La enfermedad de úlcera péptica ( PUD PUD Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) refers to the full-thickness ulcerations of duodenal or gastric mucosa. The ulcerations form when exposure to acid and digestive enzymes overcomes mucosal defense mechanisms. The most common etiologies include Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection and prolonged use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Peptic Ulcer Disease, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) se refiere a las ulceraciones de espesor total de la mucosa duodenal o gástrica. Las ulceraciones se forman cuando la exposición al AL Amyloidosis ácido y a las enzimas digestivas supera los LOS Neisseria mecanismos de defensa de la mucosa. Las etiologías más comunes son la infección por Helicobacter pylori Helicobacter pylori A spiral bacterium active as a human gastric pathogen. It is a gram-negative, urease-positive, curved or slightly spiral organism initially isolated in 1982 from patients with lesions of gastritis or peptic ulcers in Western Australia. Helicobacter pylori was originally classified in the genus campylobacter, but RNA sequencing, cellular fatty acid profiles, growth patterns, and other taxonomic characteristics indicate that the micro-organism should be included in the genus Helicobacter. It has been officially transferred to Helicobacter gen. Helicobacter ( H. pylori H. pylori A spiral bacterium active as a human gastric pathogen. It is a gram-negative, urease-positive, curved or slightly spiral organism initially isolated in 1982 from patients with lesions of gastritis or peptic ulcers in Western Australia. Helicobacter pylori was originally classified in the genus campylobacter, but RNA sequencing, cellular fatty acid profiles, growth patterns, and other taxonomic characteristics indicate that the micro-organism should be included in the genus Helicobacter. It has been officially transferred to Helicobacter gen. Helicobacter) y el uso prolongado de antiinflamatorios no esteroideos (AINE). Los LOS Neisseria pacientes pueden ser asintomáticos o presentarse con dolor Dolor Inflammation abdominal, náuseas y saciedad temprana. La enfermedad de la úlcera péptica suele responder bien al AL Amyloidosis tratamiento médico, que consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la erradicación del H. pylori H. pylori A spiral bacterium active as a human gastric pathogen. It is a gram-negative, urease-positive, curved or slightly spiral organism initially isolated in 1982 from patients with lesions of gastritis or peptic ulcers in Western Australia. Helicobacter pylori was originally classified in the genus campylobacter, but RNA sequencing, cellular fatty acid profiles, growth patterns, and other taxonomic characteristics indicate that the micro-organism should be included in the genus Helicobacter. It has been officially transferred to Helicobacter gen. Helicobacter, la eliminación de los LOS Neisseria factores de riesgo y la utilización de inhibidores de la bomba de protones (IBP). Si no se trata, puede provocar hemorragia, perforación, estenosis pilórica y cáncer gástrico.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
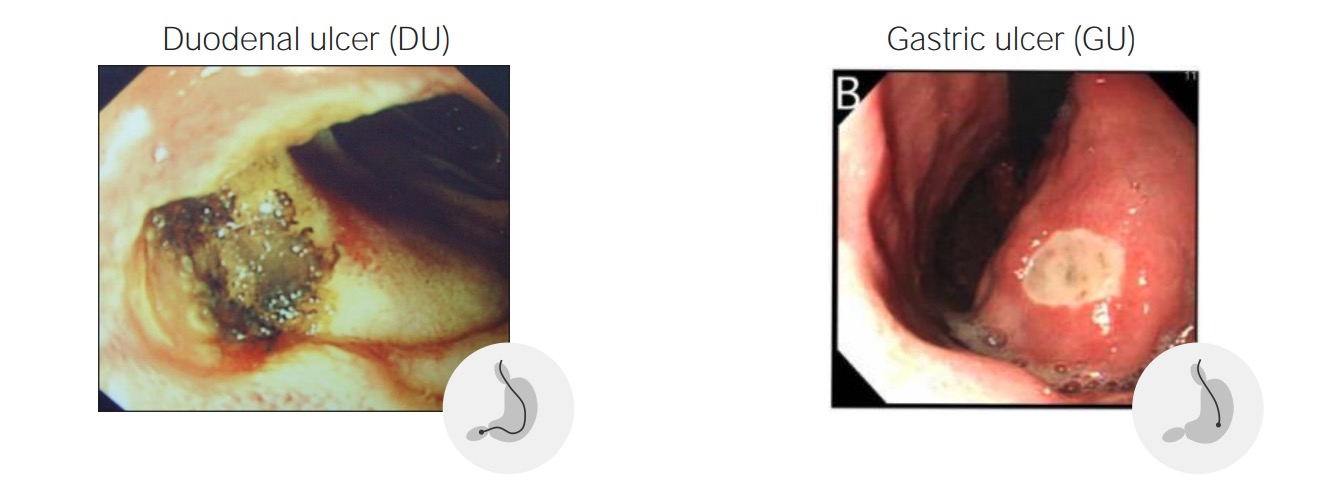
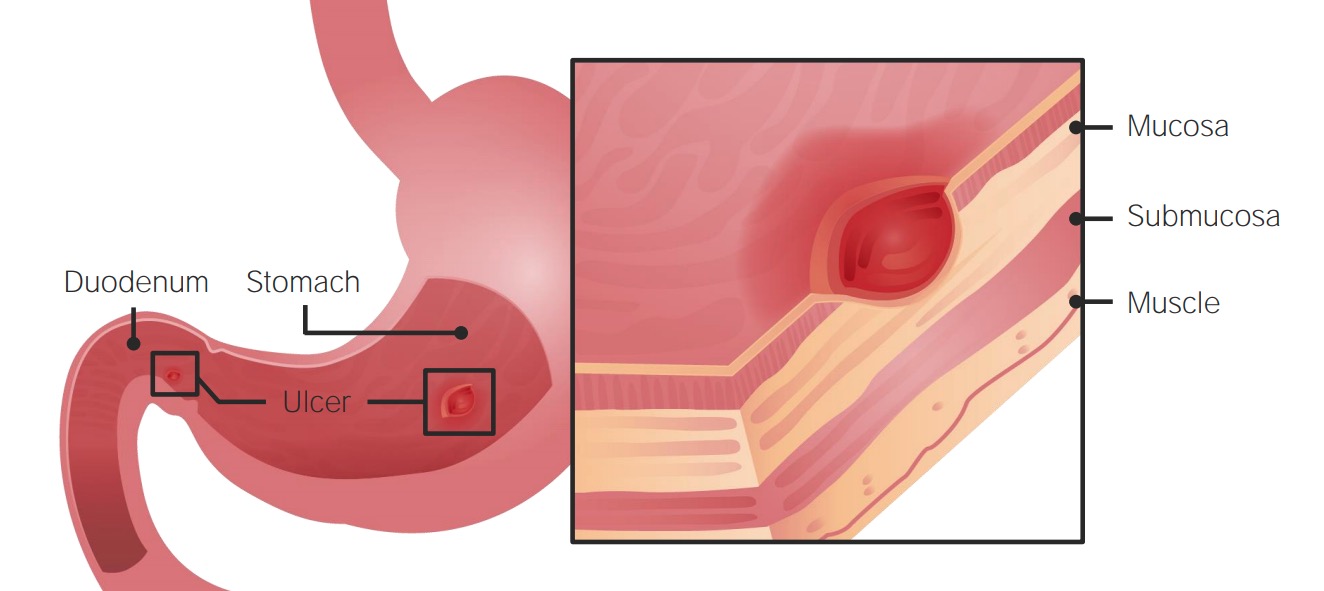
Una úlcera péptica es un defecto de la mucosa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la pared del estómago o del duodeno que penetra en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la muscularis mucosae.
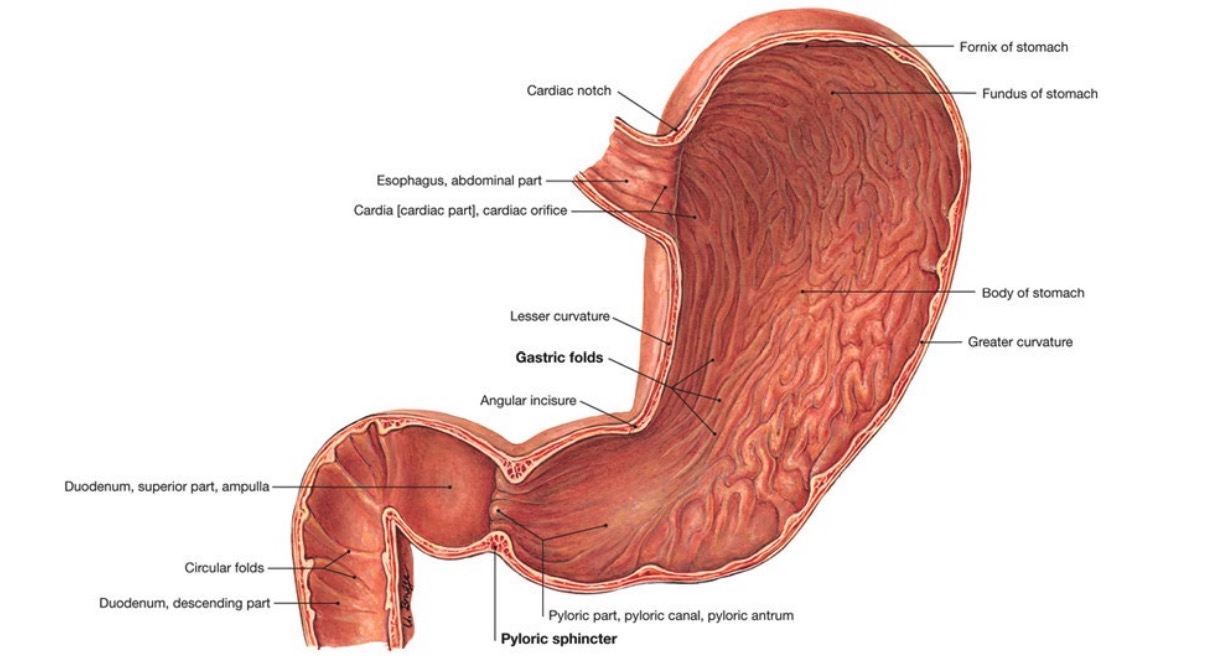
En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum muchos casos, las etiologías enumeradas no son suficientes para producir una PUD PUD Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) refers to the full-thickness ulcerations of duodenal or gastric mucosa. The ulcerations form when exposure to acid and digestive enzymes overcomes mucosal defense mechanisms. The most common etiologies include Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection and prolonged use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Peptic Ulcer Disease. Los LOS Neisseria siguientes factores de riesgo contribuyen al AL Amyloidosis desarrollo de la PUD PUD Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) refers to the full-thickness ulcerations of duodenal or gastric mucosa. The ulcerations form when exposure to acid and digestive enzymes overcomes mucosal defense mechanisms. The most common etiologies include Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection and prolonged use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Peptic Ulcer Disease:
| Tipo | Localización | Nivel de acidez |
|---|---|---|
| I | Curvatura menor del estómago en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la incisura angular | Bajo a normal |
| II | Cuerpo gástrico; coexiste con la úlcera duodenal | Aumentado |
| III | En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el canal pilórico (a menos de 3 cm del píloro) | Aumentado |
| IV | Úlcera gastroesofágica proximal | Normal |
| V | En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cualquier parte del estómago (inducido por la aspirina/ los LOS Neisseria AINE) | Normal |
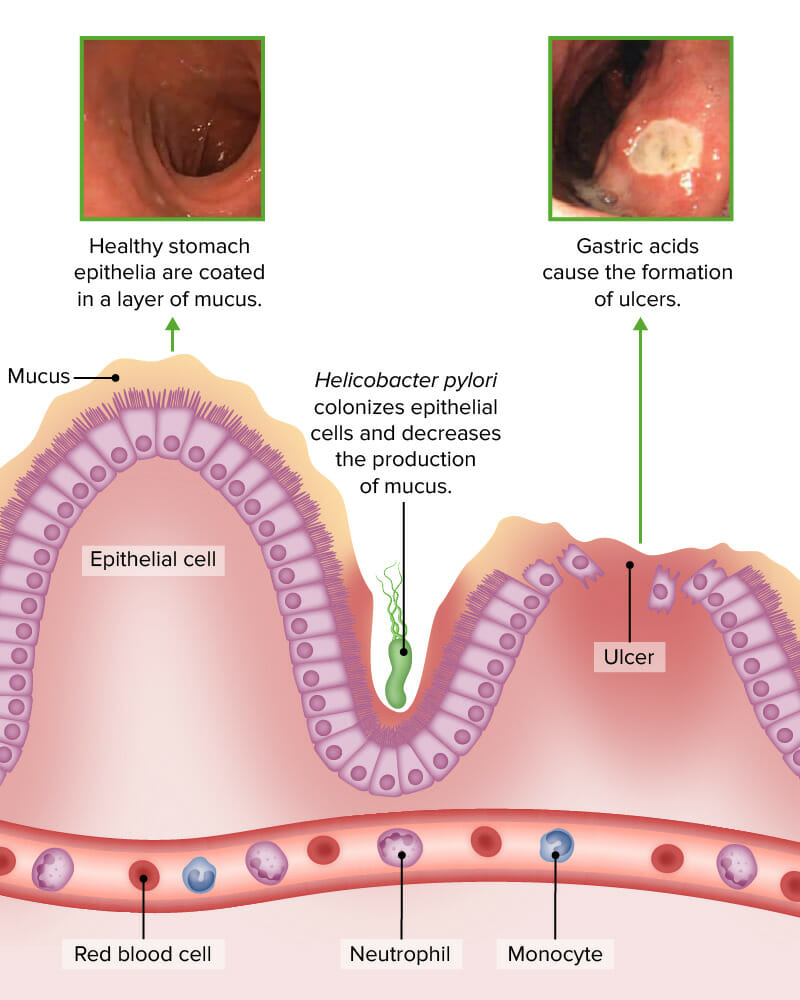
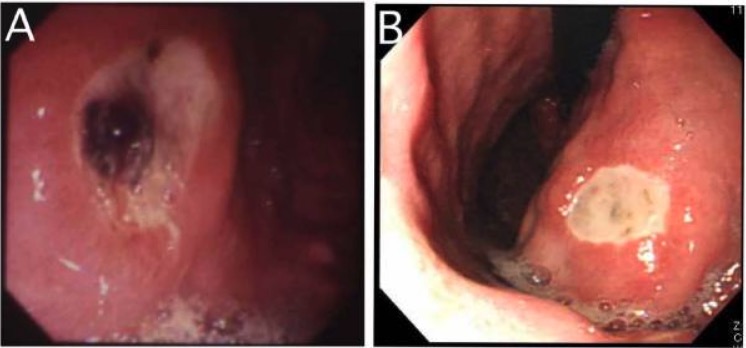
La infección por Helicobacter pylori disminuye la producción de moco y aumenta el riesgo de formación de úlceras.
Imagen por Lecturio (crédito de la fotografía superior izquierda: modificación del trabajo de “Santhosh Thomas”/YouTube; crédito de la fotografía superior derecha: modificación del trabajo de Moriya M, Uehara A, Okumura T, Miyamoto M, y Kohgo Y).Revisión de los LOS Neisseria factores de riesgo comunes: