Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
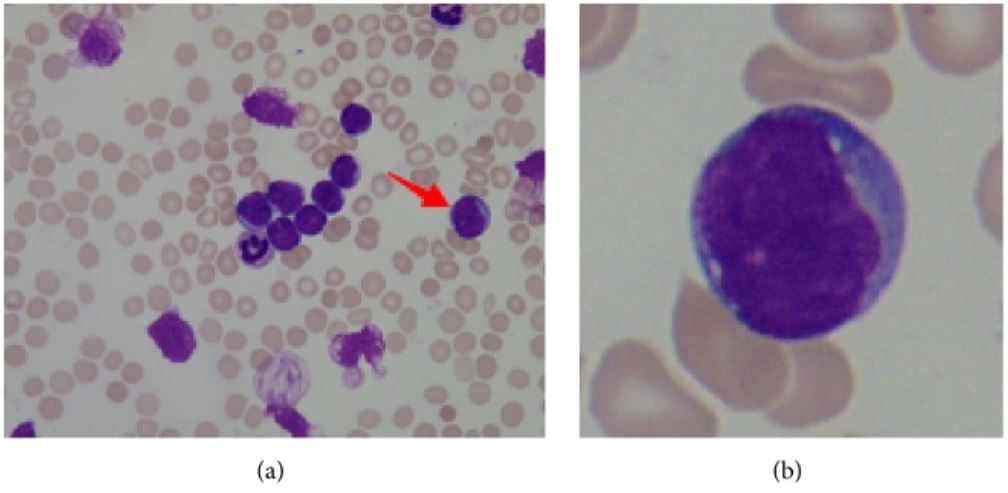
Overview Definition Acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma (ALL/LBL) are hematologic malignancies characterized by the pathological proliferation of lymphoid precursor cells (primarily the B and T cell lineages)in the bone marrow, with subsequent displacement of other blood cell precursors. Classification WHO system 2016 (supersedes the French-American-British classification): Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Etiology Mnemonic Pathophysiology Hematopoiesis Hematopoiesis starts with […]
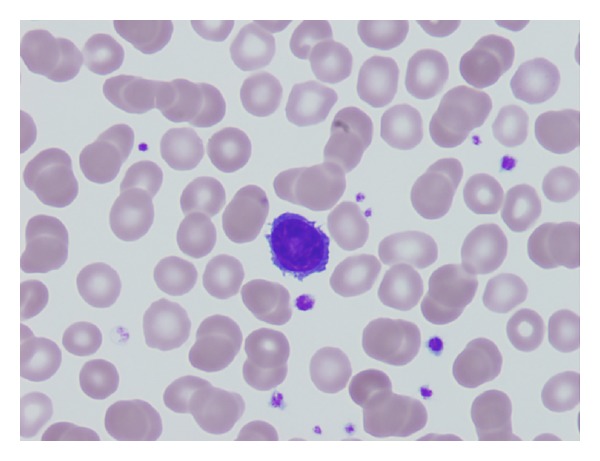
Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Overview Definition Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a hematologic malignancy characterized by the pathological proliferation of myeloid precursor cells in the bone marrow and subsequent displacement of other blood cell precursors. Classification The World Health Organization (WHO) classification system is based on multiple factors, including morphology, genetics, and clinical features: Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Etiology […]
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
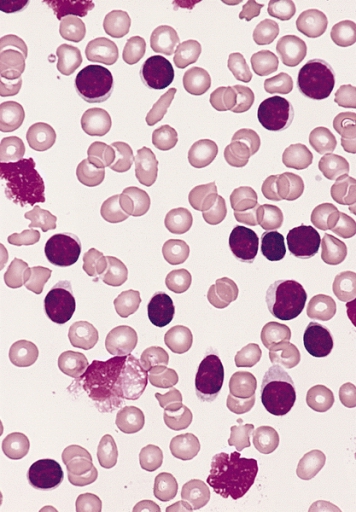
Overview Definition Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a lymphoproliferative neoplasm characterized by accumulation of functionally impaired lymphocytes, often monoclonal in origin. Terminology CLL is identical to small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), both of which are considered manifestations of B-cell neoplasm. The term CLL is used when the disease manifests primarily in the blood. The term SLL […]
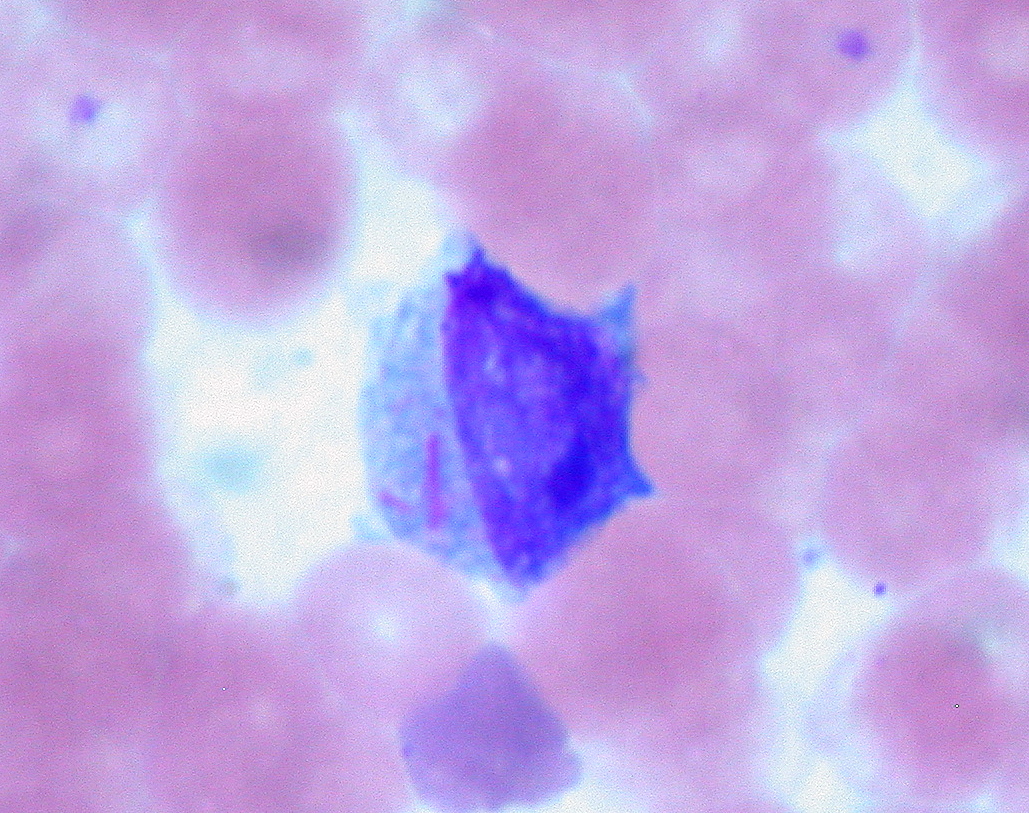
Hairy Cell Leukemia
Overview Definition Hairy cell leukemia (HCL) is a rare, chronic B-cell leukemia characterized by the accumulation of small mature B lymphocytes that have hair-like projections visible on microscopy. Epidemiology Incidence: 3 per 1 million persons per year in the United States Rare: approximately 2% of all leukemia cases Median age at diagnosis: approximately 50 years […]
Polycythemia Vera
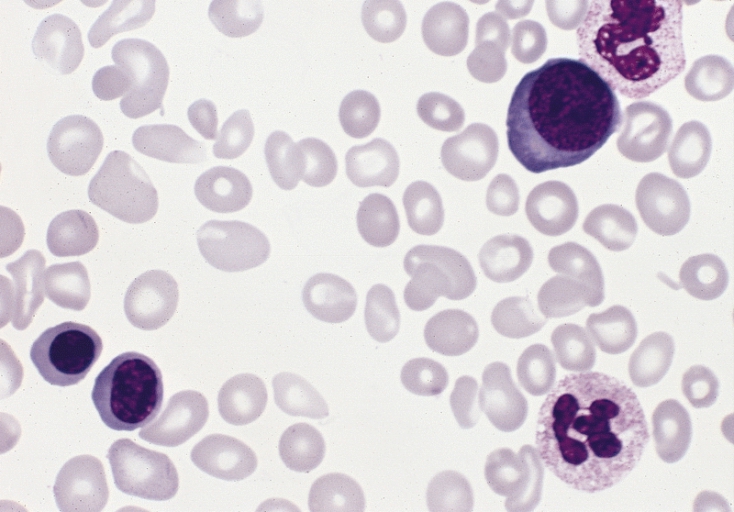
Overview Definition Polycythemia vera (PV) is a chronic myeloproliferative neoplasm characterized by the overproduction of RBCs (erythrocytosis), WBCs, and platelets. This triad differentiates PV from erythrocytosis seen with chronic hypoxia and other conditions. Classification Epidemiology Etiology and Pathophysiology Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Polycythemia vera is often diagnosed incidentally when a CBC obtained for other reasons […]
Chronic Eosinophilic Leukemia
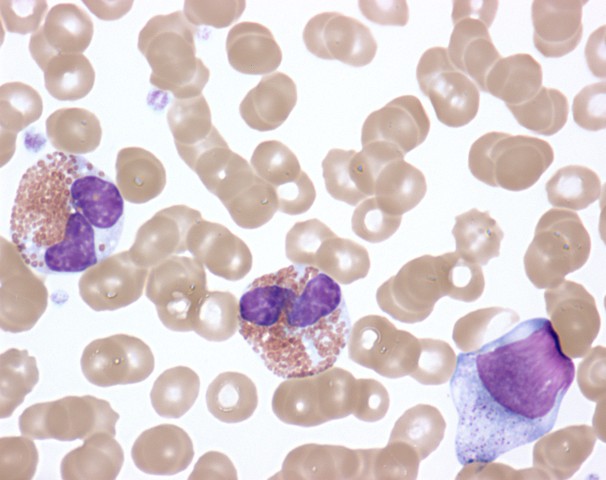
Overview Definition Chronic eosinophilic leukemia, not otherwise specified (CEL, NOS) is a rare chronic myeloproliferative neoplasm typified by clonal eosinophilic expansion in the bone marrow with increased blasts (< 20%). Classifying CEL, NOS Based on eosinophilias: CEL, NOS is classified under chronic myeloproliferative neoplasms (WHO classification): Epidemiology and etiology Pathophysiology Hematopoiesis Hematopoiesis starts with a […]
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
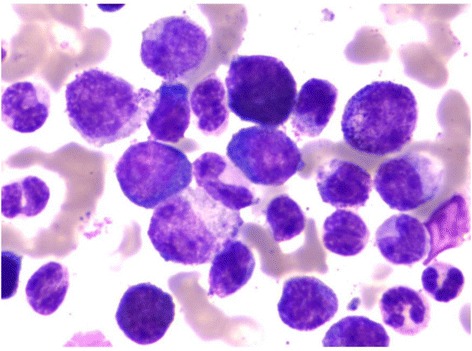
Overview Definition Chronic myeloid leukemia is a chronic myeloproliferative neoplasm characterized by uncontrolled and dysregulated proliferation of the granulocytic lineage (mature and maturing cells), with a maintained capacity for differentiation. Chronic myeloid leukemia is also known as chronic myelocytic leukemia or chronic myelogenous leukemia. Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Hematopoiesis Hematopoiesis starts with a hematopoietic stem cell, […]
Hypercoagulable States
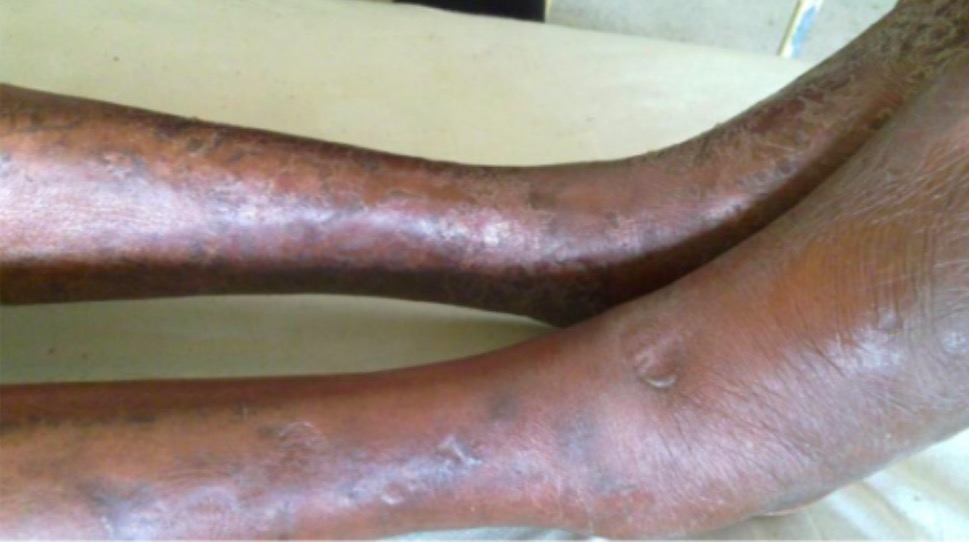
Overview Definition Hypercoagulability, also referred to as a thrombophilia, refers to the increased tendency for blood to form clots, known as thrombi. Hypercoagulable states can be inherited or acquired. Epidemiology Prevalence of inherited thrombophilias: Table: Prevalence and risk of venous thromboemolism (VTE) in inherited thrombophilias Condition Prevalence Risk of VTE Factor V Leiden 3%–7% 4.3% […]
Neutropenia
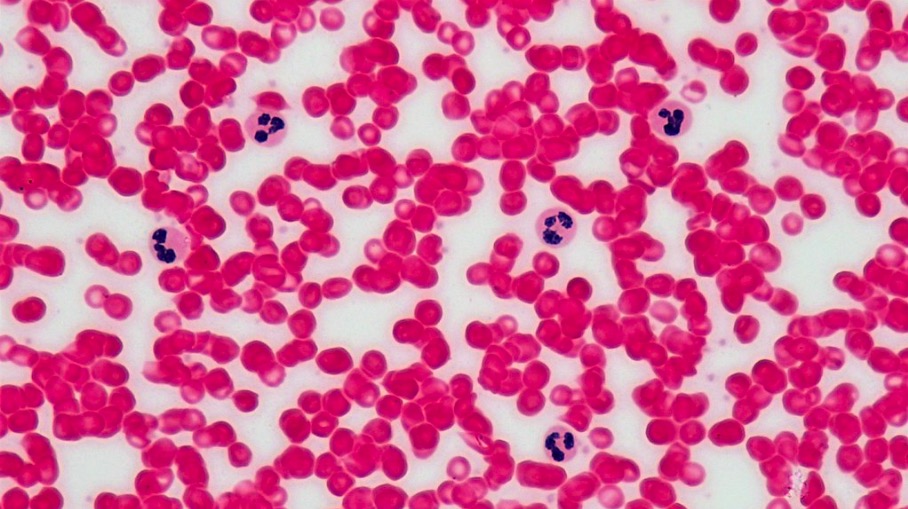
Overview Definition Neutropenia is a decrease in the number of circulating neutrophils in the blood, which is typically defined as an absolute neutrophil count (ANC) of: Neutrophils Neutrophils are the most common of all the leukocytes. Leukocytes are WBCs and are a major component of the immune system. Table: Normal ANC levels by age Age […]
Anemia: Overview and Types
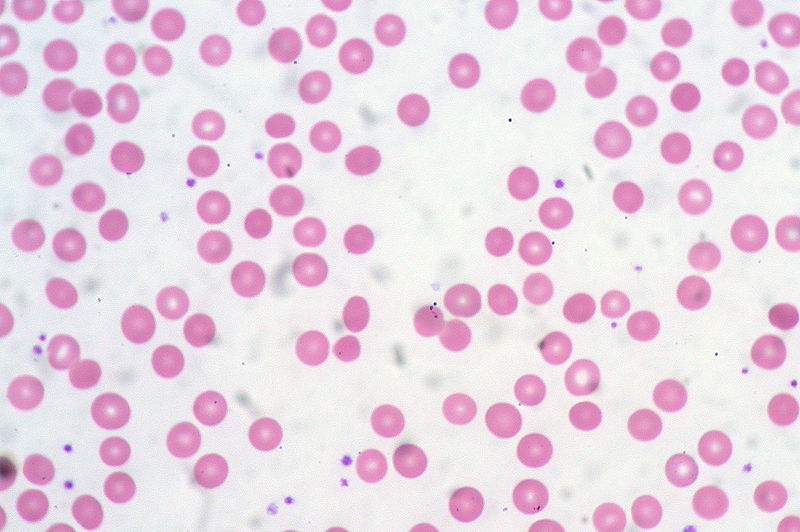
Overview Definition Anemia is a quantitative deficiency of Hb, the oxygen-carrying component of RBCs. Anemia is noted when Hb levels are approximately: Normal levels can vary depending on the laboratory reference range. Epidemiology Anatomy and physiology review Etiology Anemia can be caused by: Classification of anemia according to etiology Table: Classification of anemia according to […]