El absceso cerebral es una afección potencialmente mortal que consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la acumulación de pus en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el parénquima cerebral causada por una infección de bacterias, hongos, parásitos o protozoos. La presentación más común está compuesta por cefalea, fiebre con escalofríos, convulsiones y déficits neurológicos. El diagnóstico se basa principalmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la imagenología, ya que es difícil llegar a un diagnóstico definitivo basado únicamente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la presentación clínica. El tratamiento incluye la administración de terapia antibiótica empírica y la intervención quirúrgica. Es necesario un tratamiento inmediato; de lo contrario, se producen graves complicaciones neurológicas.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El absceso cerebral es una acumulación infecciosa de pus en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el parénquima cerebral, poco frecuente pero potencialmente mortal.
Existen dos vías de propagación de la infección al AL Amyloidosis cerebro:
Organismos causantes de abscesos cerebrales:
Factores de riesgo:
Cerebritis temprana (1–3 días):
Cerebritis tardía (4–9 días):
Formación temprana de la cápsula (10–13 días):
Formación tardía de la cápsula (+14 días):
La cápsula se vuelve gruesa y es susceptible de ser extirpada.
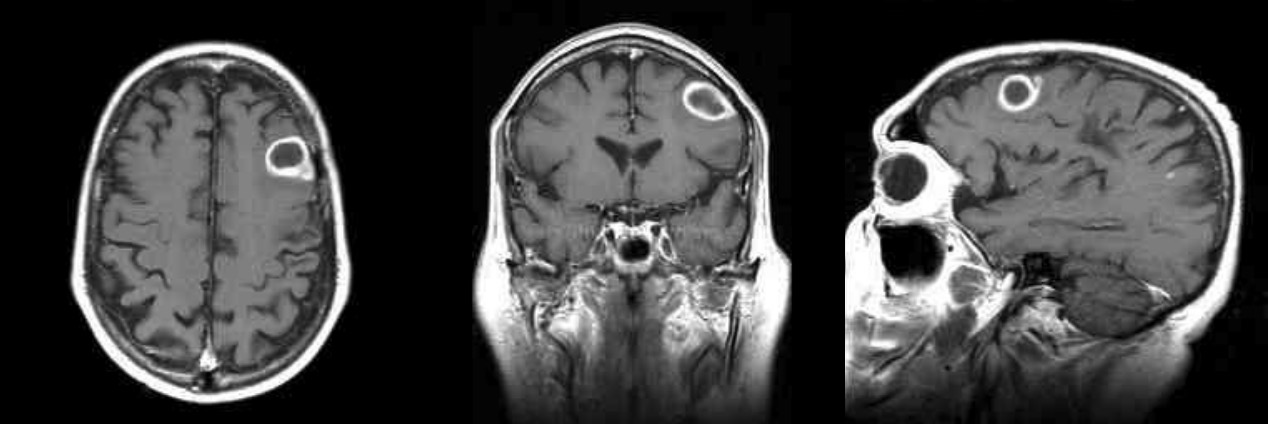
Imágenes potenciadas con gadolinio en T1: RM de un absceso cerebral que muestra la clásica lesión de “realce en anillo”
Imagen por Roy Strowd, M.D.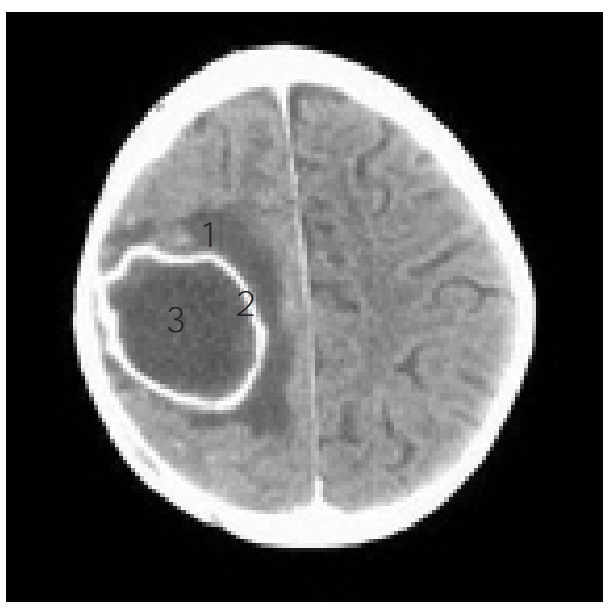
Las partes de un absceso cerebral se observan en una TC:
1: edema
2: patrón en anillo
3: núcleo del absceso
El tratamiento se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una combinación de tratamiento médico y quirúrgico.
Antibióticos:
Glucocorticoides:
Aspiración con aguja:
Extirpación quirúrgica:
La intervención quirúrgica podría evitarse si: