A terapia direcionada exerce atividade antineoplástica contra células cancerígenas ao interferir com propriedades únicas encontradas em tumores ou neoplasias malignas. Os tipos de fármacos podem ser moléculas pequenas, capazes de entrar nas células, ou anticorpos monoclonais, que têm alvos fora ou na superfície das células. Entre as áreas das células malignas que são bloqueadas ou inibidas por terapia direcionada estão as vias de sinalização (como visto nos inibidores da proteína cinase), que levam a uma diminuição da proliferação e subsequente apoptose das células tumorais. Outra forma de reduzir as células cancerígenas é ao eliminar a capacidade de reparação do DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure (visto nos inibidores da poli(ADP-ribose) polimerase), bloquear a ligação ligando-recetor (inibidores de fatores de crescimento) e aumentar a atividade imune contra a neoplasia (imunoterapias). Estes agentes são utilizados em vários tipos de cancro e em combinação com agentes quimioterápicos tradicionais.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
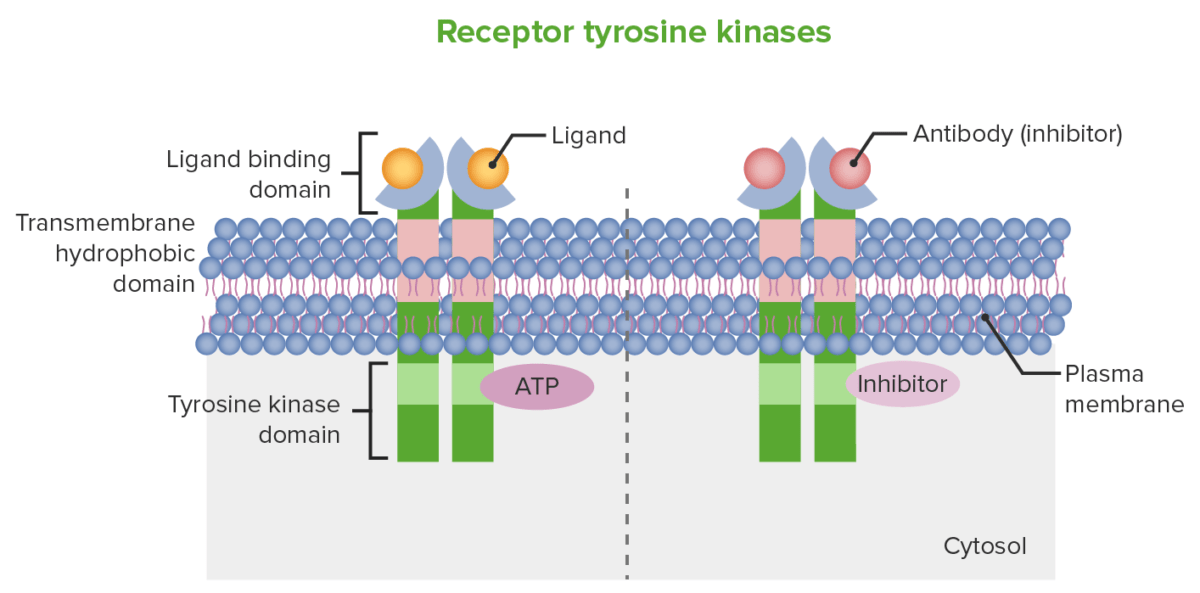
Mecanismo esquemático para inibição do recetor de tirosina cinase: À esquerda, a imagem mostra a estrutura do recetor da célula. Na superfície da célula encontra-se o domínio ligante e o domínio cinase (nesta imagem, tirosina cinase) está presente intracelularmente. À direita, a imagem mostra como um anticorpo monoclonal pode produzir atividade antineoplásica, que é através da inibição mediada por anticorpos do domínio de ligação ao ligando. Pequenas moléculas, que conseguem entrar nas células, são capazes de produzir inibição do domínio de ligação à ATP (tirosina cinase).
Imagem por Lecturio.| Imatinib Imatinib A tyrosine kinase inhibitor and antineoplastic agent that inhibits the bcr-abl kinase created by chromosome rearrangements in chronic myeloid leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia, as well as pdg-derived tyrosine kinases that are overexpressed in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | Dasatinib Dasatinib A pyrimidine and thiazole derived antineoplastic agent and protein kinase inhibitor of bcr-abl kinase. It is used in the treatment of patients with chronic myeloid leukemia who are resistant or intolerant to imatinib. Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | Nilotinib Nilotinib Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Farmacodinâmica |
|
||
| Farmacocinética |
|
||
| Indicações |
|
||
| Efeitos adversos |
|
|
|
| Contraindicações |
|
||
| Vemurafenib Vemurafenib An indole sulfonamide compound and inhibitor of BRAF kinases that is used for the treatment of unresectable or metastatic melanoma. Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | Dabrafenib DaBRAFenib Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy* | |
|---|---|---|
| Farmacodinâmica | Inibem a atividade de BRAF cinase mutada (incluindo a mutação V600) | |
| Farmacocinética |
|
|
| Indicações | ||
| Efeitos adversos |
|
|
| Contraindicações | Hipersensibilidade ao fármaco | |
| Trametinib Trametinib Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | Cobimetinib Cobimetinib Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | |
|---|---|---|
| Farmacodinâmica | Inibe a ativação de MEK e a atividade cinase | |
| Farmacocinética |
|
|
| Indicações | Melanoma Melanoma Melanoma is a malignant tumor arising from melanocytes, the melanin-producing cells of the epidermis. These tumors are most common in fair-skinned individuals with a history of excessive sun exposure and sunburns. Melanoma | |
| Efeitos adversos |
|
|
| Contraindicações | Hipersensibilidade ao fármaco | |
| Ruxolitinib Ruxolitinib Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | Barcitinib | |
|---|---|---|
| Farmacodinâmica | Inibem JAK | |
| Farmacocinética |
|
|
| Indicações |
|
|
| Efeitos adversos |
|
|
| Contraindicações | Hipersensibilidade ao fármaco | |
| Palbociclib Palbociclib Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | Abemaciclib | |
|---|---|---|
| Farmacodinâmica | Inibidor da CDK; impede a progressão pelo ciclo celular, levando a uma paragem na fase G1 | |
| Farmacocinética |
|
|
| Indicações | Cancro da mama avançado | |
| Efeitos adversos |
|
|
| Contraindicações | Hipersensibilidade ao fármaco | |
| Ibrutinib Ibrutinib Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | Acalabrutinib Acalabrutinib Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | |
|---|---|---|
| Farmacodinâmica | Inibição de BTK, o que leva à redução da proliferação de células B e do crescimento tumoral | |
| Farmacocinética |
|
|
| Indicações |
|
|
| Efeitos adversos |
|
|
| Contraindicações | Hipersensibilidade ao fármaco | |
| Crizotinib Crizotinib A piperidine and aminopyridine derivative that acts as an inhibitor of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases, including anaplastic lymphoma kinase (alk) and hepatocyte growth factor receptor (hgfr; c-met). It is used in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | Alectinib Alectinib Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | Ceritinib Ceritinib Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Farmacodinâmica | Inibe a ALK, prevenindo a proliferação e sobrevivência de tumores ALK-positivos | ||
| Farmacocinética |
|
|
|
| Indicações |
|
||
| Efeitos adversos |
|
||
| Contraindicações | Hipersensibilidade ao fármaco | ||
| Cetuximab Cetuximab A chimeric monoclonal antibody that functions as an antineoplastic agent through its binding to the epidermal growth factor receptor, where it prevents the binding and signaling action of cell growth and survival factors. Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | Panitumumab Panitumumab Recombinant human monoclonal antibody that binds to and inhibits the function of the epidermal growth factor receptor. It is used in the treatment of egfr-expressing metastatic colorectal cancer that expresses wild-type RAS gene. Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | |
|---|---|---|
| Farmacodinâmica |
|
|
| Farmacocinética |
|
|
| Indicações |
|
|
| Efeitos adversos |
|
|
| Contraindicações | Hipersensibilidade ao fármaco ou aos seus componentes | |
| Afatinib Afatinib A quinazoline and butenamide derivative that acts as a tyrosine kinase inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptors (ErbB receptors) and is used in the treatment of metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | Erlotinib Erlotinib A quinazoline derivative and antineoplastic agent that functions as a protein kinase inhibitor for egfr associated tyrosine kinase. It is used in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | Gefitinib Gefitinib A selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor for the epidermal growth factor receptor (egfr) that is used for the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Farmacodinâmica | Inibidor da tirosina quinase de EGFR | ||
| Farmacocinética |
|
|
|
| Indicações | CPNPC (com mutações) |
|
CPNPC (com mutações no EGFR) |
| Efeitos adversos |
|
||
| Contraindicações | Hipersensibilidade ao fármaco ou aos seus componentes | ||
| Bevacizumab Bevacizumab An anti-vegf humanized murine monoclonal antibody. It inhibits vegf receptors and helps to prevent pathologic angiogenesis. Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | Ziv-aflibercept Ziv-Aflibercept Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | Sorafenib Sorafenib A niacinamide and phenylurea derivative that inhibits multiple intracellular and cell surface kinases thought to be involved in angiogenesis, including raf kinases and vegf receptors. It is used in the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma, and for treatment of thyroid carcinoma refractory to radioactive iodine therapy. Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Farmacodinâmica | Anticorpo monoclonal para o ligando do VEGF | Proteína de fusão recombinante que atua como um recetor falso | Inibe as tirosina cinases de VEGFR (e também PDGF) |
| Farmacocinética |
|
|
|
| Indicações |
|
CCR metastático |
|
| Efeitos adversos |
|
||
| Contraindicações |
|
Nenhuma indicada |
|
| Trastuzumab Trastuzumab A humanized monoclonal antibody against the ErbB-2 receptor (HER2). As an antineoplastic agent, it is used to treat breast cancer where HER2 is overexpressed. Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | Pertuzumab Pertuzumab Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | Lapatinib Lapatinib A quinazoline derivative that inhibits epidermal growth factor receptor and HER2 tyrosine kinases. It is used for the treatment of advanced or metastatic breast cancer, where tumors overexpress HER2. Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Farmacodinâmica | Anticorpo monoclonal que liga ao HER2 HER2 A cell surface protein-tyrosine kinase receptor that is overexpressed in a variety of adenocarcinomas. It has extensive homology to and heterodimerizes with the EGF receptor, the ERBB-3 receptor, and the ERBB-4 receptor. Activation of the erbB-2 receptor occurs through heterodimer formation with a ligand-bound erbB receptor family member. Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy (domínio extracelular) | Inibidor duplo de cinases (inibe o EGFR e o HER2 HER2 A cell surface protein-tyrosine kinase receptor that is overexpressed in a variety of adenocarcinomas. It has extensive homology to and heterodimerizes with the EGF receptor, the ERBB-3 receptor, and the ERBB-4 receptor. Activation of the erbB-2 receptor occurs through heterodimer formation with a ligand-bound erbB receptor family member. Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy) | |
| Farmacocinética |
|
|
|
| Indicações |
|
Cancro da mama | Cancro da mama |
| Efeitos adversos |
|
|
|
| Contraindicações | Hipersensibilidade ao fármaco | ||
| Olaparib | Rucaparib | Niraparib | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Farmacodinâmica | Inibidor da enzima PARP | ||
| Farmacocinética |
|
|
|
| Indicações |
|
|
Cancro do ovário, da trompa de Falópio ou peritoneal primário |
| Efeitos adversos comuns |
|
||
| Efeitos adversos |
|
|
|
| Contraindicações | Hipersensibilidade ao fármaco | Nenhuma indicada | Hipersensibilidade ao fármaco |
| Fármacos | Atividade |
|---|---|
Inibidores de proteína cinase:
|
Inibem a ação das enzimas proteína cinases |
Inibidores dos recetores de fatores de crescimento:
|
|
| Inibidores de PARP | ↓ Capacidade de reparação do DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure |
| Inibidores de BCL2 | Promovem a apoptose de células cancerígenas (que dependem desta via) |
| Inibidores de CD20 | Ligam-se ao antigénio da superfície celular e iniciam a lise de células B |
| Inibidores da via Hedgehog | Ligam-se à componente proteica e inibem a transdução de sinal da via Hedgehog, ↓ a proliferação das células (no carcinoma basocelular) |
| Inibidores de pontos de controlo imunes | Inibem os pontos de controlo imunes (CTLA4, PD-1 PD-1 An inhibitory t-lymphocyte receptor that has specificity for CD274 antigen and programmed cell death 1 ligand 2 protein. Signaling by the receptor limits T cell proliferation and interferon gamma synthesis. The receptor also may play an essential role in the regulatory pathway that induces peripheral tolerance. T cells: Types and Functions), permitindo a ativação e proliferação de células T |
| Inibidores de mTOR mTOR Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome | Inibem a atividade da mTOR mTOR Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome cinase, levando à redução da síntese de proteínas, proliferação celular e angiogénese |
| Inibidores do proteassoma | Bloqueam a atividade proteassómica, interrompendo a sinalização e aumentando a apoptose celular |
| Asparaginase Asparaginase A hydrolase enzyme that converts l-asparagine and water to l-aspartate and NH3. Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia | Esgota a asparagina, reduzindo assim a fonte de células leucémicas |
| Talidomida |
|