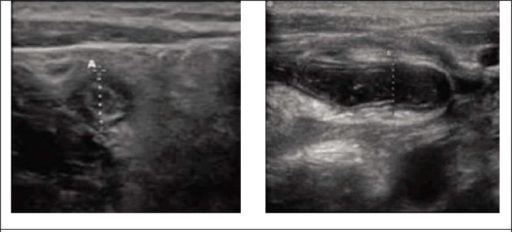
Vistas ultrasonográficas en la apendicitis: axial (izquierda) y transversal (derecha). Se muestra el diámetro total entre los calibradores.
Imagen: “Sonographic views of appendix.” por Ebrahim Karimi, Mohammad Aminianfar, Keivan Zarafshani, and Arash Safaie. Licencia: CC BY 3.0La linfadenitis mesentérica se refiere a la inflamación de los LOS Neisseria ganglios linfáticos mesentéricos (generalmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cuadrante inferior derecho) que a menudo ocurre cuando el sistema inmunitario entérico reacciona fuertemente a una infección (e.g., infecciones virales, infección por Yersinia enterocolitica Yersinia enterocolitica A species of the genus yersinia, isolated from both man and animal. It is a frequent cause of bacterial gastroenteritis in children. Yersinia spp./Yersiniosis). El estiramiento de las cápsulas de los LOS Neisseria ganglios linfáticos puede provocar un dolor Dolor Inflammation similar al AL Amyloidosis experimentado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la apendicitis; sin embargo, la linfadenitis mesentérica es autolimitada.
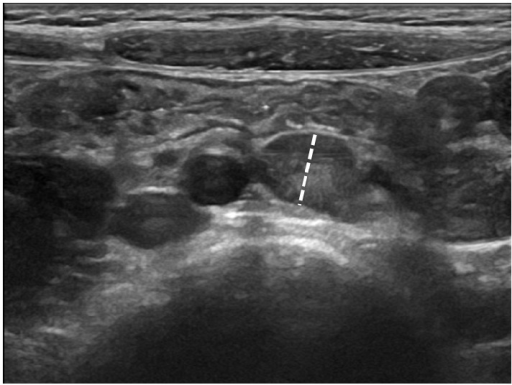
Ultrasonido del cuadrante inferior derecho que muestra ganglios linfáticos mesentéricos prominentes de hasta 9 mm, sugestivos de linfadenitis mesentérica
Imagen: “Abdominal ultrasound showing large hypoechoic mesenteric lymph nodes in a 6-year-old girl with acute nonspecific mesenteric lymphadenitis” por Rossana Helbling, Elisa Conficconi, Marina Wyttenbach, Cecilia Benetti, Giacomo D. Simonetti, Mario G. Bianchetti, Flurim Hamitaga, Sebastiano A.G. Lava, Emilio F. Fossali, and Gregorio P. Milani. Licencia: CC BY 4.0Dos trastornos importantes de las vías biliares que pueden causar obstrucción son la atresia Atresia Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS) biliar y los LOS Neisseria quistes de colédoco. Ambos se presentan con ictericia obstructiva y heces acólicas. El tratamiento es quirúrgico.
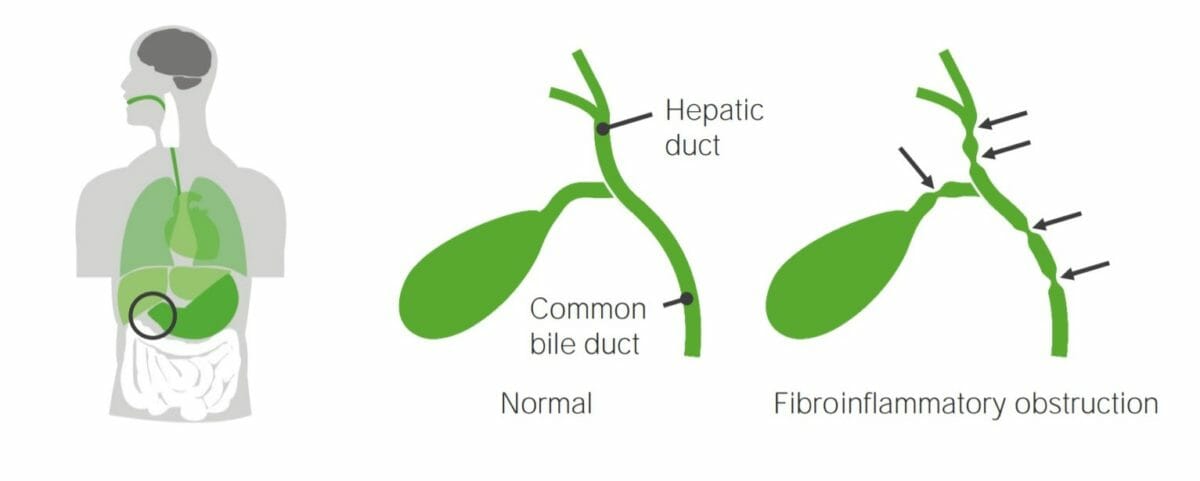
Atresia biliar
Imagen por Lecturio.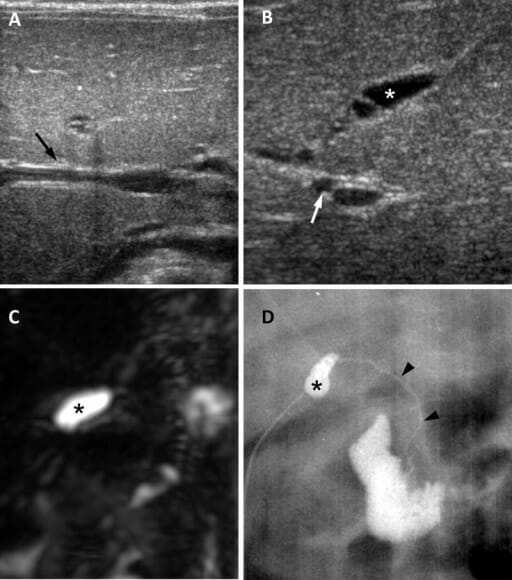
Atresia de vías biliares en una niña de 65 días: (A) Ultrasonido en el plano transversal muestra un signo de cordón triangular negativo (flecha). (B) La imagen de ultrasonido en el plano subcostal oblicuo muestra una vesícula biliar atrésica que mide 0,8 cm (asterisco) y una arteria hepática agrandada que mide 1,5 mm (flecha). (C) Una colangiopancreatografía por RM 3D no muestra un árbol biliar extrahepático visible y la presencia de una vesícula biliar pequeña (asterisco). (D) La colangiografía intraoperatoria muestra una vesícula biliar pequeña (asterisco) y un colédoco permeable pero extremadamente hipoplásico.
Imagen: “Biliary atresia in a 65-day-old girl” por Department of Radiology and Center for Imaging Science, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine. Licencia: CC BY 4.0