El cáncer gástrico es la 4ta causa de muerte por cáncer en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum todo el mundo. La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos son adenocarcinomas. Los LOS Neisseria factores de riesgo modificables son la infección por Helicobacter pylori Helicobacter pylori A spiral bacterium active as a human gastric pathogen. It is a gram-negative, urease-positive, curved or slightly spiral organism initially isolated in 1982 from patients with lesions of gastritis or peptic ulcers in Western Australia. Helicobacter pylori was originally classified in the genus campylobacter, but RNA sequencing, cellular fatty acid profiles, growth patterns, and other taxonomic characteristics indicate that the micro-organism should be included in the genus Helicobacter. It has been officially transferred to Helicobacter gen. Helicobacter, el tabaquismo y las dietas ricas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum nitratos. Los LOS Neisseria síndromes hereditarios, la anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types perniciosa y la gastrectomía parcial previa son algunos de los LOS Neisseria factores de riesgo endógenos. Cuando se producen síntomas como plenitud epigástrica, vómitos y pérdida de peso, es probable que el cáncer esté en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum fase avanzada. El diagnóstico se confirma con esofagogastroduodenoscopia y biopsia. La imagenología y la laparoscopia ayudan a determinar el estadio del cáncer. Por lo tanto, la estadificación dicta el abordaje terapéutico. El tratamiento consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum gastrectomía y quimiorradioterapia. La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos se diagnostican en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum fases avanzadas, lo que indica un pronóstico generalmente malo.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Factores de riesgo endógenos:
Factores de riesgo exógenos:
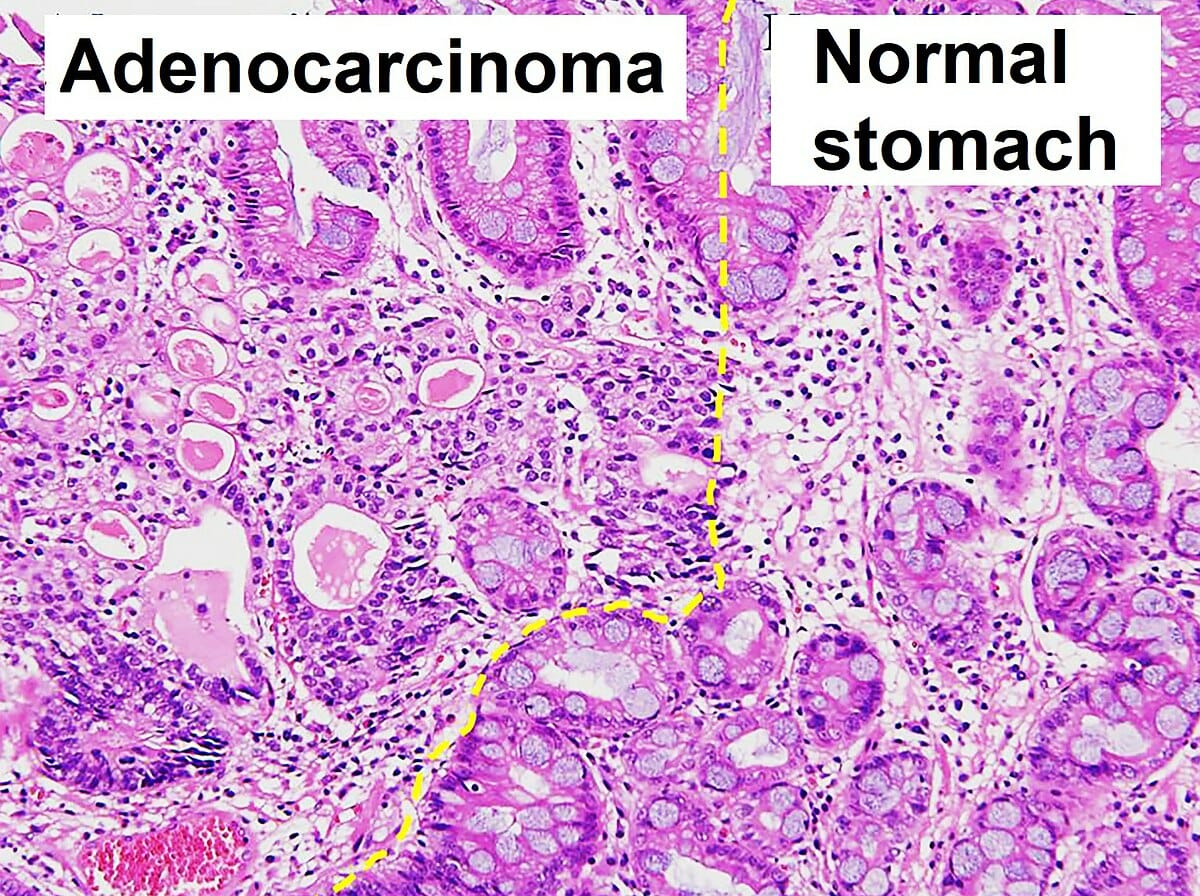
Histopatología del adenocarcinoma gástrico y patología normal
Imagen: “Histopathology of gastric adenocarcinoma and normal histology” por Ji Min Choi et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0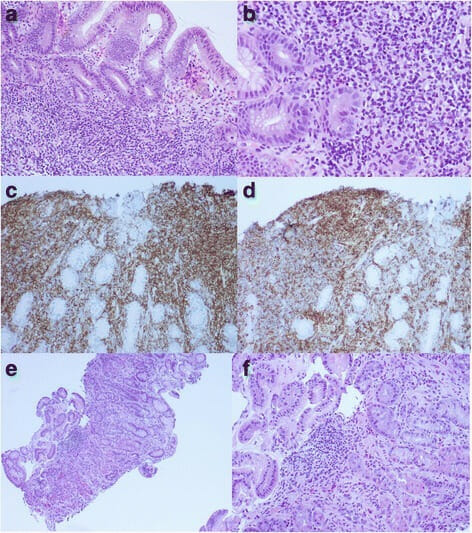
Linfoma del tejido linfoide asociado a la mucosa gástrica e infección por Helicobacter pylori:
a. La biopsia gástrica muestra un pequeño infiltrado linfocítico intralaminar de características monótonas (tinción H&E, aumento 100x).
b. Focos de lesión linfoepitelial (tinción H&E, aumento 200x)
c. Hojas de células B pequeñas CD20+ vistas en la inmunotinción CD20 (aumento 200x)
d. La inmunotinción también revela una expresión aberrante de CD43 (ampliación 200x).
e. La repetición de la biopsia gástrica 6 meses después de la erradicación del H. pylori muestra infiltrados intralaminares dispersos de pequeños linfocitos, células plasmáticas y unos pocos agregados linfoides pequeños y sueltos, lo que indica una remisión completa (tinción H&E, aumento 100x).
f. Los mismos hallazgos se observan con un aumento de 200x (tinción de H&E).
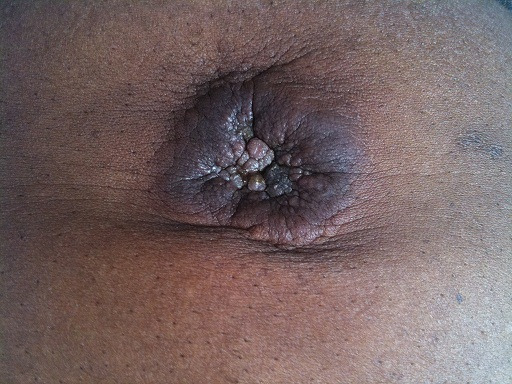
Nódulo de la hermana Maria Jose en un paciente con cáncer metastásico del tracto gastrointestinal
Imagen: “Sister Mary Joseph nodule” por Touré PS, Tall CT, Dioussé P, Berthé A, Diop MM, Sarr MM, Diop B, Léye YM, Diop BM, Ka MM. Licencia: CC BY 2.0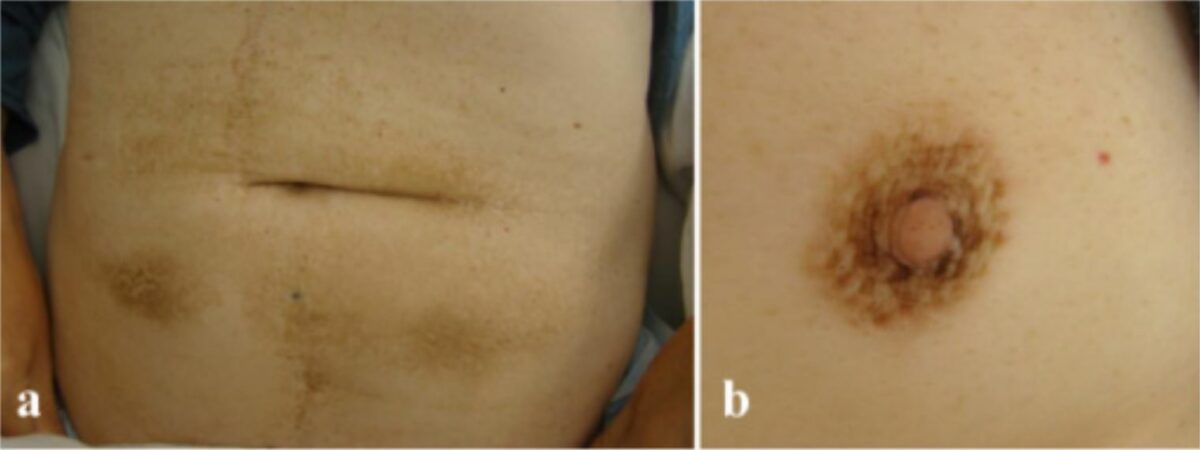
Acantosis nigricans en a) el abdomen y b) la areola
Imagen: “Malignant acanthosis nigricans associated with prostate cancer” por Kubicka-Wołkowska J, Dębska-Szmich S, Lisik-Habib M, Noweta M, Potemski P. Licencia: CC BY 4.0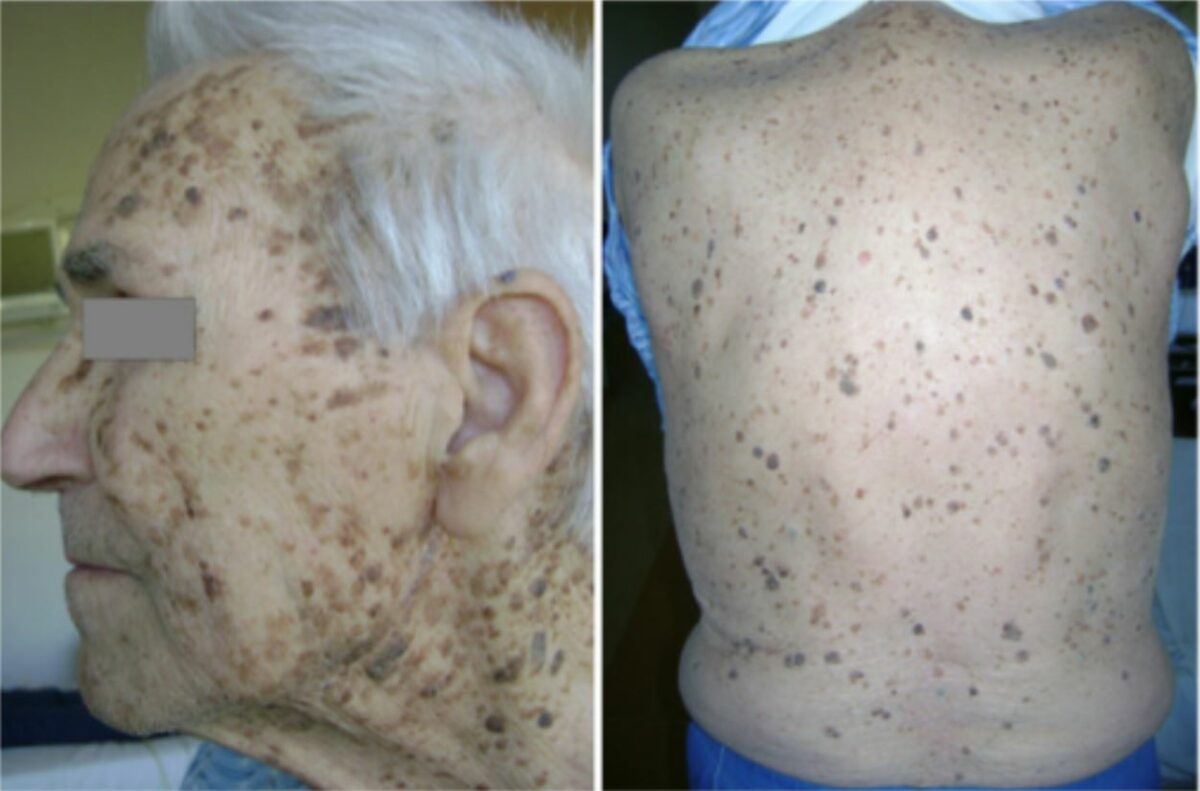
Paciente con adenocarcinoma gástrico oculto: innumerables queratosis seborreicas concentradas en la cara, el cuello, la espalda y el pecho.
Imagen: “Leser-Trélat syndrome” por Ponti G, Luppi G, Losi L, Giannetti A, Seidenari S. Licencia: CC BY 2.0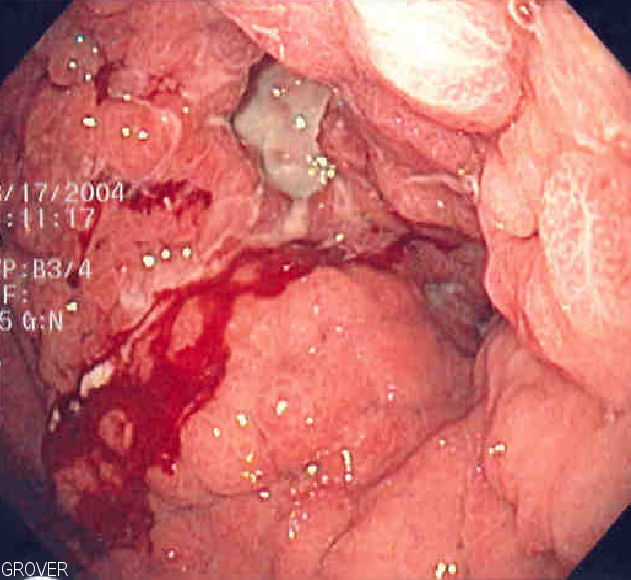
Imagen endoscópica de la linitis plástica, en la que todo el estómago está invadido por el cáncer, dando lugar a un aspecto de botella de cuero
Imagen: “Linitis plastica” por Samir. Licencia: Dominio Público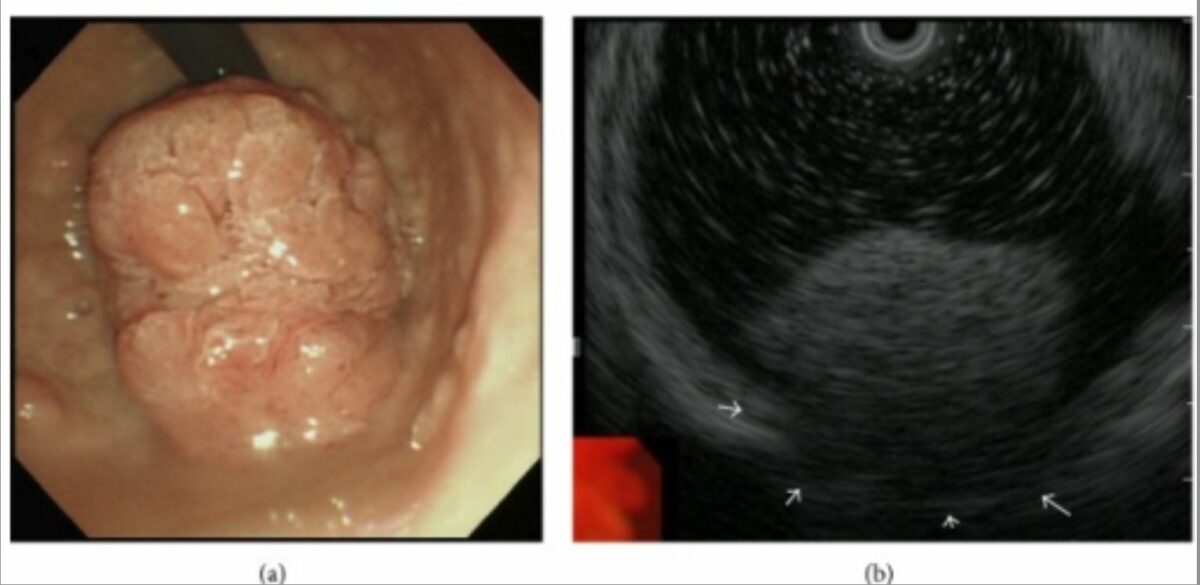
Tumor polipoide que se expresa en el anillo pilórico:
a: La endoscopia gástrica superior revela un tumor gigante de tipo polipoide que se extiende desde el bulbo del duodeno hasta el anillo pilórico.
b: El ultrasonido endoscópico sugiere la invasión tumoral de la túnica muscular (flechas blancas).
| T ( tumor Tumor Inflammation primario) | N (nódulos linfáticos afectados) | M (metástasis a distancia) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TX | No se puede evaluar | N0 | No hay nódulos linfáticos regionales | M0 | No hay metástasis a distancia |
| T0 | No hay evidencias de tumor Tumor Inflammation | N1 | 1–2 nódulos regionales | M1 | Metástasis confirmadas |
| Tis | Carcinoma in situ Carcinoma in situ A lesion with cytological characteristics associated with invasive carcinoma but the tumor cells are confined to the epithelium of origin, without invasion of the basement membrane. Leukoplakia | N2 | 3–6 nódulos regionales | ||
| T1 | Invasión hasta la submucosa | N3 | 7 o más nódulos regionales | ||
| T2 | Invasión de la muscularis propria | ||||
| T3 T3 A T3 thyroid hormone normally synthesized and secreted by the thyroid gland in much smaller quantities than thyroxine (T4). Most T3 is derived from peripheral monodeiodination of T4 at the 5′ position of the outer ring of the iodothyronine nucleus. The hormone finally delivered and used by the tissues is mainly t3. Thyroid Hormones | Invasión de la serosa | ||||
| T4a | Perfora la serosa | ||||
| T4b | Estructuras adyacentes afectadas | ||||
| Etapa | TNM | Características |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | TisN0M0 | Nódulos negativos; limitado a la mucosa |
| 1 | T1-2N0M0 | Nódulos negativos; invasión de la submucosa hasta la muscularis propria |
| 2a | T1N1-3M0 T2N1-3M |
Nódulos positivos; invasión de la muscularis propria |
| 2b | T3N0M0 T4aN0M0 |
Nódulos negativos; invasión hasta la serosa |
| 3 |
T3
T3
A T3 thyroid hormone normally synthesized and secreted by the thyroid gland in much smaller quantities than thyroxine (T4). Most T3 is derived from peripheral monodeiodination of T4 at the 5′ position of the outer ring of the iodothyronine nucleus. The hormone finally delivered and used by the tissues is mainly t3.
Thyroid Hormones,N1-3,M0 T4a,N1-3, M0 |
Nódulos positivos; invasión hasta la serosa |
| 4a | T4b, cualquier N, M0 | Nódulos positivos; más allá de la serosa, hasta las estructuras adyacentes |
| 4b | Cualquier T, N, M1 | Metástasis a distancia |
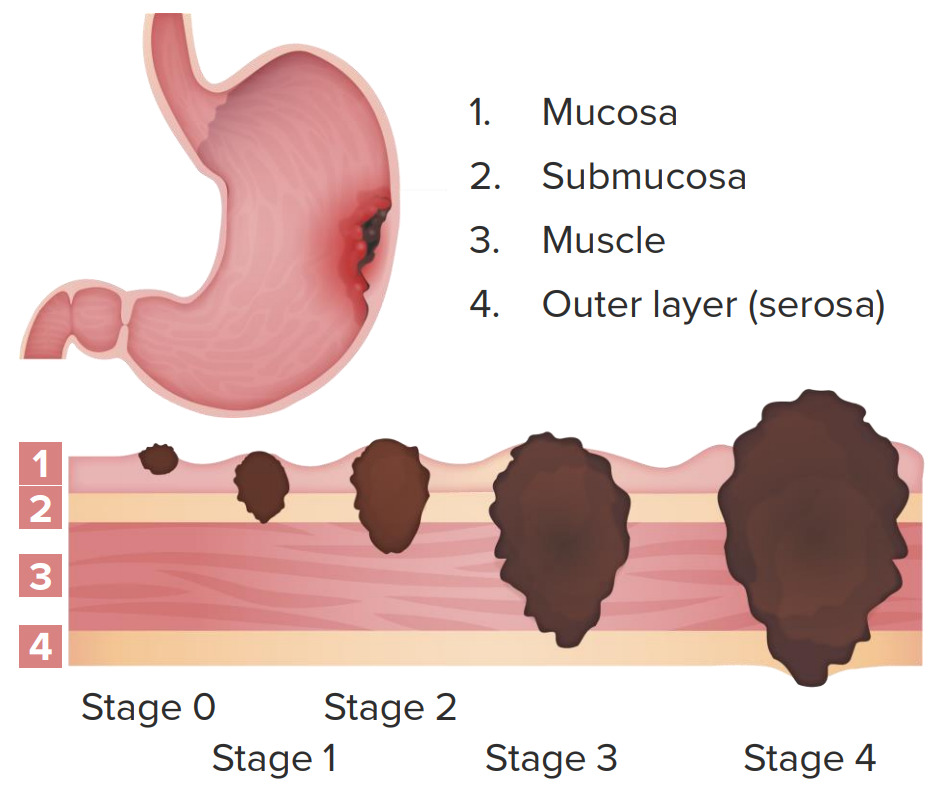
Estadificación clínica del cáncer gástrico:
Estadio 0: nódulos negativos; limitado a la mucosa
Estadio 1: nódulos negativos; invasión de la submucosa y parte de la muscularis propria
Estadio 2: nódulos negativos con invasión hasta la serosa o nódulos positivos con invasión hasta la muscularis propria
Estadio 3: nódulos positivos; invasión de la serosa
Estadio 4: nódulos positivos; invasión hasta las estructuras adyacentes con o sin metástasis a distancia