La terapia dirigida ejerce actividad antineoplásica contra las células cancerosas al AL Amyloidosis interferir con las propiedades únicas que se encuentran en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria tumores o malignidades. Los LOS Neisseria tipos de medicamentos pueden ser moléculas pequeñas, que pueden ingresar a las células, o anticuerpos monoclonales, que tienen sus dianas fuera o sobre la superficie de las células. Entre las áreas de las células malignas que se bloquean o inhiben mediante la terapia dirigida se encuentran las vías de señalización (como se observa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria inhibidores de la proteína cinasa), que conducen a una disminución de la proliferación y la subsiguiente apoptosis Apoptosis A regulated cell death mechanism characterized by distinctive morphologic changes in the nucleus and cytoplasm, including the endonucleolytic cleavage of genomic DNA, at regularly spaced, internucleosomal sites, I.e., DNA fragmentation. It is genetically-programmed and serves as a balance to mitosis in regulating the size of animal tissues and in mediating pathologic processes associated with tumor growth. Ischemic Cell Damage de las células tumorales. Otro medio de reducir las células cancerosas es eliminar la capacidad de reparación del ADN (visto en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria inhibidores de la poli(ADP-ribosa) polimerasa), bloquear la unión del ligando al AL Amyloidosis receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors (inhibidores del factor de crecimiento) y aumentar la actividad inmunitaria contra la neoplasia (inmunoterapias). Estos agentes se utilizan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum múltiples tipos de cáncer y en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum combinación con agentes quimioterapéuticos tradicionales.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
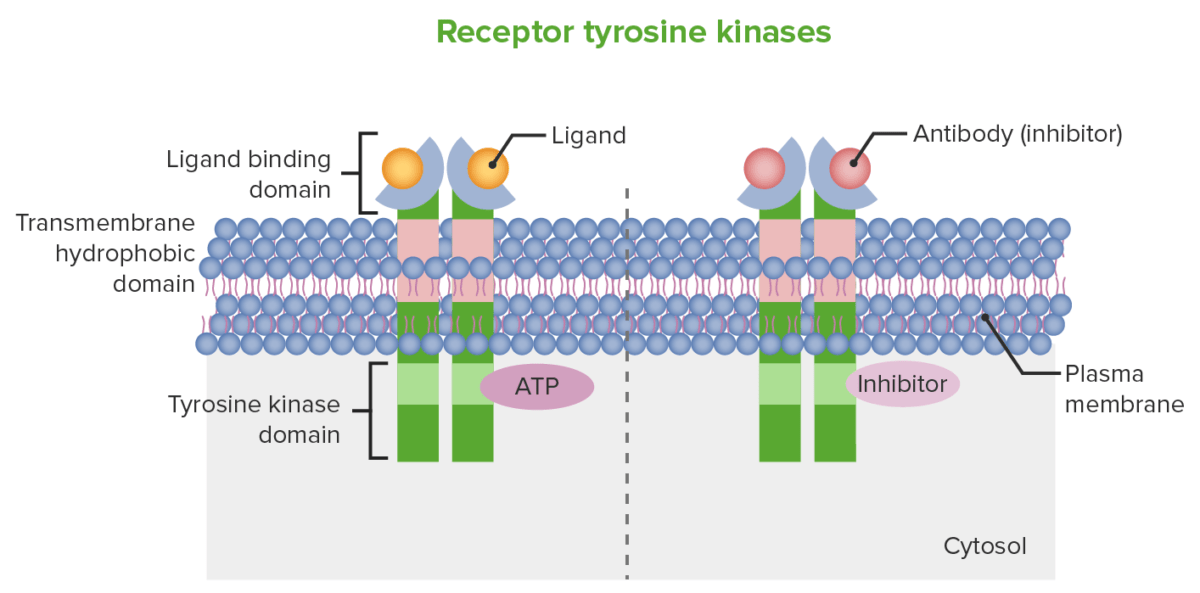
Mecanismo esquemático de la inhibición del receptor tirosina quinasa: A la izquierda, la imagen muestra la estructura del receptor de la célula. En la superficie celular se encuentra el dominio de unión al ligando y el dominio quinasa (en esta imagen, tirosina quinasa) se encuentra intracelularmente. A la derecha, la imagen muestra cómo un anticuerpo monoclonal puede producir actividad antineoplásica, que es a través de la inhibición mediada por anticuerpos del dominio de unión al ligando. Las moléculas pequeñas, que pueden ingresar a las células, pueden producir la inhibición del dominio de unión al ATP (tirosina quinasa).
Imagen por Lecturio.| Imatinib Imatinib A tyrosine kinase inhibitor and antineoplastic agent that inhibits the bcr-abl kinase created by chromosome rearrangements in chronic myeloid leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia, as well as pdg-derived tyrosine kinases that are overexpressed in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | Dasatinib Dasatinib A pyrimidine and thiazole derived antineoplastic agent and protein kinase inhibitor of bcr-abl kinase. It is used in the treatment of patients with chronic myeloid leukemia who are resistant or intolerant to imatinib. Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | Nilotinib Nilotinib Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Farmacodinamia |
|
||
| Farmacocinética |
|
||
| Indicaciones |
|
||
| Efectos secundarios |
|
|
|
| Contraindicaciones |
|
||
| Vemurafenib Vemurafenib An indole sulfonamide compound and inhibitor of BRAF kinases that is used for the treatment of unresectable or metastatic melanoma. Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | Dabrafenib DaBRAFenib Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy* | |
|---|---|---|
| Farmacodinamia | Inhibir la actividad quinasa de BRAF mutado (incluida la mutación V600) | |
| Farmacocinética |
|
|
| Indicaciones | ||
| Efectos secundarios |
|
|
| Contraindicaciones | Hipersensibilidad al AL Amyloidosis medicamento | |
| Trametinib Trametinib Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | Cobimetinib Cobimetinib Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | |
|---|---|---|
| Farmacodinamia | Inhibe la activación de MEK y la actividad de la quinasa | |
| Farmacocinética |
|
|
| Indicaciones |
|
Melanoma Melanoma Melanoma is a malignant tumor arising from melanocytes, the melanin-producing cells of the epidermis. These tumors are most common in fair-skinned individuals with a history of excessive sun exposure and sunburns. Melanoma |
| Efectos secundarios |
|
|
| Contraindicaciones | Hipersensibilidad al AL Amyloidosis medicamento | |
| Ruxolitinib Ruxolitinib Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | Barcitinib | |
|---|---|---|
| Farmacodinamia | Inhiben JAK | |
| Farmacocinética |
|
|
| Indicaciones |
|
|
| Efectos secundarios |
|
|
| Contraindicaciones | Hipersensibilidad al AL Amyloidosis medicamento | |
| Palbociclib Palbociclib Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | Abemaciclib | |
|---|---|---|
| Farmacodinamia | Inhibidor de la CDK; previene la progresión a través del ciclo celular, lo que lleva a la interrupción en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la fase G1 | |
| Farmacocinética |
|
|
| Indicaciones | Cáncer de mama avanzado | |
| Efectos secundarios |
|
|
| Contraindicaciones | Hipersensibilidad al AL Amyloidosis medicamento | |
| Ibrutinib Ibrutinib Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | Acalabrutinib Acalabrutinib Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | |
|---|---|---|
| Farmacodinamia | Inhibe la BTK, lo que reduce la proliferación de linfocitos B y el crecimiento tumoral | |
| Farmacocinética |
|
|
| Indicaciones |
|
|
| Efectos secundarios |
|
|
| Contraindicaciones | Hipersensibilidad al AL Amyloidosis medicamento | |
| Crizotinib Crizotinib A piperidine and aminopyridine derivative that acts as an inhibitor of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases, including anaplastic lymphoma kinase (alk) and hepatocyte growth factor receptor (hgfr; c-met). It is used in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | Alectinib Alectinib Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | Ceritinib Ceritinib Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Farmacodinamia | Inhiben ALK, previniendo la proliferación y supervivencia de tumores ALK positivos | ||
| Farmacocinética |
|
|
|
| Indicaciones |
|
||
| Efectos secundarios |
|
||
| Contraindicaciones | Hipersensibilidad al AL Amyloidosis medicamento | ||
| Cetuximab Cetuximab A chimeric monoclonal antibody that functions as an antineoplastic agent through its binding to the epidermal growth factor receptor, where it prevents the binding and signaling action of cell growth and survival factors. Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | Panitumumab Panitumumab Recombinant human monoclonal antibody that binds to and inhibits the function of the epidermal growth factor receptor. It is used in the treatment of egfr-expressing metastatic colorectal cancer that expresses wild-type RAS gene. Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | |
|---|---|---|
| Farmacodinamia |
|
|
| Farmacocinética |
|
|
| Indicaciones |
|
|
| Efectos secundarios |
|
|
| Contraindicaciones | Hipersensibilidad al AL Amyloidosis medicamento o a sus componentes | |
| Afatinib Afatinib A quinazoline and butenamide derivative that acts as a tyrosine kinase inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptors (ErbB receptors) and is used in the treatment of metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | Erlotinib Erlotinib A quinazoline derivative and antineoplastic agent that functions as a protein kinase inhibitor for egfr associated tyrosine kinase. It is used in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | Gefitinib Gefitinib A selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor for the epidermal growth factor receptor (egfr) that is used for the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Farmacodinamia | Inhibidor de la tirosina quinasa del EGFR | ||
| Farmacocinética |
|
|
|
| Indicaciones | Cáncer de pulmón de células no pequeñas (con mutaciones) |
|
Cáncer de pulmón de células no pequeñas (con mutaciones del EGFR) |
| Efectos secundarios |
|
||
| Contraindicaciones | Hipersensibilidad al AL Amyloidosis medicamento o sus componentes | ||
| Bevacizumab Bevacizumab An anti-vegf humanized murine monoclonal antibody. It inhibits vegf receptors and helps to prevent pathologic angiogenesis. Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | Ziv-aflibercept Ziv-Aflibercept Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | Sorafenib Sorafenib A niacinamide and phenylurea derivative that inhibits multiple intracellular and cell surface kinases thought to be involved in angiogenesis, including raf kinases and vegf receptors. It is used in the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma, and for treatment of thyroid carcinoma refractory to radioactive iodine therapy. Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Farmacodinamia | Anticuerpo monoclonal dirigido al AL Amyloidosis ligando VEGF | Proteína de fusión recombinante que actúa como receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors señuelo | Inhibe las tirosina quinasas del VEGFR (y también al AL Amyloidosis PDGF) |
| Farmacocinética |
|
|
|
| Indicaciones |
|
Cáncer colorrectal metastásico |
|
| Efectos secundarios |
|
||
| Contraindicaciones |
|
Ninguno listado |
|
| Trastuzumab Trastuzumab A humanized monoclonal antibody against the ErbB-2 receptor (HER2). As an antineoplastic agent, it is used to treat breast cancer where HER2 is overexpressed. Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | Pertuzumab Pertuzumab Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | lapatinib Lapatinib A quinazoline derivative that inhibits epidermal growth factor receptor and HER2 tyrosine kinases. It is used for the treatment of advanced or metastatic breast cancer, where tumors overexpress HER2. Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Farmacodinamia | Anticuerpo monoclonal que se une a HER2 HER2 A cell surface protein-tyrosine kinase receptor that is overexpressed in a variety of adenocarcinomas. It has extensive homology to and heterodimerizes with the EGF receptor, the ERBB-3 receptor, and the ERBB-4 receptor. Activation of the erbB-2 receptor occurs through heterodimer formation with a ligand-bound erbB receptor family member. Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy (dominio extracelular) | Inhibidor dual de quinasa (inhibe EGFR y HER2 HER2 A cell surface protein-tyrosine kinase receptor that is overexpressed in a variety of adenocarcinomas. It has extensive homology to and heterodimerizes with the EGF receptor, the ERBB-3 receptor, and the ERBB-4 receptor. Activation of the erbB-2 receptor occurs through heterodimer formation with a ligand-bound erbB receptor family member. Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy) | |
| Farmacocinética |
|
|
|
| Indicaciones |
|
Cáncer de mama | Cáncer de mama |
| Efectos secundarios |
|
|
|
| Contraindicaciones | Hipersensibilidad al AL Amyloidosis medicamento | ||
| Olaparib | Rucaparib | Niraparib | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Farmacodinamia | Inhibidor de la enzima PARP | ||
| Farmacocinética |
|
|
|
| Indicaciones |
|
|
Cáncer de ovario, trompa de Falopio o peritoneal primario |
| Efectos secundarios comunes |
|
||
| Efectos secundarios |
|
|
|
| Contraindicaciones | Hipersensibilidad al AL Amyloidosis medicamento | Ninguno listado | Hipersensibilidad al AL Amyloidosis medicamento |
| Medicamentos | Actividad |
|---|---|
Inhibidores de la proteína quinasa:
|
Inhiben la acción de las enzimas proteína quinasa |
Inhibidores del
receptor
Receptor
Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell.
Receptors del factor de crecimiento:
|
|
| Inhibidores de PARP | ↓ Capacidad de reparación del ADN |
| Inhibidores de BCL2 | Promueven la apoptosis Apoptosis A regulated cell death mechanism characterized by distinctive morphologic changes in the nucleus and cytoplasm, including the endonucleolytic cleavage of genomic DNA, at regularly spaced, internucleosomal sites, I.e., DNA fragmentation. It is genetically-programmed and serves as a balance to mitosis in regulating the size of animal tissues and in mediating pathologic processes associated with tumor growth. Ischemic Cell Damage de las células cancerosas (que dependen de esta vía) |
| Inhibidores de CD20 | Se unen al AL Amyloidosis antígeno de la superficie celular e inician la lisis de los LOS Neisseria linfocitos B |
| Inhibidores de la vía Hedgehog | Se unen al AL Amyloidosis componente proteico e inhiben la transducción de señales de Hedgehog, ↓ proliferación de células ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum carcinoma de células basales) |
| Inhibidores de puntos de control inmunitario | Inhiben puntos de control inmunitario (CTLA4, PD-1 PD-1 An inhibitory t-lymphocyte receptor that has specificity for CD274 antigen and programmed cell death 1 ligand 2 protein. Signaling by the receptor limits T cell proliferation and interferon gamma synthesis. The receptor also may play an essential role in the regulatory pathway that induces peripheral tolerance. T cells: Types and Functions), lo que permite la activación y proliferación de linfocitos T |
| Inhibidores de mTOR mTOR Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome | Inhiben la actividad de la quinasa mTOR mTOR Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome, lo que reduce la síntesis de proteínas, la proliferación celular y la angiogénesis |
| Inhibidores del proteasoma | Bloquean la actividad del proteasoma, interrumpiendo la señalización y aumentando la apoptosis Apoptosis A regulated cell death mechanism characterized by distinctive morphologic changes in the nucleus and cytoplasm, including the endonucleolytic cleavage of genomic DNA, at regularly spaced, internucleosomal sites, I.e., DNA fragmentation. It is genetically-programmed and serves as a balance to mitosis in regulating the size of animal tissues and in mediating pathologic processes associated with tumor growth. Ischemic Cell Damage celular |
| Asparaginasa | Reduce la asparagina, lo que reduce la fuente de células leucémicas |
| Talidomida |
|