Los linfomas no Hodgkin son un grupo diverso de neoplasias malignas hematológicas que son trastornos proliferativos clonales de células B maduras o progenitoras, células T o células asesinas naturales. La mayoría de los casos pediátricos son agresivos y de alto grado (pero curables); en adultos, los subtipos de bajo grado son más comunes. Al igual que el linfoma de Hodgkin, que tiene distintas características patológicas y tratamientos, el linfoma no Hodgkin a menudo se presenta con signos constitucionales de fiebre, sudores nocturnos y pérdida de peso. Las características clínicas incluyen linfadenopatía y hepatoesplenomegalia, pero algunas personas presentan compromiso extraganglionar y hallazgos de laboratorio anormales. Los linfomas no Hodgkin de células B incluyen el linfoma difuso de células B grandes, linfoma folicular, linfoma de Burkitt, linfoma de células del manto y linfoma de la zona marginal. Los linfomas no Hodgkin de células T incluyen el linfoma de células T del adulto y la micosis fungoide. El diagnóstico se realiza mediante biopsia de ganglio linfático, biopsia de médula ósea o ambas. El tratamiento es con quimioterapia o medicamentos dirigidos. La radioterapia se usa en adultos, pero no en niños, y el trasplante de células madre se usa para pacientes con enfermedad agresiva.
Last updated: Aug 7, 2022
Los LOS Neisseria linfomas no Hodgkin son un grupo diverso de neoplasias malignas hematológicas que son trastornos proliferativos clonales de células B maduras o progenitoras, células T o células asesinas naturales.
La patogenia del linfoma no Hodgkin implica múltiples lesiones genéticas que afectan a los LOS Neisseria protooncogenes y a los LOS Neisseria genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure supresores de tumores. Las células anormales también parecen escapar de la vigilancia inmunológica.
La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria linfomas se presentan con linfadenopatía indolora con afectación variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables de la sangre periférica, médula ósea, tubo digestivo, piel o sistema nervioso central (SNC).
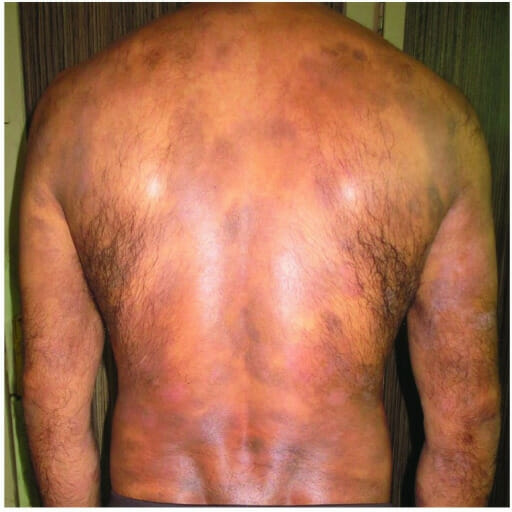
Micosis fungoide en un hombre de 40 años con erupción generalizada
Imagen: “Mycosis fungoides in a 40-year-old man manifested as generalized atrophic patches” por F1000Research. Licencia: CC BY 4.0El diagnóstico adecuado requiere examen histológico, inmunofenotipificación, genotipificación y consideración de las características clínicas. La estadificación es similar a la del linfoma de Hodgkin.
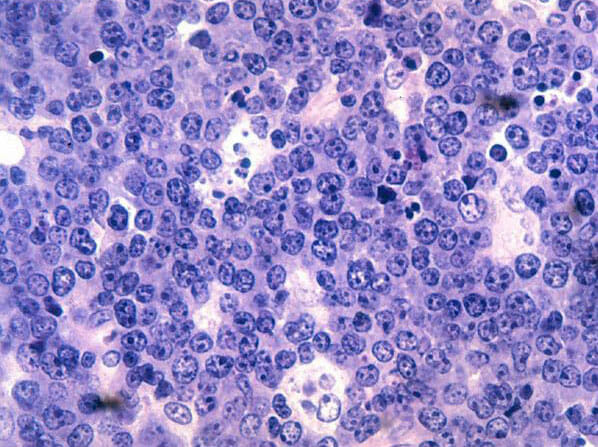
Histopatología del linfoma de Burkitt:
Se observan linfocitos de células B malignos. Obsérvese la clásica apariencia de “cielo estrellado” secundaria a muchos macrófagos pálidos y agrandados que han fagocitado células tumorales apoptóticas muertas (pequeños fragmentos teñidos de azul/púrpura) en este tumor que se divide muy rápidamente. Tinción hematoxilina y eosina.
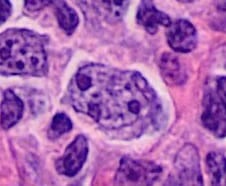
Histopatología de un centroblasto (célula más grande que contiene núcleos vesiculares con 1–3 núcleos basófilos junto a la membrana nuclear) en el linfoma folicular
Imagen: “Histopathology of a centroblast in follicular lymphoma” por Mikael Häggström, MD Licencia: Dominio Público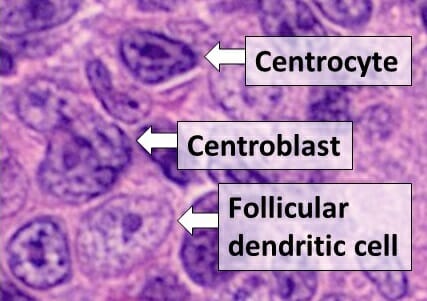
Histología de tipos de células en un centro germinal, visto en linfoma folicular, con centrocitos, centroblastos y una célula dendrítica folicular
Imagen: “Centrocyte, centroblast and follicular dendritic cell in a follicular_lymphoma” por Mikael Häggström, MD Licencia: Dominio Público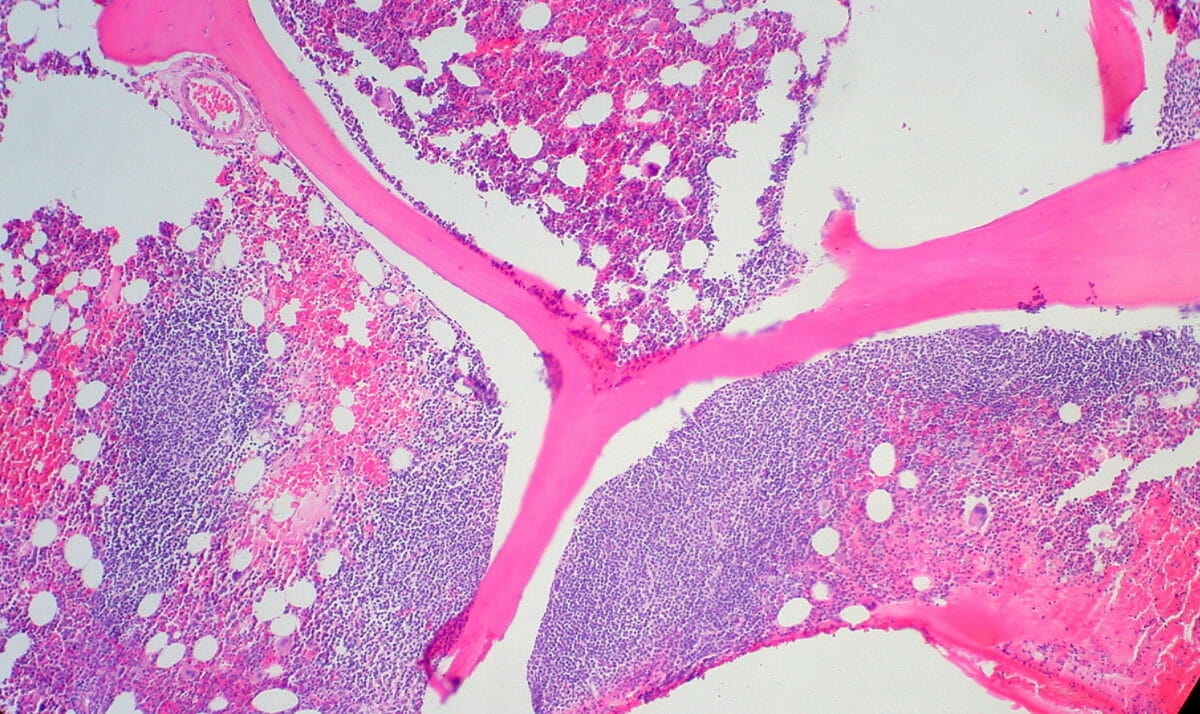
Biopsia de médula ósea de un hombre de 34 años con linfoma folicular que muestra infiltrado paratrabecular característico
Imagen: “Follicular Lymphoma in Bone Marrow” por Ed Uthman. Licencia: CC BY 2.0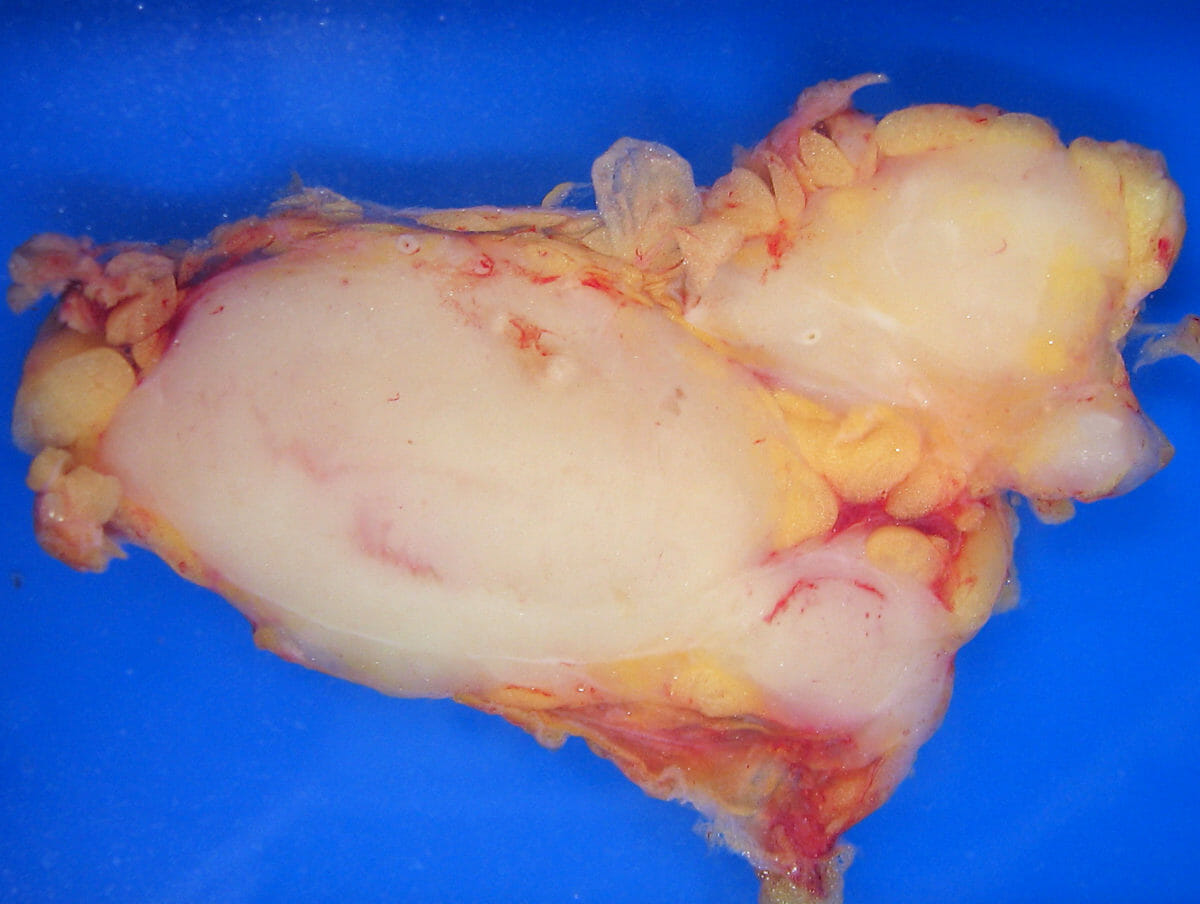
Patología macroscópica de linfoma folicular en un ganglio linfático
Imagen: “Lymphoma_macro” por Emmanuelm. Licencia: CC BY 3.0| Estadio I | compromiso de un solo grupo de ganglios linfáticos o de un solo órgano extralinfático |
|---|---|
| Estadio II | afectación de ≥ 2 grupos de ganglios linfáticos del mismo lado del diafragma |
| Estadio III | afectación de los LOS Neisseria ganglios linfáticos, el bazo o ambos, a ambos lados del diafragma |
| Estadio IV | afectación difusa o diseminada de ≥ 1 órgano extralinfático (hígado, médula ósea, pulmón) con o sin afectación de ganglios linfáticos |
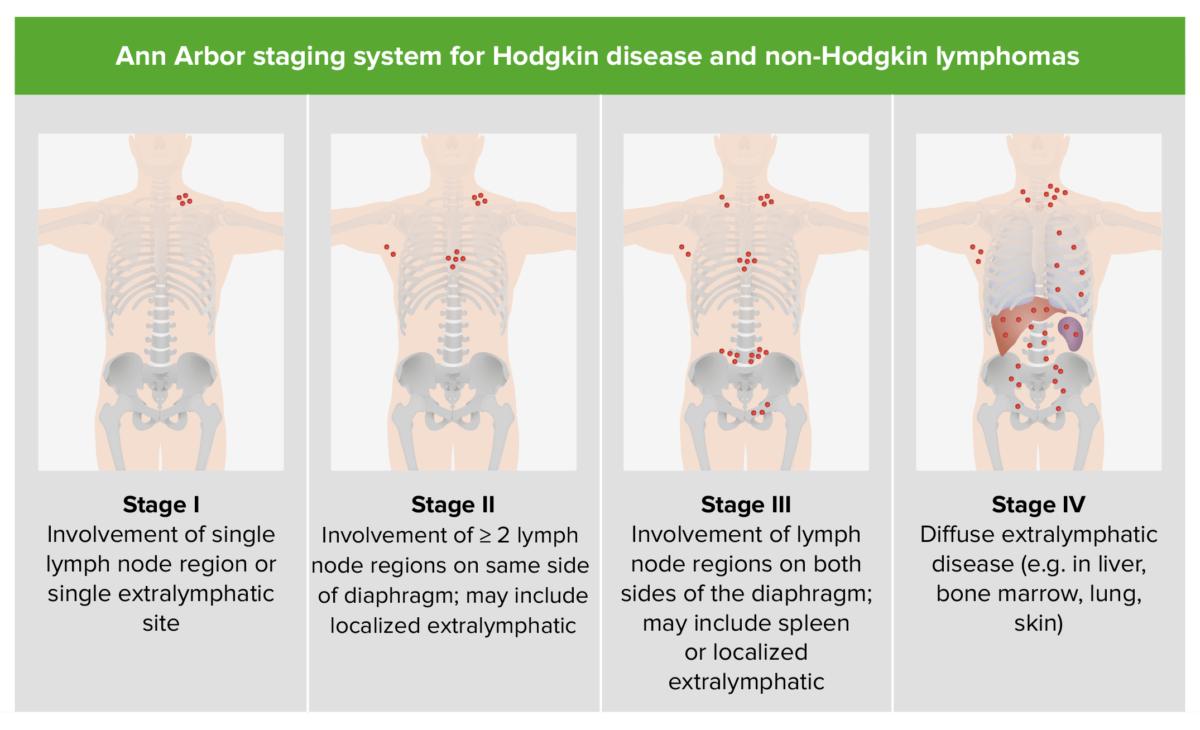
Estadificación del linfoma no Hodgkin (igual que para la enfermedad de Hodgkin)
Imagen por Lecturio.El tratamiento se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum muchos factores, incluidos el subtipo histológico, el estadio y las comorbilidades. CD19 se expresa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum gran medida en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum casi todas las neoplasias malignas de células B, lo que lo convierte en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors atractivo para nuevas terapias dirigidas.
Los LOS Neisseria linfomas no Hodgkin de alto grado son agresivos pero tienen un mejor pronóstico, mientras que los LOS Neisseria de bajo grado progresan lentamente, pero son difíciles de curar.
Los LOS Neisseria factores del Índice Pronóstico Internacional que se asocian a un peor pronóstico:
Supervivencia general a 5 años para los LOS Neisseria linfomas no Hodgkin en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum general:
| Origen | Tipo | Factores de riesgo y genética | Epidemiología | Patología y características clínicas |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Célula B (85%–90%) | DLBCL DLBCL Malignant lymphoma composed of large B lymphoid cells whose nuclear size can exceed normal macrophage nuclei, or more than twice the size of a normal lymphocyte. The pattern is predominantly diffuse. Most of these lymphomas represent the malignant counterpart of B-lymphocytes at midstage in the process of differentiation. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas | Surge de forma esporádica o de la transformación de un linfoma de bajo grado (e.g., linfoma folicular) |
|
|
| Linfoma folicular | t(14;18) → sobreexpresión de BCL2 (gen que regula la apoptosis Apoptosis A regulated cell death mechanism characterized by distinctive morphologic changes in the nucleus and cytoplasm, including the endonucleolytic cleavage of genomic DNA, at regularly spaced, internucleosomal sites, I.e., DNA fragmentation. It is genetically-programmed and serves as a balance to mitosis in regulating the size of animal tissues and in mediating pathologic processes associated with tumor growth. Ischemic Cell Damage) |
|
|
|
| Linfoma de Burkitt |
|
|
|
|
| Linfoma de células del manto | t(11;14) → sobreexpresión de ciclina D1 |
|
|
|
| MZL |
|
|
|
|
| Linfoma linfoplasmocitario (macroglobulinemia de Waldenström) | Mutación del gen MYD88 en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos |
|
|
|
| Célula T (10%–15%) | Linfoma de células T del adulto | Asociado con el retrovirus HTLV-1 |
|
|
| Micosis fungoide (linfoma cutáneo de células T) |
|
|
|