La histoplasmosis Histoplasmosis Histoplasmosis is an infection caused by Histoplasma capsulatum, a dimorphic fungus. Transmission is through inhalation, and exposure to soils containing bird or bat droppings increases the risk of infection. Most infections are asymptomatic; however, immunocompromised individuals generally develop acute pulmonary infection, chronic infection, or even disseminated disease. Histoplasma/Histoplasmosis es una infección causada por el Histoplasma capsulatum Histoplasma capsulatum Histoplasma/Histoplasmosis, un hongo dimórfico. El hongo existe como moho a bajas temperaturas y como levadura a altas temperaturas. H. capsulatum es la infección fúngica endémica más común en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum EE. UU. y es más prevalente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria estados del medio oeste y sureste a lo largo de los LOS Neisseria valles de los LOS Neisseria ríos Ohio y Mississippi. La transmisión es mediante la inhalación, y la exposición a suelos que contengan excremento de aves o murciélagos, aumenta el riesgo de infección. La mayoría de las infecciones son asintomáticas; sin embargo, los LOS Neisseria individuos inmunocomprometidos suelen desarrollar una infección pulmonar aguda, una infección crónica o incluso una enfermedad diseminada. El diagnóstico se realiza a través de diferentes modalidades, mediante la visualización y/o crecimiento del organismo causante realizado mediante microscopía directa, histopatología o estudios de cultivo. El tratamiento depende de la gravedad de la enfermedad. Los LOS Neisseria medicamentos antifúngicos que se utilizan son la anfotericina B y el itraconazol.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La histoplasmosis Histoplasmosis Histoplasmosis is an infection caused by Histoplasma capsulatum, a dimorphic fungus. Transmission is through inhalation, and exposure to soils containing bird or bat droppings increases the risk of infection. Most infections are asymptomatic; however, immunocompromised individuals generally develop acute pulmonary infection, chronic infection, or even disseminated disease. Histoplasma/Histoplasmosis es una infección causada por un hongo dimórfico. Se puede utilizar la siguiente mnemotecnia para recordar las diferentes formas del hongo:
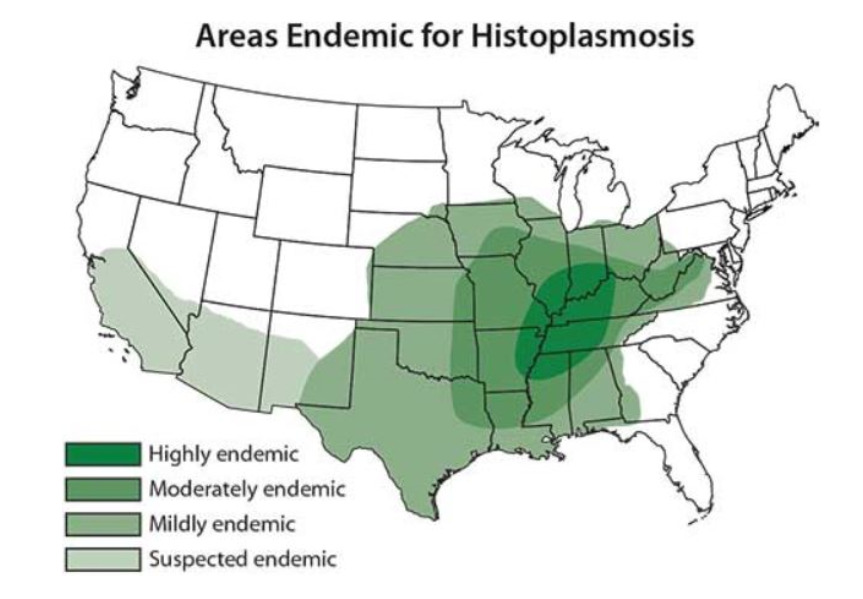
Mapa de Estados Unidos que ilustra las zonas endémicas de histoplasmosis
Imagen: “Map showing areas endemic for histoplasmosis in the US” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoLa presentación clínica varía en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum función del estado inmunitario del huésped y de los LOS Neisseria factores de riesgo subyacentes.
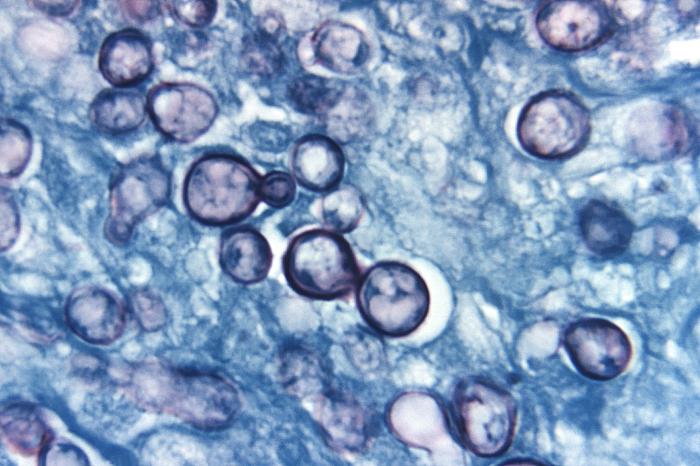
Microfotografía de una muestra de tejido teñida con plata metanamina extraída de un paciente con histoplasmosis:
Nótese la presencia de células típicas de levadura, algunas de las cuales estaban en proceso de replicación por gemación.
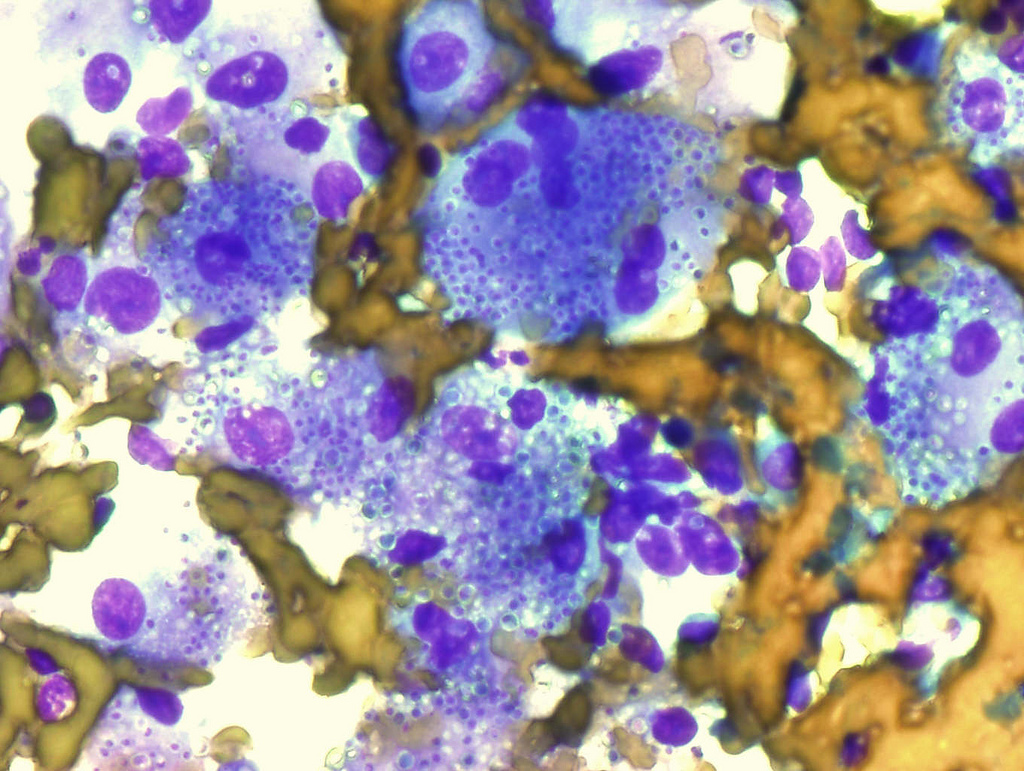
Macrófagos en un ganglio linfático que contiene numerosos Histoplasma capsulatum (tinción Diff-Quick)
Imagen: “Macrophages in lymph node containing numerous Histoplasma capsulatum” por Rosen Y. Licencia: CC BY-SA 2.0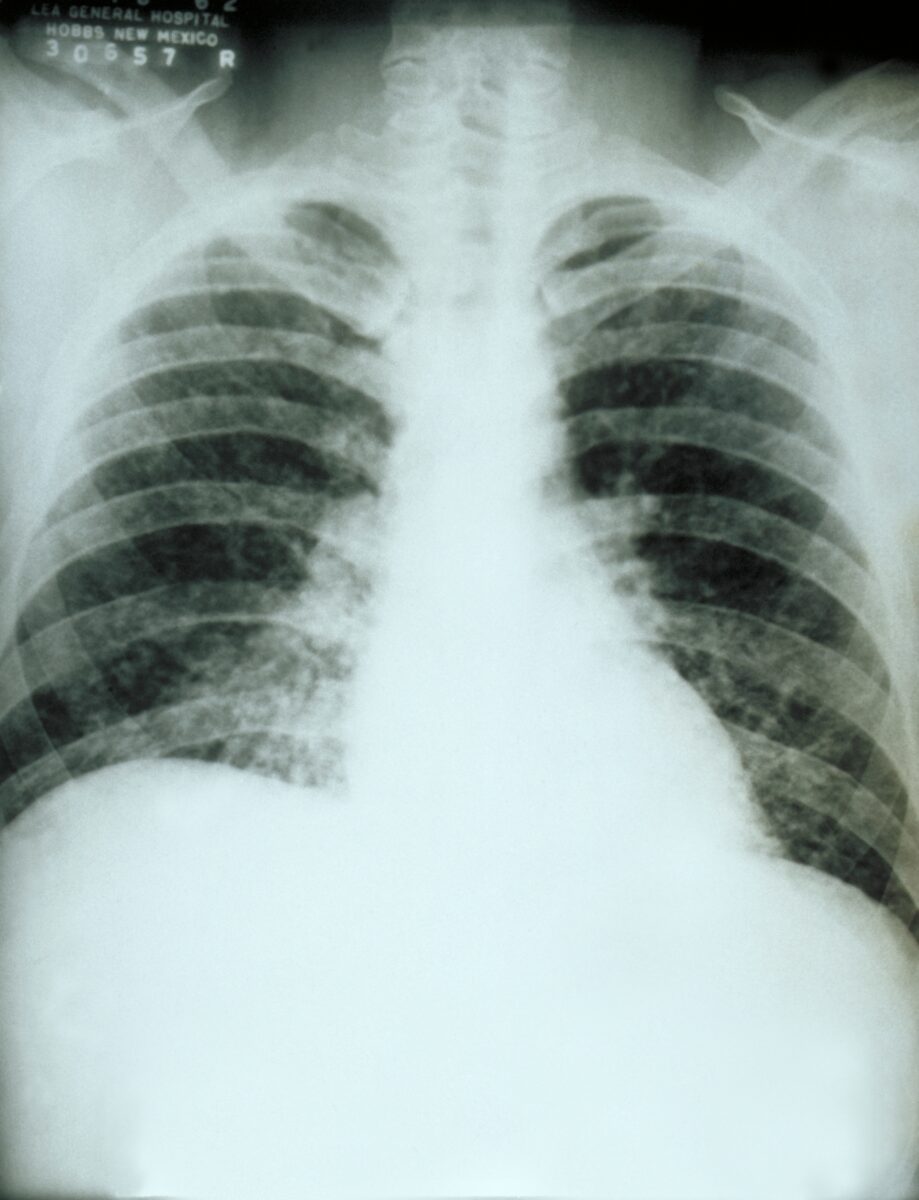
Radiografía de tórax:
Infiltración pulmonar difusa por histoplasmosis pulmonar aguda causada por Histoplasma capsulatum
| Afección | Tratamiento |
|---|---|
| Enfermedad pulmonar moderada o síntomas que duran más de 4 semanas | Itraconazol |
| Enfermedad pulmonar de moderada a grave | Anfotericina B + itraconazol |
| Histoplasmosis Histoplasmosis Histoplasmosis is an infection caused by Histoplasma capsulatum, a dimorphic fungus. Transmission is through inhalation, and exposure to soils containing bird or bat droppings increases the risk of infection. Most infections are asymptomatic; however, immunocompromised individuals generally develop acute pulmonary infection, chronic infection, or even disseminated disease. Histoplasma/Histoplasmosis pulmonar crónica | Itraconazol |
| Histoplasmosis Histoplasmosis Histoplasmosis is an infection caused by Histoplasma capsulatum, a dimorphic fungus. Transmission is through inhalation, and exposure to soils containing bird or bat droppings increases the risk of infection. Most infections are asymptomatic; however, immunocompromised individuals generally develop acute pulmonary infection, chronic infection, or even disseminated disease. Histoplasma/Histoplasmosis diseminada leve: síntomas leves con un solo foco (sin afectación del SNC) | Itraconazol |
| Histoplasmosis Histoplasmosis Histoplasmosis is an infection caused by Histoplasma capsulatum, a dimorphic fungus. Transmission is through inhalation, and exposure to soils containing bird or bat droppings increases the risk of infection. Most infections are asymptomatic; however, immunocompromised individuals generally develop acute pulmonary infection, chronic infection, or even disseminated disease. Histoplasma/Histoplasmosis diseminada grave sin afectación del SNC | Anfotericina B + itraconazol |
| Afectación del SNC | Anfotericina B (a largo plazo) + itraconazol |