La diarrea se describe como la evacuación de grandes cantidades de heces que suelen ser sueltas, líquidas o acuosas, lo que provoca una pérdida excesiva de líquidos y electrolitos. La diarrea es una de las enfermedades más comunes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria niños, representando los LOS Neisseria mayores porcentajes de morbilidad y mortalidad a nivel mundial en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el grupo de edad pediátrico. La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos son infecciosos, causados por el rotavirus Rotavirus A genus of Reoviridae, causing acute gastroenteritis in birds and mammals, including humans. Transmission is horizontal and by environmental contamination. Seven species (rotaviruses A through G) are recognized. Rotavirus, mientras que el resto son causados por bacterias ( Escherichia coli Escherichia coli The gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli is a key component of the human gut microbiota. Most strains of E. coli are avirulent, but occasionally they escape the GI tract, infecting the urinary tract and other sites. Less common strains of E. coli are able to cause disease within the GI tract, most commonly presenting as abdominal pain and diarrhea. Escherichia coli, Salmonella Salmonella Salmonellae are gram-negative bacilli of the family Enterobacteriaceae. Salmonellae are flagellated, non-lactose-fermenting, and hydrogen sulfide-producing microbes. Salmonella enterica, the most common disease-causing species in humans, is further classified based on serotype as typhoidal (S. typhi and paratyphi) and nontyphoidal (S. enteritidis and typhimurium). Salmonella) y parásitos ( Entamoeba histolytica Entamoeba Histolytica A species of parasitic protozoa causing entamoebiasis and amebic dysentery (dysentery, amebic). Characteristics include a single nucleus containing a small central karyosome and peripheral chromatin that is finely and regularly beaded. Amebicides). El tratamiento se basa principalmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum rehidratación; la terapia antibiótica se utiliza solo cuando está indicada. El pronóstico es excelente si la diarrea se trata con prontitud.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La diarrea se define como una pérdida excesiva de heces que suelen ser sueltas o acuosas.
La cuantificación de la producción de heces varía:
Lactantes y niños pequeños:
Niños mayores:
Lactantes y niños pequeños:
Niños mayores:
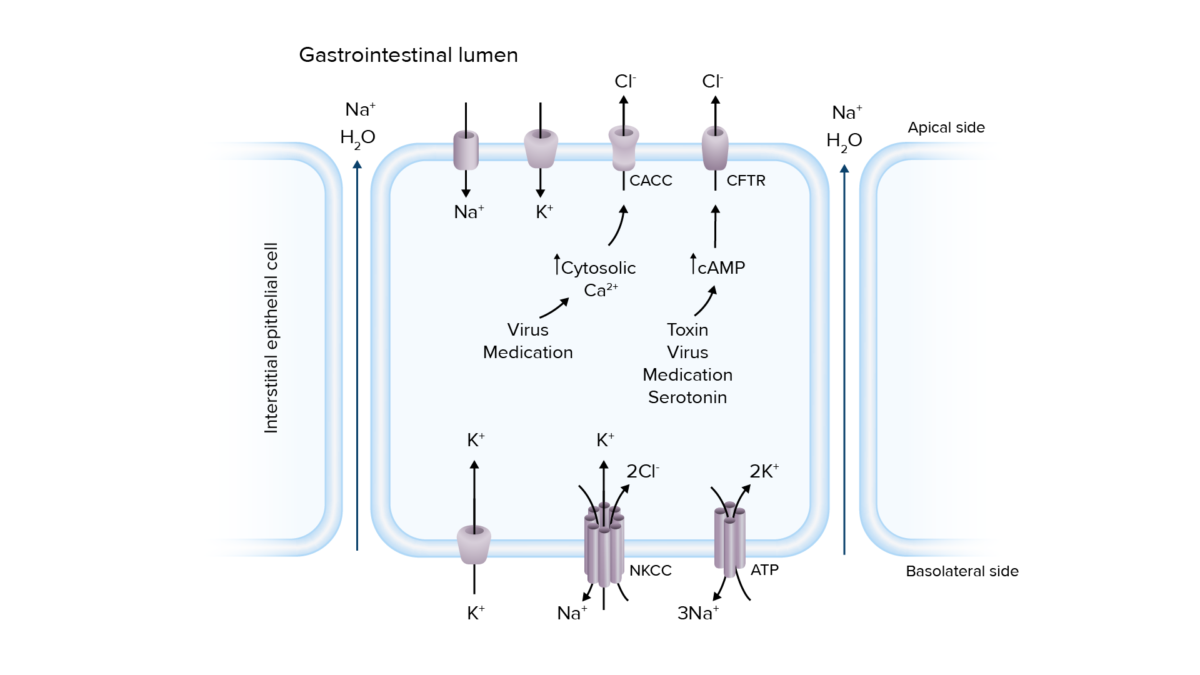
Patogénesis de la diarrea secretora:
La sobreactivación de los canales de transporte de iones puede conducir a la secreción de electrolitos y agua en el lumen intestinal, lo que provoca diarrea.
Ca2+: calcio
CaCC: canales de cloruro activados por el calcio
AMPc: monofosfato de adenosina cíclico
CFTR: regulador de la conductancia transmembrana de la fibrosis quística
Cl–: cloruro
K+: potasio
Na+: sodio
NKCC: cotransportador sodio-cloruro de potasio
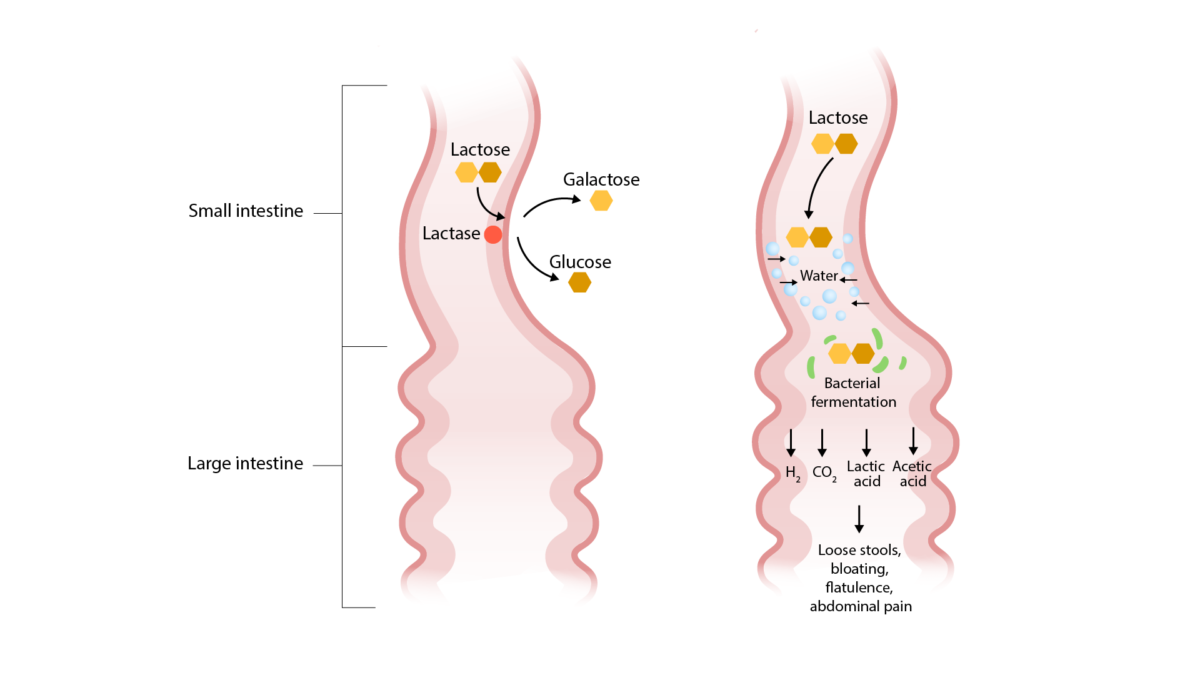
Patogénesis de la deficiencia de lactasa (una etiología de la diarrea osmótica):
La lactosa no se descompone y permanece en la luz del intestino delgado, atrayendo agua y provocando una diarrea osmótica. La fermentación bacteriana de la lactosa provoca los síntomas de hinchazón, flatulencia y dolor abdominal.
| Leve | Moderada | Severa | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pérdida de peso |
|
|
|
| Mucosa seca (1er signo) | – | +/-, parece seca | +, parece muy seca |
| Turgencia de la piel (último signo) | + | +/– | ++/+ |
| Depresión de la fontanela anterior | – | + | ++/+ |
| Estado mental | Normal | Fatiga/irritabilidad | Apatía/letargo |
| Enoftalmos | – | + | + |
| Respiración | Normal | Profunda, puede ser taquipneica | Profunda y taquipneica |
| Frecuencia cardíaca | Normal | Elevada | Muy elevada |
| Hipotensión | – | + | + |
| Perfusión distal | Normal |
|
|
| Diuresis | Disminuida | Oliguria Oliguria Decreased urine output that is below the normal range. Oliguria can be defined as urine output of less than or equal to 0. 5 or 1 ml/kg/hr depending on the age. Renal Potassium Regulation | Oliguria Oliguria Decreased urine output that is below the normal range. Oliguria can be defined as urine output of less than or equal to 0. 5 or 1 ml/kg/hr depending on the age. Renal Potassium Regulation/ anuria Anuria Absence of urine formation. It is usually associated with complete bilateral ureteral (ureter) obstruction, complete lower urinary tract obstruction, or unilateral ureteral obstruction when a solitary kidney is present. Acute Kidney Injury |
Por lo general, no es necesario realizar estudios y solo están indicados en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum casos de deshidratación moderada o grave, inmunocompromiso y sepsis Sepsis Systemic inflammatory response syndrome with a proven or suspected infectious etiology. When sepsis is associated with organ dysfunction distant from the site of infection, it is called severe sepsis. When sepsis is accompanied by hypotension despite adequate fluid infusion, it is called septic shock. Sepsis and Septic Shock, así como en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum casos crónicos.
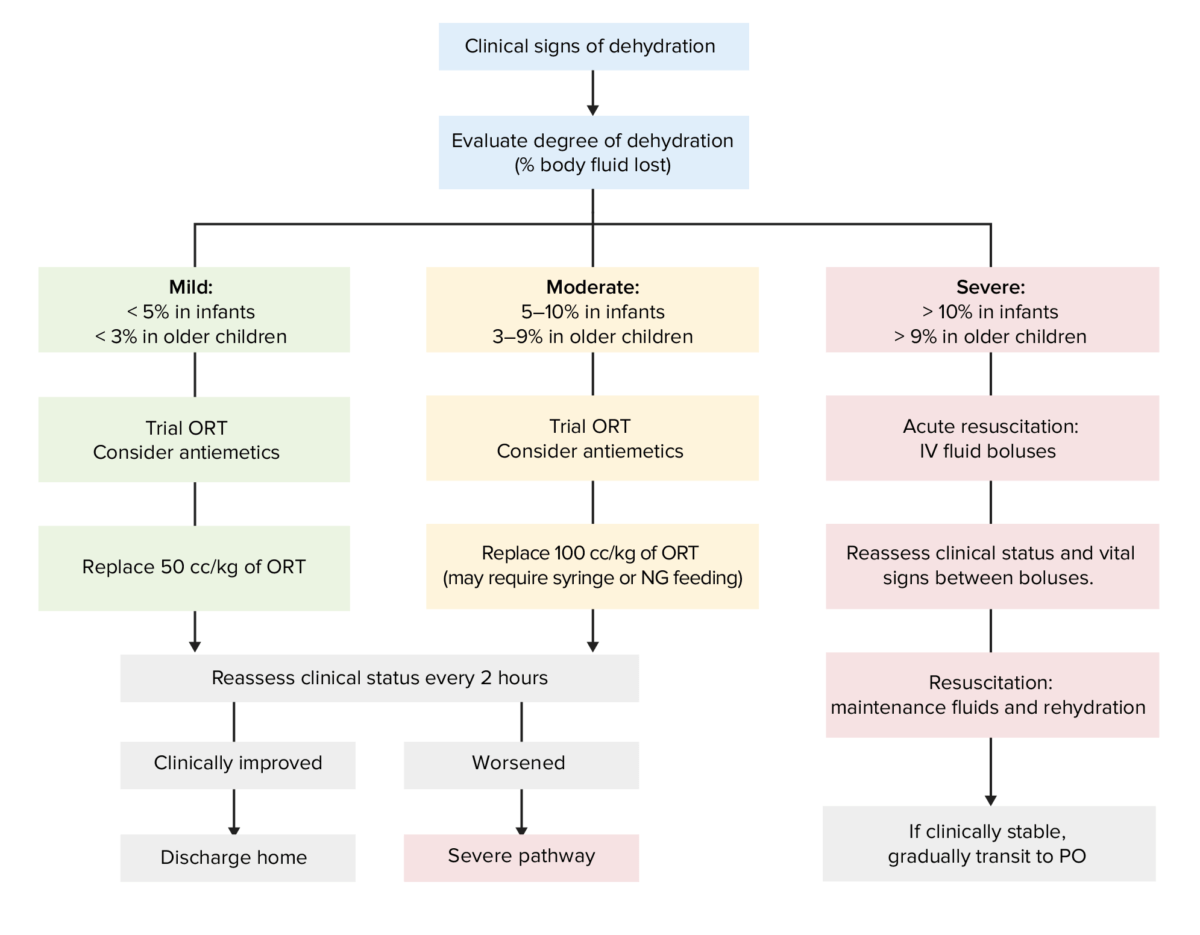
Diagrama de flujo para la evaluación y el tratamiento de la deshidratación en función de la gravedad de los síntomas
ORT: terapia de sustitución oral
PO: per os (utilizado para indicar la ingesta/administración oral)
NG: nasogástrica