Las mordeduras de perros y gatos pueden provocar la destrucción de tejidos superficiales y profundos, así como graves infecciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las heridas. Las mordeduras de perro se producen con mayor frecuencia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum hombres y niños y suelen causar traumatismos por aplastamiento o desgarro. Las mordeduras de gato son más frecuentes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las mujeres adultas y provocan heridas punzantes. Dado que las heridas punzantes permiten la inoculación de bacterias en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria tejidos profundos, las mordeduras de gato se asocian con mayor frecuencia a la infección. El diagnóstico es clínico, y deben obtenerse cultivos si la herida parece infectada. El tratamiento requiere un cuidado estricto de las heridas y antibióticos para las heridas de alto riesgo o infectadas.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Se carece de datos internacionales, pero las estadísticas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum Estados Unidos incluyen:
| Mordeduras de perro | Mordeduras de gato |
|---|---|
| Aproximadamente el 90% de las mordeduras de animales | Aproximadamente el 10% de las mordeduras de animales |
| Hombres > mujeres | Mujeres > hombres |
| Niños > adultos | Adultos > niños |
| Con menos frecuencia son el resultado de una provocación | Con mayor frecuencia es el resultado de una provocación |
Además del riesgo de contraer el virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la rabia por la mordedura de un animal, las infecciones de las heridas pueden ser causadas por los LOS Neisseria siguientes organismos:
| Mordeduras de perro | Mordeduras de gato | Ambos |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Factores relacionados con el paciente:
Factores relacionados con las mordeduras:
| Mordeduras de perro | Mordeduras de gato | |
|---|---|---|
| Localización | Niños: cabeza, cara, cuello Adultos: manos, brazos |
Extremidades |
| Tipo de herida | Aplastamiento y desgarro | Punzante |
| Consecuencias | Las estructuras profundas se ven lesionadas con frecuencia (tendones, huesos y vasos sanguíneos). | Inoculación de bacterias en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria tejidos profundos |
| Riesgo de infección profunda | Menos probable | Más probable (y requiere menor tiempo para manifestarse) |
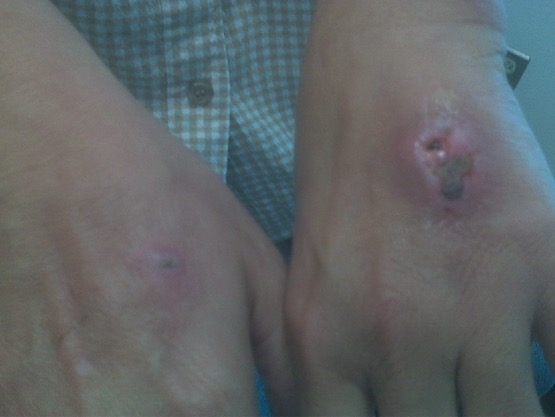
Heridas bilaterales, ulcerosas y nodulares en el dorso de las manos de un paciente tras sufrir mordeduras de perro
Imagen: “Ulcerative, nodular wounds” por Warren Alpert Brown University School of Medicine, 1125 North Main Street, Providence, RI 02906, USA. Licencia: CC BY 4.0El diagnóstico de una mordedura de gato o de perro es clínico, pero se puede utilizar lo siguiente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum casos seleccionados:
Las heridas con bajo riesgo de infección no requieren profilaxis antibiótica. La profilaxis antibiótica está indicada en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum:
Heridas de alto riesgo:
Condiciones de alto riesgo:
Al AL Amyloidosis igual que las mordeduras de perro y gato, las mordeduras de humanos pueden conllevar un riesgo importante de infección.
La infección tras una mordedura de humano suele ser polimicrobiana. Los LOS Neisseria microorganismos más comunes son:
Consideraciones generales y evaluación