La pielonefritis es una infección que afecta a la pelvis Pelvis The pelvis consists of the bony pelvic girdle, the muscular and ligamentous pelvic floor, and the pelvic cavity, which contains viscera, vessels, and multiple nerves and muscles. The pelvic girdle, composed of 2 "hip" bones and the sacrum, is a ring-like bony structure of the axial skeleton that links the vertebral column with the lower extremities. Pelvis: Anatomy renal y al AL Amyloidosis parénquima renal. Esta condición surge principalmente como una complicación de la infección de la vejiga que asciende al AL Amyloidosis tracto urinario superior. La pielonefritis puede ser aguda o crónica (que resulta de infecciones persistentes o crónicas). Los LOS Neisseria síntomas agudos típicos son dolor Dolor Inflammation de costado, fiebre y náuseas con vómitos. El tipo crónico depende de la patología subyacente. El diagnóstico se establece a través de la presentación clínica, respaldada por hallazgos de laboratorio ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum sangre y orina). La imagenología se realiza si se observa una enfermedad grave o si no hay respuesta al AL Amyloidosis tratamiento inicial (antibióticos). La TC es el estudio de elección, dada su capacidad para detectar anomalías renales asociadas a la infección, incluida la extensión de la enfermedad. El absceso perirrenal es una infección que afecta el espacio perirrenal entre el riñón y la fascia Fascia Layers of connective tissue of variable thickness. The superficial fascia is found immediately below the skin; the deep fascia invests muscles, nerves, and other organs. Cellulitis de Gerota. El absceso perirrenal puede ser una extensión de la pielonefritis o de la diseminación hematógena de una infección sistémica. El diagnóstico se establece mediante TC. El tratamiento incluye antibióticos, con drenaje del absceso (que es tanto diagnóstico como terapéutico).
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
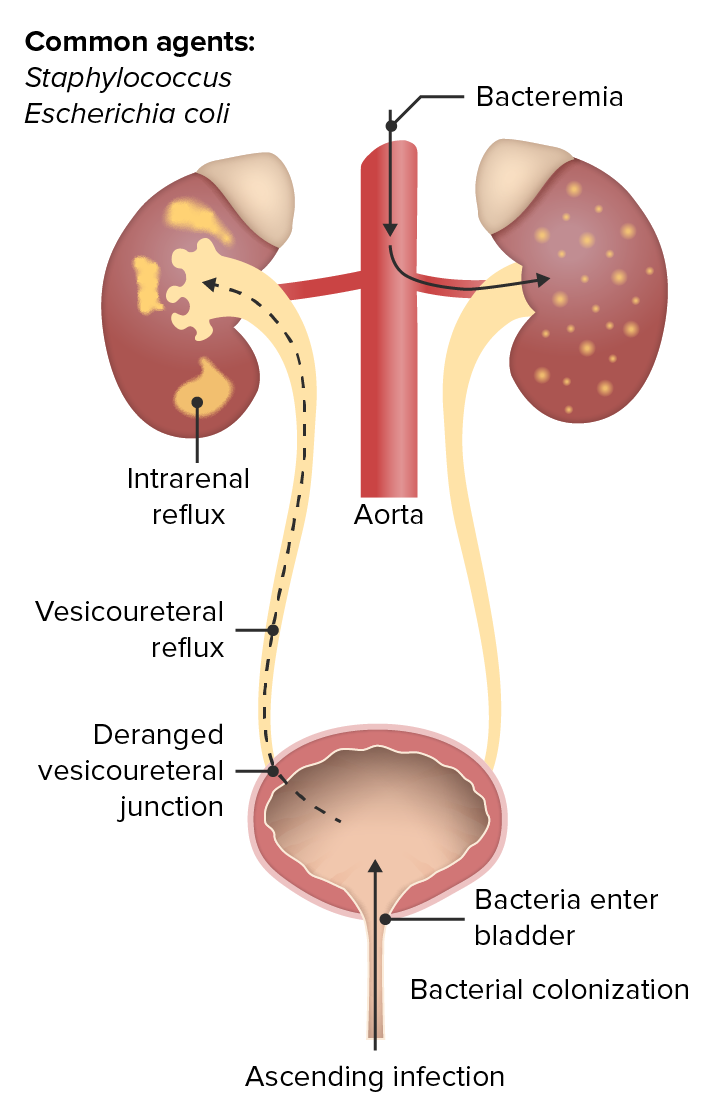
Infección hematógena ascendente del tracto urinario
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0La pielonefritis aguda es el proceso infeccioso de inicio repentino y la inflamación de los LOS Neisseria riñones a partir de una infección ascendente o diseminación hematógena de infecciones sistémicas.
