El lupus eritematoso sistémico (LES) es una afección inflamatoria autoinmune crónica que provoca el depósito de inmunocomplejos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria órganos, lo que da lugar a manifestaciones sistémicas. Las mujeres, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum particular las de ascendencia afroamericana, son las más comúnmente afectadas. La presentación clínica puede variar mucho. Las características clínicas notables incluyen erupción malar, artritis no destructiva, nefritis lúpica, serositis Serositis Inflammation of a serous membrane. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, citopenia, enfermedad tromboembólica, convulsiones y/o psicosis. El diagnóstico se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum criterios clínicos e incluye pruebas para determinar anticuerpos antinucleares (ANA, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés), anticuerpos específicos para LES y hallazgos clínicos específicos. El objetivo del tratamiento es controlar los LOS Neisseria síntomas y prevenir el daño de los LOS Neisseria órganos mediante el uso de corticosteroides, hidroxicloroquina e inmunosupresores.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Se desconoce el mecanismo exacto. Es probable que los LOS Neisseria pacientes tengan una predisposición genética a las células inmunitarias autorreactivas (linfocitos B y T).
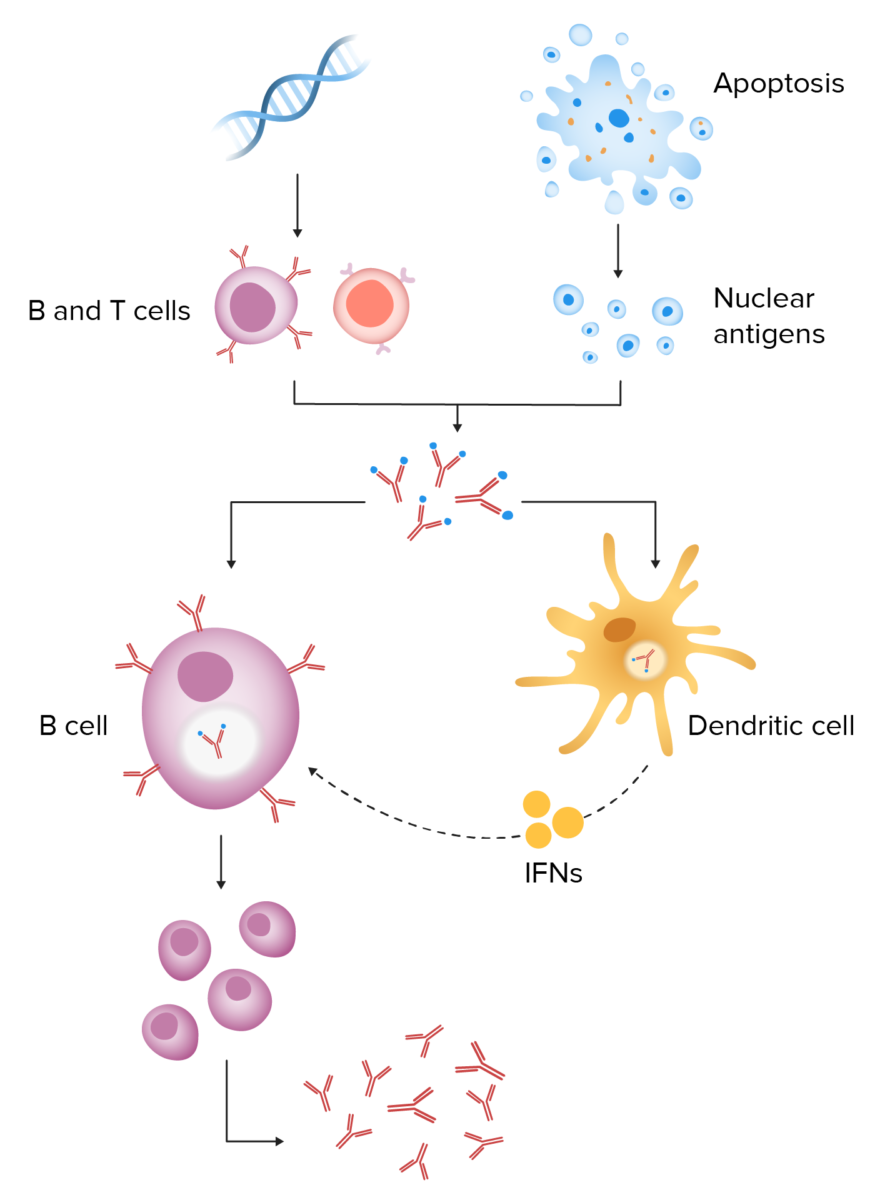
Patogénesis del lupus eritematoso sistémico:
La predisposición genética da como resultado linfocitos B y T autorreactivos. Cuando un desencadenante ambiental provoca la apoptosis celular, la eliminación defectuosa de los desechos celulares da como resultado una mayor exposición a los antígenos nucleares. Estos antígenos y autoanticuerpos conducen a la formación de inmunocomplejos. La endocitosis de los inmunocomplejos produce la liberación de interferón de las células dendríticas, lo que conduce a la activación continua de los linfocitos B y la producción persistente de anticuerpos.
La presentación clínica del LES es muy variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables y puede incluir varios sistemas.
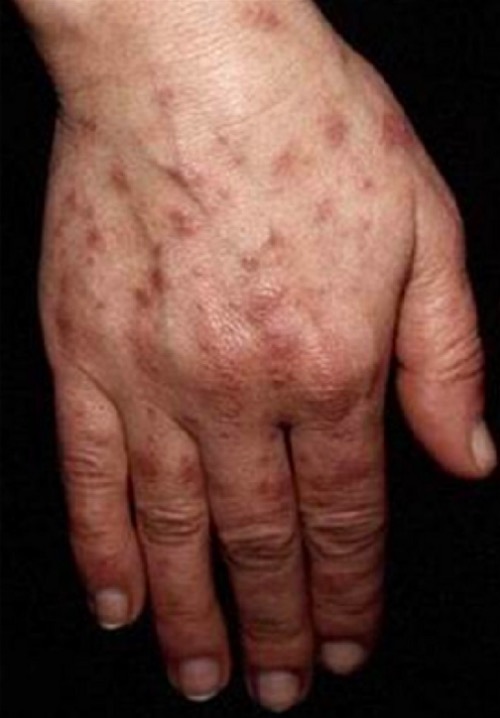
Lesiones fotosensibles en la mano de un paciente con LES
Imagen: “Photosensitive lesions” por Faculdade de Medicina de Lisboa, Clinica Universitária de Dermatologia, Avenido Prof. Egas Moniz, 1649-035 Lisboa, Portugal. Licencia: CC BY 3.0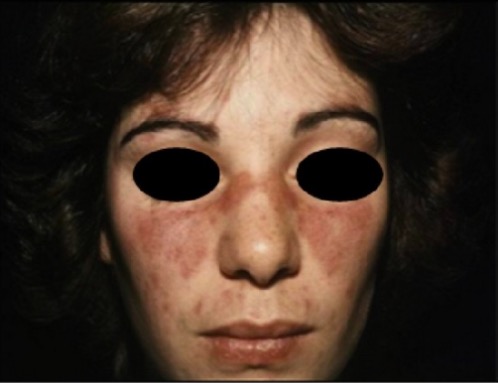
Erupción malar de LES: erupción típica en “mariposa” que no afecta los pliegues nasolabiales
Imagen: “Malar rash” por Faculdade de Medicina de Lisboa, Clinica Universitária de Dermatologia, Avenido Prof. Egas Moniz, 1649-035 Lisboa, Portugal. Licencia: CC BY 3.0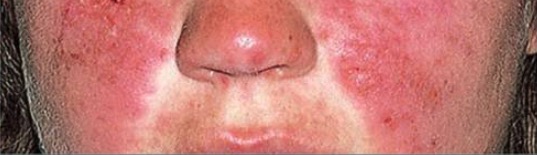
Erupción malar típica en un paciente con LES: obsérvese que no afecta los pliegues nasolabiales.
Imagen: “Typical features” por Department of Bacteriology and Immunology, Haartman Institute, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland. Licencia: CC BY 4.0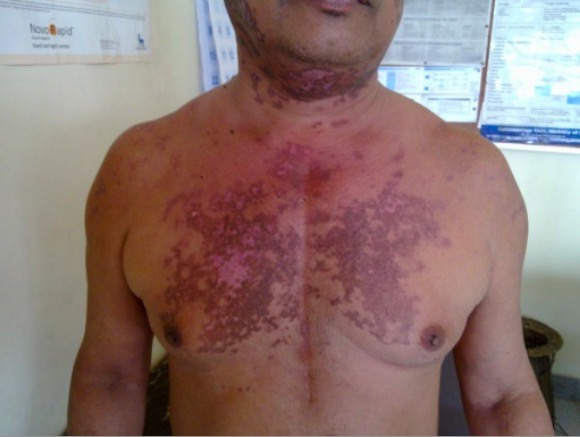
Erupción discoide en paciente con LES
Imagen : “Discoid rash on patient’s neck and chest” por Wards 45 and 46 A, National Hospital of Sri Lanka, Regent Street, Colombo, Sri Lanka. Licencia: CC BY 2.0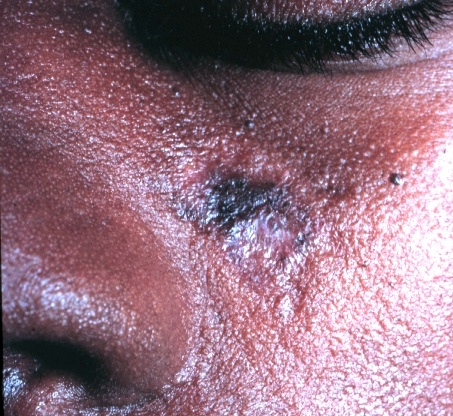
Presentación cutánea del lupus discoide:
La imagen muestra una placa descamada y cicatrización.
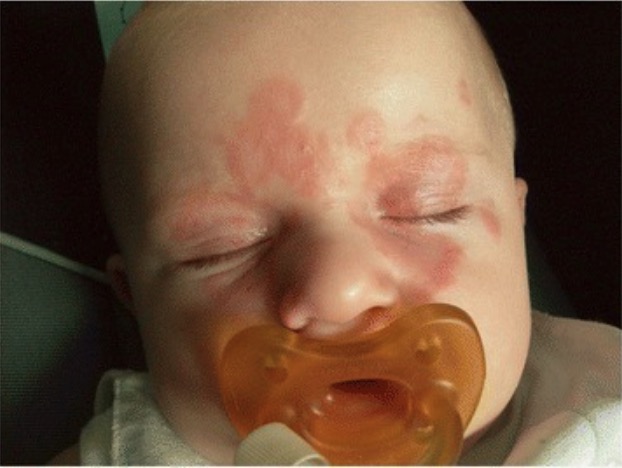
Presentación cutánea del lupus neonatal:
La erupción muestra lesiones anulares con bordes elevados.
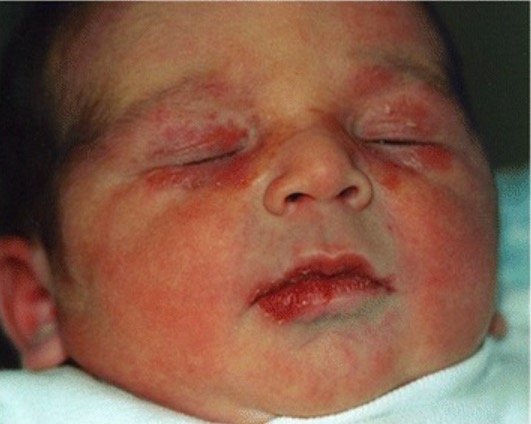
Presentación cutánea del lupus neonatal:
Se observan lesiones periorbitarias, descamativas y eritematosas.
Ante la sospecha inicial de LES: ANA
Si los LOS Neisseria ANA son positivos, se debe evaluar lo siguiente:
| Dominio | Criterios | Puntuación |
|---|---|---|
| Hallazgos clínicos | ||
| Constitucional | Fiebre | 2 |
| Mucocutáneos | Alopecia Alopecia Alopecia is the loss of hair in areas anywhere on the body where hair normally grows. Alopecia may be defined as scarring or non-scarring, localized or diffuse, congenital or acquired, reversible or permanent, or confined to the scalp or universal; however, alopecia is usually classified using the 1st 3 factors. Alopecia no cicatricial | 2 |
| Úlceras bucales | 2 | |
| Lupus cutáneo subagudo o discoide | 4 | |
| Lupus cutáneo agudo | 6 | |
| Musculoesqueléticos | > 2 articulaciones involucradas | 6 |
| Neurosiquiátricos | Delirium Delirium Delirium is a medical condition characterized by acute disturbances in attention and awareness. Symptoms may fluctuate during the course of a day and involve memory deficits and disorientation. Delirium | 2 |
| Psicosis | 3 | |
| Convulsiones | 5 | |
| Serositis Serositis Inflammation of a serous membrane. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus | Derrame pleural o pericárdico | 5 |
| Pericarditis Pericarditis Pericarditis is an inflammation of the pericardium, often with fluid accumulation. It can be caused by infection (often viral), myocardial infarction, drugs, malignancies, metabolic disorders, autoimmune disorders, or trauma. Acute, subacute, and chronic forms exist. Pericarditis aguda | 6 | |
| Hematológicos | Leucopenia | 3 |
| Trombocitopenia | 4 | |
| Hemólisis autoinmune | 4 | |
| Renales | Proteinuria Proteinuria The presence of proteins in the urine, an indicator of kidney diseases. Nephrotic Syndrome in Children | 4 |
| Biopsia renal con nefritis lúpica clase II o V | 8 | |
| Biopsia renal con nefritis lúpica clase III o IV | 10 | |
| Hallazgos inmunológicos | ||
| Anticuerpos específicos de LES | Anticuerpo anti-ADN de doble cadena o anticuerpo anti-Smith | 6 |
| Niveles de complemento | C3 o C4 bajos | 3 |
| C3 y C4 bajos | 4 | |
| Anticuerpos antifosfolípidos | Anticuerpo anticardiolipina o anticoagulante lúpico o anticuerpo anti-beta 2-glucoproteína | 2 |
Para ayudar a recordar algunos criterios, recuerde “SOAP BRAIN MD” ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés):
Como no existe un tratamiento definitivo disponible, el tratamiento está dirigido a controlar los LOS Neisseria brotes agudos, suprimir los LOS Neisseria síntomas y prevenir el daño a los LOS Neisseria órganos.
Para recordar las 3 causas más comunes de muerte en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum LES, recuerde: “ Los LOS Neisseria pacientes con lupus mueren con enrojecimiento en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las mejillas (Redness In their Cheeks)”.