La linfadenopatía es el agrandamiento de los LOS Neisseria ganglios linfáticos (> 1 cm) y es benigna y autolimitada en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la mayoría de los LOS Neisseria pacientes. Las etiologías incluyen malignidad, infección y trastornos autoinmunes, así como causas iatrogénicas como el uso de ciertos medicamentos. La linfadenopatía generalizada a menudo indica una enfermedad sistémica subyacente. El diagnóstico se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una revisión completa de los LOS Neisseria antecedentes médicos y un examen físico, que generalmente identifican la causa subyacente. Cuando se desconoce la causa, puede ser necesaria una biopsia. El tratamiento está dirigido a la infección subyacente, el tumor Tumor Inflammation maligno u otra causa.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La linfadenopatía es el aumento de tamaño de los LOS Neisseria ganglios linfáticos, por lo general > 1 cm. Se considera localizada si el agrandamiento se limita a los LOS Neisseria ganglios linfáticos de 1 región anatómica y generalizada cuando hay afectación de ≥ 2 regiones.
Muy a menudo, la linfadenopatía es una reacción a una infección local. Con menos frecuencia, puede deberse a un proceso maligno o a una enfermedad sistémica crónica. Las siguientes condiciones incluyen linfadenopatía en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum su presentación clínica:
Para recordar las diversas causas de la linfadenopatía, recuerde “MIAMI” ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés):
Los LOS Neisseria sistemas inmunológico y linfático están altamente interrelacionados. Los LOS Neisseria linfocitos se transportan a través de los LOS Neisseria vasos linfáticos a los LOS Neisseria ganglios linfáticos. Los LOS Neisseria seres humanos tienen entre 500–600 ganglios linfáticos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum todo el cuerpo. La linfadenopatía, o inflamación de los LOS Neisseria ganglios linfáticos, puede ocurrir en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum respuesta a una infección, una neoplasia maligna o una enfermedad crónica.
Las células, el plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products y las partículas extrañas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el espacio intersticial se convierten en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum fluido linfático al AL Amyloidosis ingresar a los LOS Neisseria vasos linfáticos. Dentro de los LOS Neisseria ganglios linfáticos, este fluido se filtra del exceso de líquido y células anormales (e.g., infectadas, malignas, dañadas, presentadoras de antígeno). Esto desencadena una respuesta inmune que involucra proliferación celular, lo que hace HACE Altitude Sickness que los LOS Neisseria ganglios se agranden (linfadenopatía reactiva).
La linfadenopatía es resultado de 1 de los LOS Neisseria procesos patológicos:
Los LOS Neisseria signos y síntomas asociados con la linfadenopatía dependerán de la causa y el tipo (localizada versus generalizada).
Antecedentes:
Examen físico:
Pruebas de laboratorio:
Pedidas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum base a los LOS Neisseria antecedentes relevantes del paciente y los LOS Neisseria hallazgos del examen físico para confirmar el diagnóstico sospechado:
Imagenología:
El tipo de prueba solicitada se guía por los LOS Neisseria antecedentes, el examen físico y los LOS Neisseria factores de riesgo.
Biopsia del ganglio linfático:
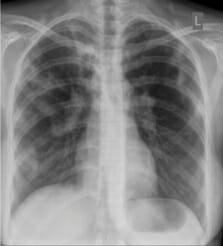
Radiografía de tórax de tuberculosis pulmonar que muestra linfadenopatía hiliar bilateral y opacificación parcheada en la zona pulmonar superior derecha y en la zona pulmonar media con sombras fibróticas
Imagen: “Chest X-ray of patchy opacities of pulmonary tuberculosis” por Basem Abbas Al Ubaidi. Licencia: CC BY 4.0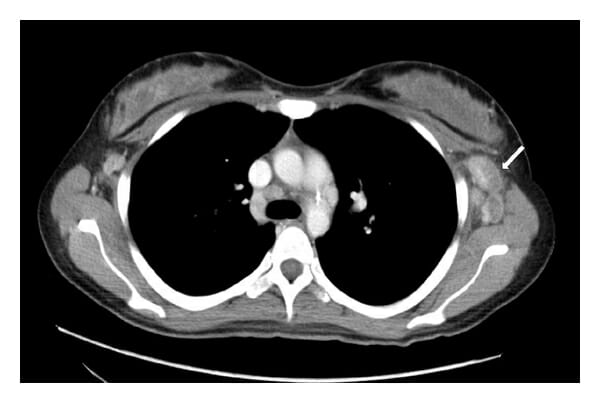
Linfadenopatía axilar en TC torácica con contraste (flecha)
Imagen: “Axillary-lymphadenopathy-on-CT-thorax-with-contrast” por Yu Zuo, Michelle Foshat, You-wen Qian, Brent Kelly, Brock Harper, Bernard Karnath. Licencia: CC BY 4.0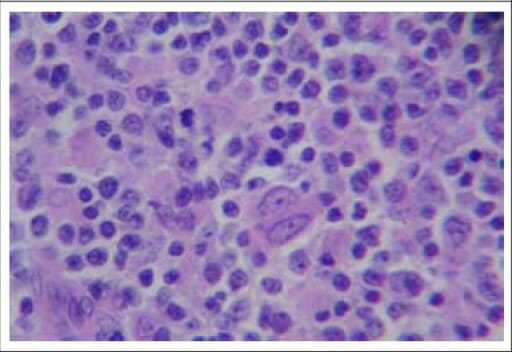
Imagen histopatológica de un ganglio linfático cervical izquierdo con evidencia de linfoma no Hodgkin (tinción H&E, 400x)
Imagen: “F2: Histopathological picture of left cervical lymph node showing evidence of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (H&E stain, ×400)” por Sudipta Pandit et al. Licencia: CC BY 2.5