Asociado con el desarrollo de pielonefritis y absceso perirrenal:
Estudios de imagen:
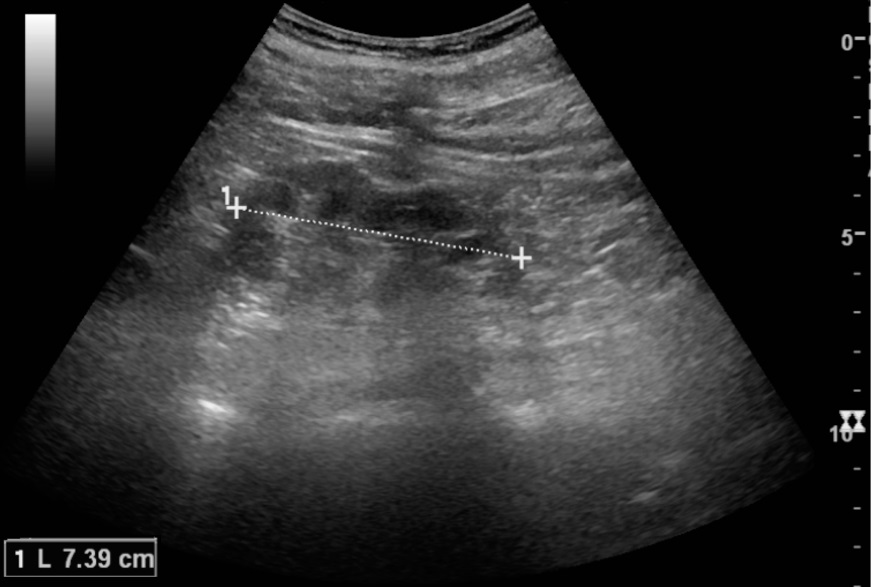
La pielonefritis crónica se manifiesta en la reducción de la longitud del riñón (7 cm) y el adelgazamiento cortical focal:
La longitud normal del riñón es de 10-12 cm. Obsérvese la medida del riñón ilustrada por los 2 signos “+” y la línea discontinua
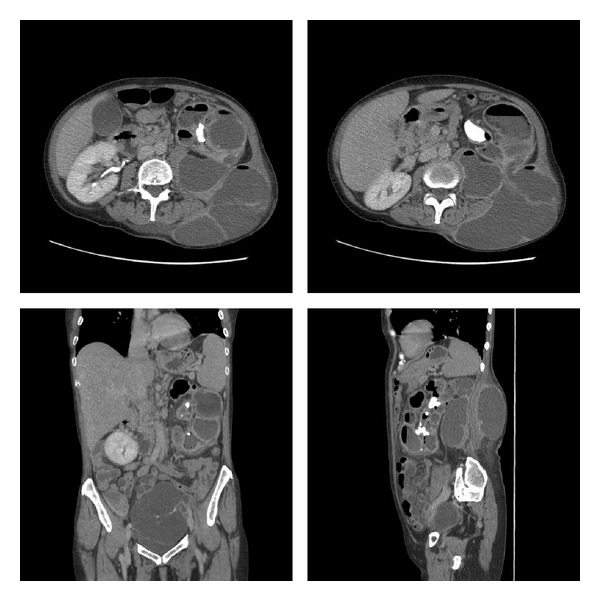
Pielonefritis xantogranulomatosa: TC de abdomen y pelvis con contraste intravenoso y fase tardía que demuestra un riñón izquierdo con parénquima reemplazado por múltiples colecciones hipodensas grandes que contienen líquido y gas, un cálculo coraliforme izquierdo y comunicación entre el riñón y una colección grande en el flanco. Obsérvese también la masa pélvica multiloculada de 13,5 x 7,7 cm.
Imagen: “Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis” por Zaid UB. Licencia: CC BY 3.0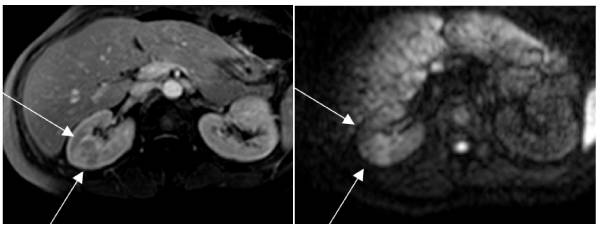
RM que muestra pielonefritis:
Izquierda: secuencia potenciada en T1 que muestra un gran foco de pielonefritis en el riñón derecho
Derecha: La misma área en difusión. La gran lesión cuneiforme es evidente debido al intenso edema.
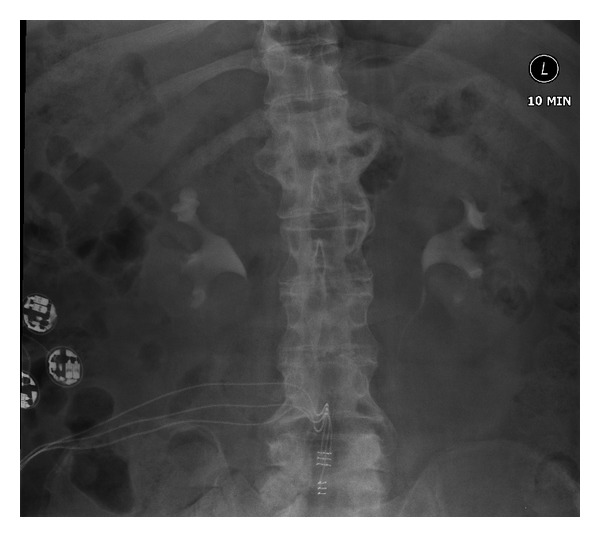
Pielonefritis crónica:
La urografía intravenosa muestra un cierto embotamiento del cáliz del polo superior derecho con una cierta reducción del espesor cortical en el polo superior derecho compatible con una pielonefritis crónica. Por lo demás, tanto el sistema pelvicocefálico como los uréteres parecen normales.
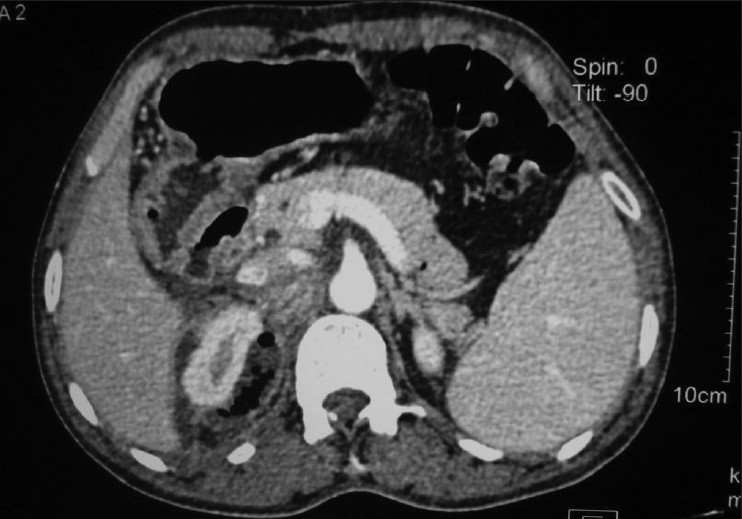
Absceso perinéfrico: imagen axial de TC a través del polo superior del riñón derecho que muestra un absceso perinéfrico que llega hasta la vena cava inferior
Imagen: “Axial CT image through the upper pole of the right kidney showing perinephric abscess reaching posterior to IVC.” por Wani NA. Licencia: CC BY 2.0El tratamiento depende de la gravedad de la presentación clínica y los LOS Neisseria factores de riesgo de resistencia a los LOS Neisseria medicamentos: